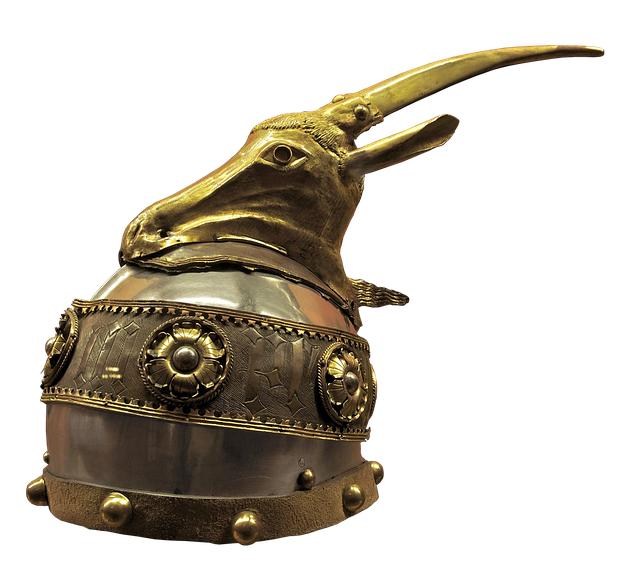
In a significant cultural milestone, the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York has joined forces with the Hellenic Republic of greece too announce the return of an remarkable artifact: the ancient bronze head of a griffin. This remarkable piece, which dates back to antiquity, not only holds immense artistic value but also serves as a testament to the rich heritage of Greek civilization. The collaboration between the esteemed museum and the Greek government underscores a growing commitment to cultural repatriation and the restoration of past artifacts to their countries of origin. As the griffin, a mythological creature symbolizing strength and protection, makes its journey back to Greece, it invites a renewed reflection on the importance of preservation, cultural identity, and the shared history that binds nations together. This article explores the meaning of the griffin’s return and the broader implications for cultural heritage in our increasingly interconnected world.
The Significance of the griffin Head Restoration in Cultural Heritage
The recent restoration of the ancient bronze Griffin head marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing dialog about cultural heritage and the preservation of historical artifacts. As a symbol of power and protection in ancient mythology, the Griffin resonates strongly with Greek identity and history. This restoration not only returns a significant piece of art to its rightful cultural context, but it also signifies a reaffirmation of the values of stewardship and integrity in cultural heritage practices. The collaborative efforts between institutions such as The Metropolitan Museum of Art and the Hellenic Republic of Greece reinforce the importance of international cooperation in the protection and promotion of our shared human history.
Furthermore, the symbol of the Griffin itself—often depicted guarding treasures and sacred spaces—serves as a metaphor for the broader stewardship of cultural artifacts that transcend geographical boundaries. The restoration project exemplifies how communities can unite to safeguard their legacies and educate future generations about their ancient roots. Key aspects of this significance include:
- Reinforcement of Cultural Identity: the Griffin head serves as a reminder of the philosophical and artistic achievements of ancient civilizations.
- Educational Opportunities: Its return provides a platform for educational programs that explore ancient Greek culture.
- Strengthening International Ties: This project enhances collaboration between countries in the sphere of cultural heritage.

Exploring the Historical Context of the Griffin and Its Role in Ancient greece
The griffin, with its majestic blend of eagle and lion characteristics, has long been a symbol of strength, courage, and protection in various ancient cultures. In ancient Greece,this mythical creature was more than just a legend; it served a significant role in the art,mythology,and religious practices of the time. As guardians of treasures, griffins were often depicted in sculpture, pottery, and architectural decor, blending seamlessly into the narratives of deities and heroes within Greek mythology.
Research indicates that the prevalence of griffins in Greek artistry was likely influenced by their origins in Mesopotamian and Egyptian cultures, where they were revered as protectors of the divine. Throughout the ages, they became emblematic of the Hellenistic period, reflecting both the artistic innovation and the cultural exchanges that characterized the era as Greek civilization interacted with neighboring cultures. Their depiction in the form of bronze, such as the recently returned head, allows scholars and enthusiasts alike to delve deeper into the intricate connections between art, mythology, and societal values in ancient Greece.

The Collaborative efforts Between The Metropolitan Museum and the Hellenic Republic
The recent collaboration between one of the world’s premier cultural institutions and the Hellenic republic marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing conversation about global heritage and the restitution of cultural artifacts. The Ancient Bronze Head of a Griffin,a captivating masterpiece of ancient Greek art,will soon grace its rightful home in greece following extensive negotiations and mutual agreement. This initiative reflects both parties’ commitment to honoring and preserving the cultural legacy of Greece while fostering international dialogue around shared historical treasures.
As part of this landmark agreement, several objectives have emerged to enhance cultural exchanges and increase public engagement with ancient art. Key points of collaboration include:
- Joint Exhibitions: Plans for future exhibitions showcasing ancient Greek artifacts at the Metropolitan Museum in New York.
- Educational Programs: Initiatives aimed at promoting educational outreach that emphasizes the significance of Greek heritage.
- Research Initiatives: Collaborative research projects to study and document artifacts from both nations’ institutions.
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Exchange Programs | Facilitating cultural exchanges for scholars and curators. |
| Restitution Efforts | Continual discussions on art repatriation and heritage preservation. |

Implications for Future Art Repatriation Initiatives and International Relations
The recent return of the ancient bronze head of a griffin to Greece marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing dialogue surrounding cultural heritage and the ethics of art ownership. This growth may serve as a blueprint for future repatriation initiatives, suggesting a trend toward collaborative approaches between museums and nations.As institutions like The Metropolitan Museum of Art engage in the process of redressing historical injustices, the implications extend beyond artworks to enhance diplomatic relations between countries that share rich histories. The transparent negotiation between the Met and the Hellenic Republic demonstrates a growing recognition of the importance of cultural heritage in fostering mutual respect and understanding.
Looking ahead, several factors will play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of art repatriation and international relations:
- Legal Frameworks: Countries may need to establish clearer policies governing the ownership and stewardship of artifacts.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Collaborative initiatives could encourage cultural exchange and tourism, benefiting economies.
- Public Awareness: Raising awareness about the significance of cultural heritage can strengthen public support for repatriation efforts.
| Stakeholder | Role in Repatriation |
|---|---|
| Museums | Facilitate the return of artifacts and engage in dialogue with source countries. |
| Governments | Establish frameworks for the legal return and protection of cultural heritage. |
| Cultural Organizations | Advocate for the preservation and respectful handling of cultural artifacts. |

Public Access and Educational Programs Surrounding the Griffins Return
In a groundbreaking collaboration between The Metropolitan Museum of Art and The Hellenic Republic of Greece, the anticipated return of the ancient bronze head of a griffin not only celebrates artistic heritage but also ushers in a series of engaging public access and educational initiatives. These programs aim to foster a deeper understanding of ancient art and its contemporary significance. Visitors will have the possibility to participate in:
- Interactive Workshops: Hands-on activities focusing on techniques of ancient sculpture.
- Lectures and Panel Discussions: Talks featuring renowned archaeologists, historians, and artists exploring the cultural impact of the griffin in ancient mythology.
- Guided Tours: Specialty tours to view the griffin alongside other classical pieces, enhancing the context of its return.
Additionally,the Met plans to reveal a dedicated digital platform where visitors can access resources related to the griffin’s history,its symbolic implications,and its significance in ancient Greek art. This platform will host:
| Resource Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Curated Articles | In-depth analysis and historical context of the griffin in ancient culture. |
| Virtual Exhibitions | Online displays showcasing artifacts linked to the griffin theme. |
| Educational Videos | Documentaries and interviews with experts in the field. |

Preserving Ancient Artifacts: Best Practices for Museums and Cultural Institutions
In the field of cultural heritage,the return of artifacts such as the ancient bronze head of a griffin to Greece exemplifies the importance of ethical stewardship. Museums and cultural institutions are increasingly called to adopt best practices for preserving artifacts that extend beyond mere storage.Key strategies involve:
- Stable Environmental conditions: Maintaining consistent temperature and humidity levels to prevent deterioration.
- Regular Condition Assessments: Performing routine checks to identify any signs of damage or wear.
- Proper Handling Techniques: Training staff in the proper methods of artifact handling to avoid physical damage.
- Public Openness: engaging with the community about the significance of artifacts and their rightful custodianship.
The collaboration between institutions also plays a vital role in artifact preservation. Partnerships between museums and national governments ensure that artifacts are not only returned but are also exhibited responsibly. This cooperation can involve:
- Joint Conservation Projects: Sharing resources and expertise to stabilize and restore artifacts.
- Educational Programs: Developing curricula that educate the public on the history and context of the artifacts.
- Visitor Engagement: Creating immersive experiences that foster appreciation for the cultural significance of the pieces.
| Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Conservation | Maintaining artifacts in suitable conditions to prevent deterioration. |
| Repatriation | Returning artifacts to their countries of origin to rectify historical injustices. |
| Community Outreach | Involving local communities in discussions about cultural heritage. |
To Conclude
the return of the ancient bronze head of a griffin to the Metropolitan Museum of art represents a significant milestone in the ongoing dialogue surrounding cultural heritage and the rightful ownership of antiquities. This collaboration between the museum and the Hellenic Republic of Greece not only underscores a commitment to preserving and respecting the past but also paves the way for future partnerships aimed at addressing the complex histories of cultural artifacts. as the art world and international communities continue to grapple with issues of repatriation and restitution, this artifact’s return serves as a hopeful reminder of the shared cultural narratives that connect us all. Moving forward, both institutions will likely continue to explore avenues for collaboration, ensuring that such treasures are celebrated within their cultural context and accessible to a broader audience. The story of the griffin head is not just one of art; it is a testament to the enduring power of history and the importance of honoring our collective heritage.