In recent weeks, the escalating tensions in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) have drawn international attention, particularly regarding the role of neighboring Rwanda in the ongoing conflict. As accusations of Rwandan support for rebel groups in the DRC intensify, the European Union has grappled with a response to address the deteriorating situation. However,a significant delay in the adoption of proposed sanctions against Rwanda by Luxembourg has sparked debate among EU member states and raised concerns about the effectiveness of collective action. This article delves into the intricacies of the conflict in the DRC, the implications of Luxembourg’s hesitance, and the broader geopolitical stakes at play in this volatile region of Central Africa.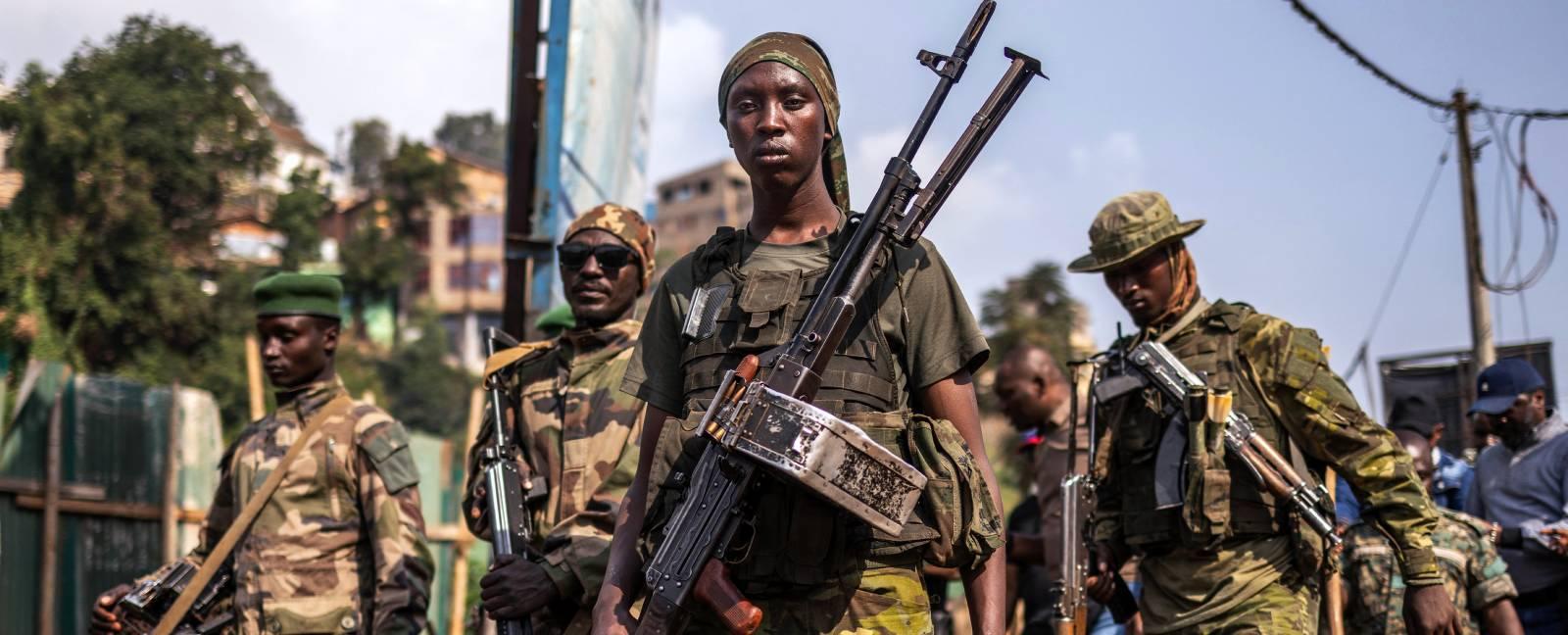
Understanding the Roots of the DRC Conflict and Rwandas Role
The ongoing conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has deep ancient roots intertwined with complex socio-political dynamics. At its core, the turmoil can be traced back to the aftermath of the Rwandan Genocide of 1994, which led to a massive influx of Rwandan Hutu refugees into eastern Congo. The presence of these refugees, alongside the Rwandan government’s pursuit of their enemies, significantly destabilized the region. This led to various groups, including local militias and foreign armed forces, engaging in a scramble for control over the DRC’s rich resources, including gold, diamonds, and coltan, aggravating the conflict further.
Rwanda’s involvement in the DRC conflict has often been characterized by accusations of intervention aimed at securing its national interests. various reports indicate that Rwandan authorities have supported armed groups within the eastern DRC as a means to exert influence over the region, safeguarding Rwanda from perceived threats and bolstering its economic foothold through resource extraction. Additionally, the government’s motivations can be summarized as follows:
- Security concerns: Addressing threats from militias that operate along the border.
- Economic interests: Capitalizing on the DRC’s mineral wealth.
- Political influence: Expanding Rwanda’s regional presence and mitigating historical rivalries.
The ramifications of this involvement have not only fueled ongoing violence but have also obstructed peace processes in the region. The precarious balance of power and the interplay between local, regional, and international actors continue to complicate efforts toward a sustainable resolution, rendering the conflict in the DRC one of the most challenging humanitarian crises in modern history.
| Key Players | Influence on Conflict |
|---|---|
| Rwandan Government | Active military engagement; support for factions. |
| DRC Armed Forces | Efforts to stabilize and reclaim territory. |
| Local Militias | Control over resources; perpetuation of violence. |
| International Community | Attempts at mediation and sanctions; complex geopolitical interests. |

Luxembourgs Position: Analyzing the Delayed EU Sanctions
Luxembourg’s recent decision to stall the adoption of EU sanctions against Rwanda has stirred up considerable debate within the European Union.as tensions rise in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), member states are grappling with the implications of a delayed response.Luxembourg’s position underscores a complex diplomatic balancing act where humanitarian concerns and political strategy intersect, prompting questions about the EU’s collective stance on human rights violations in the region. Critics argue that this postponement could embolden further aggression by Rwanda in the DRC, complicating efforts for peace and stability.
Several factors seem to influence Luxembourg’s hesitant stance, including:
- strategic Partnerships: Luxembourg maintains significant economic ties with Rwanda, which may be at the forefront of its decision-making process.
- Regional Stability: Officials are wary that sanctions could disrupt fragile diplomatic relations and exacerbate tensions with neighboring countries.
- Humanitarian Concerns: The government argues that sanctions could have adverse effects on ordinary citizens, potentially leading to greater humanitarian crises.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Strategic Partnerships | Economic ties between Luxembourg and Rwanda may sway the decision-making process. |
| Regional Stability | Concerns over exacerbating tensions with neighboring nations play a crucial role. |
| Humanitarian Concerns | Risk of harming ordinary citizens could deter immediate sanctions. |

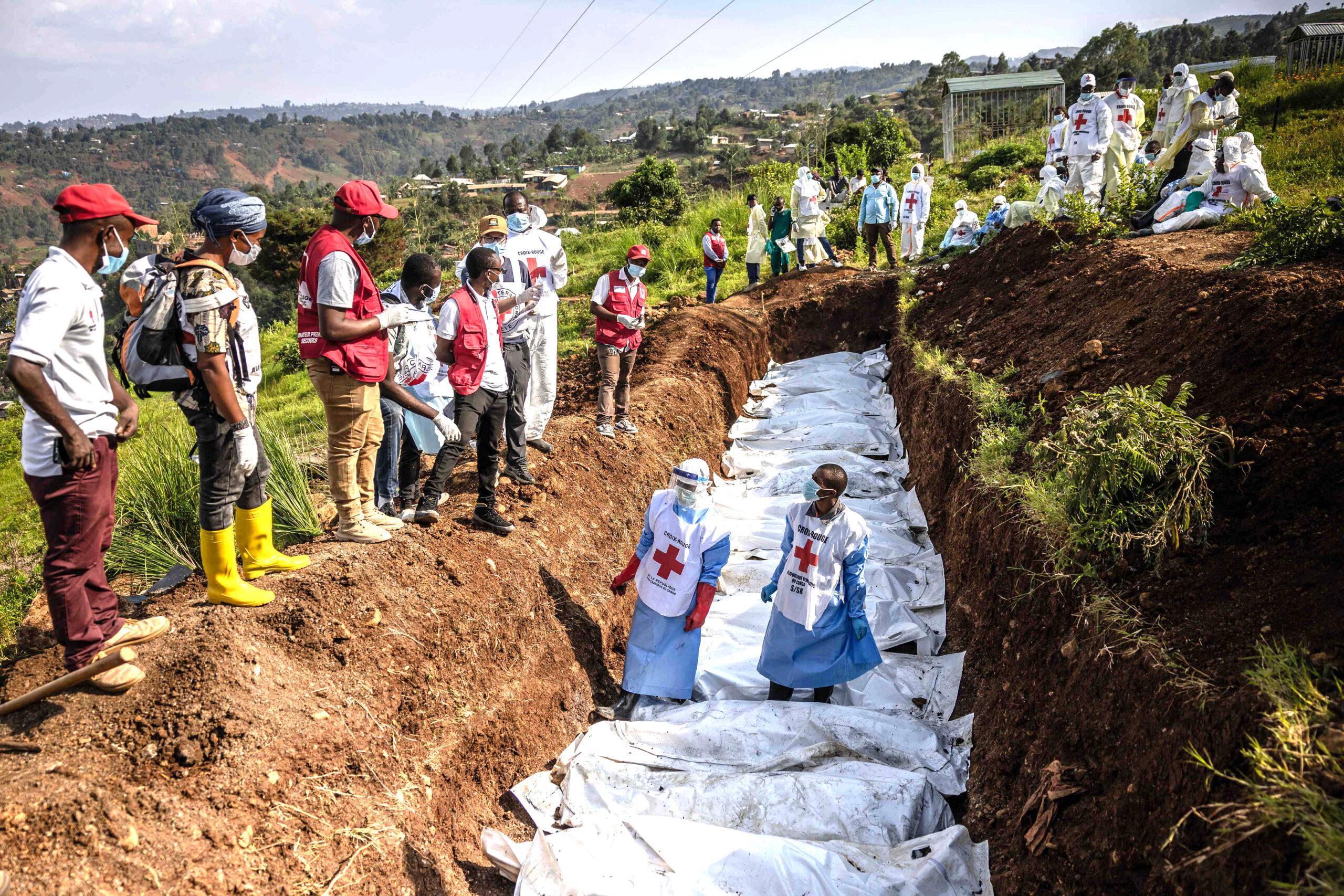
The Humanitarian Impact: Exploring the Consequences for DRC Citizens
The prolonged conflict in the Democratic Republic of the congo (DRC) has unleashed a wave of humanitarian crises, impacting the daily lives of millions of citizens.In particular, displacement has become a pressing issue, with vast numbers fleeing their homes to escape violence. According to recent reports, approximately 5.5 million people are currently displaced within DRC, making it one of the most significant displacement crises in the world. This situation has led to dire conditions, with many living in overcrowded camps that lack basic services such as clean water and adequate sanitation.
Furthermore, the ongoing unrest has severely impacted access to essential services including healthcare and education. The consequences are dire, as citizens face heightened risks of malnutrition, disease outbreaks, and limited educational opportunities for children. The humanitarian landscape is characterized by:
- Increased mortality rates due to preventable diseases.
- Food insecurity affecting millions, exacerbated by disrupted agricultural activities.
- Health facilities under strain, struggling to provide basic care due to lack of resources.
| Humanitarian Challenge | Impact on Citizens |
|---|---|
| Displacement | Over 5.5 million internally displaced people. |
| Food Insecurity | Millions facing malnutrition. |
| Healthcare Access | Increased mortality rates,with healthcare facilities overwhelmed. |
| Education Disruption | Loss of learning opportunities for children. |

Recommendations for a Unified EU Approach to Addressing the Crisis
To effectively address the ongoing crisis in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and its ramifications for regional stability, EU member states must adopt a cohesive and strategic approach. this entails a thorough reassessment of current policies regarding Rwanda and its actions in the DRC. Key recommendations include:
- Enhanced Diplomatic Engagement: Establishing regular dialogues with both Congolese authorities and Rwandan officials to mitigate tensions and encourage cooperation.
- Revised Sanctions Criteria: Creating clear and measurable benchmarks for sanctions against entities exacerbating the conflict, focusing on accountability and clarity.
- Support for humanitarian Aid: Increasing financial and logistical support to organizations providing essential services to affected populations in the DRC.
- Collaboration with African Union: Strengthening partnerships with the African Union to maximize regional input and foster collectively beneficial solutions.
Moreover, consolidating intelligence-sharing mechanisms among EU nations can ensure timely and informed responses to emerging threats.A proposed framework could include the following components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Joint Crisis Task Force | A dedicated team focused on monitoring and responding to developments in the DRC. |
| Shared Data Platforms | Utilizing technology to facilitate knowledge exchange about security and humanitarian needs. |
| Regular Review meetings | Scheduled assessments of policy effectiveness to adapt strategies as the situation evolves. |

International Responses: The Role of Global Powers in Resolving Tensions
The ongoing conflict in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) has necessitated an urgent response from global powers, particularly given the involvement of neighboring Rwanda.As tensions escalate,the role of nations and international organizations becomes increasingly critical. Luxembourg’s delay in adopting EU sanctions against Rwanda reflects the complex web of diplomatic relations and the balancing act global powers must perform when addressing regional conflicts.
In light of these tensions, several nations have begun to engage in discussions aimed at de-escalation and conflict resolution. Key initiatives include:
- Diplomatic Engagement: Countries like the United States and France are working behind the scenes to foster dialog between DRC and Rwanda.
- Humanitarian Aid: Enhanced support has been proposed for civilians affected by the conflict.
- Sanction Debates: Ongoing negotiations within the EU regarding potential sanctions against Rwanda as a response to its alleged involvement in DRC’s unrest.
To further assess the positions of key global players, the following table summarizes their stance on the conflict:
| Country/association | Stance | Actions Taken |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Support for DRC sovereignty | Diplomatic discussions with African leaders |
| European Union | Carefully weighing sanctions | Ongoing dialogue with member states |
| United Nations | Promoting peace talks | Mediating discussions between conflicting parties |
Future Prospects: pathways to Peace in the DRC and Regional Stability
the ongoing conflict in the Democratic republic of the Congo (DRC) presents significant challenges, but it also offers pathways toward lasting peace and regional stability. In order to navigate this complex landscape, several crucial factors must be considered:
- Strengthening Diplomatic Relations: Engaging in proactive diplomacy among DRC, Rwanda, and neighboring states can bridge divides and promote collaboration.
- Support for Local Governance: Empowering local leaders and communities is essential for building trust and fostering long-term stability within the region.
- International Engagement: A coordinated global response, focusing on humanitarian support and conflict resolution, can alleviate tensions and provide a framework for peace.
Moreover, international actors must balance their approach to sanctions and incentives to cultivate a cooperative environment. Building on existing protocols, such as the follow-up of the Lusaka Ceasefire Agreement and other regional accords, could be vital. A focus on:
| Stakeholders | Potential Contributions |
|---|---|
| UN Peacekeeping Missions | Provide security and monitor ceasefires |
| African Union | Facilitate dialogue and reconciliation processes |
| International ngos | Deliver humanitarian aid and promote civil society engagement |
Encouraging collaboration between these stakeholders could pave the way for a shared commitment to peace, ultimately fostering regional stability in the heart of Africa.
Key Takeaways
the ongoing conflict in the Democratic Republic of the congo remains a complex and evolving crisis, with significant implications for regional stability and international relations. Luxembourg’s recent decision to delay the adoption of EU sanctions against Rwanda has sparked debate among member states, highlighting the challenges of achieving a unified European response to the situation. As the humanitarian toll in the DRC continues to rise, the international community faces pressing questions about accountability and intervention.The need for a coordinated approach is more critical than ever,as the actions taken—or not taken—by European nations will influence not only the lives of those directly affected by the conflict but also the geopolitical landscape of Central Africa.As the situation unfolds, continued dialogue and strategic action will be essential in addressing the multifaceted issues at play and fostering a path towards lasting peace and stability.
















