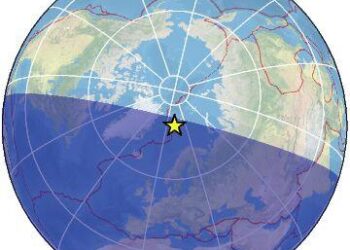
On April 9,2024,at precisely 02:51 a.m. Longyearbyen time, a weak magnitude 2.5 earthquake shook teh remote region of Nordaustlandet, part of the Svalbard archipelago. This tremor, while not uncommon in the geologically active landscape of the Arctic, has drawn the attention of seismologists and residents alike. Situated far from major population centers, Svalbard and Jan Mayen are subject to a variety of natural phenomena, including volcanic activity and tectonic shifts. The recent earthquake serves as a reminder of the dynamic geological processes that shape this rugged and isolated part of the world. As researchers continue to monitor seismic activity in the region, the event highlights the importance of understanding local geology and the potential implications for both the environment and the communities that inhabit these northern territories. This article delves into the details of the earthquake, its meaning, and the broader context of seismic activity in Svalbard.
Weak Magnitude 2.5 Earthquake Strikes nordaustlandet Region in Svalbard
A magnitude 2.5 earthquake hit the Nordaustlandet region in Svalbard early Tuesday morning, registered at 02:51 am Longyearbyen time. The tremor, while classified as weak, is a reminder of the seismic activity that occasionally affects this remote Arctic region. Residents and monitoring agencies alike reported the quake felt as only a minor disturbance, with no immediate reports of damage or injuries. Such seismic events are not uncommon in an area that is geologically dynamic, influenced by the North Atlantic tectonic environment.
This minor quake has prompted geologists to examine the broader context of seismic activity in Svalbard. The area is characterized by its dramatic landscape,comprising glaciers,mountains,and an active geological history. Key points of interest include:
- Tectonic Setting: Svalbard lies at the junction of the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates.
- Monitoring Efforts: Local institutions have enhanced seismic monitoring to better understand frequency and intensity of earthquakes.
- Impact Awareness: Awareness campaigns continue to inform residents about safety measures in the event of more meaningful seismic activity.

Timing and Location: Understanding the Epicenter of the Recent Seismic Activity
The recent seismic event, measuring a modest magnitude of 2.5, struck the Nordaustlandet region of Svalbard & Jan Mayen in the early hours of april 9, 2024, at precisely 02:51 am (Longyearbyen time). Nestled in the Arctic Circle, this remote archipelago is not only known for its stunning landscapes but also for its geological activity. The earthquake’s epicenter was located offshore, a characteristic common to seismic occurrences in this geologically active area, which is influenced by the complex interactions between tectonic plates beneath the icy surface.
This minor tremor, while not significant in terms of potential damage, adds to the ongoing interest in the seismic patterns of the region. With such events often serving as indicators of deeper geological processes, they raise various questions among researchers about the stability of the surrounding terrain. Key points to consider include:
- Frequency of seismic events: Analyzing past data can reveal patterns.
- Geological implications: understanding the tectonic settings of the area can help predict future activity.
- Public awareness: Even low-magnitude quakes can increase local interest in earthquake preparedness.

Potential Impacts on Local Infrastructure and Wildlife
The recent mild earthquake registered near Nordaustlandet poses subtle yet significant risks to both local infrastructure and wildlife habitats. Key areas that could be affected include:
- Transportation Networks: The integrity of roads, airstrips, and harbor facilities may be compromised, affecting transportation logistics.
- Utilities and Services: Essential services such as power and water supply systems may experience disruptions, impacting local communities.
- Research Facilities: the region’s scientific outposts, crucial for environmental monitoring, could face structural challenges, hindering vital research efforts.
Along with infrastructure concerns, the quake could have notable implications for local wildlife. The tremor disrupts the natural order, impacting both terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Potential consequences include:
- Wildlife Displacement: The shaking may force species to relocate,leading to increased competition for resources in unfamiliar territories.
- Habitat Alteration: Changes in landscapes, such as landslides or shifts in waterways, could destroy or transform critical habitats.
- Food Chain Disruptions: The disturbance may ripple through the food web, affecting predator-prey dynamics and breeding patterns.

Monitoring Earthquake Patterns in Svalbard: What Scientists are Observing
On April 9, 2024, a weak magnitude 2.5 earthquake struck the nordaustlandet region of Svalbard at 02:51 AM local time. This seismic event, while minor, has become a focal point for scientists monitoring activity in this remote Arctic region. The geological activity in Svalbard is frequently enough linked to its complex tectonic setting, characterized by interactions between the Eurasian and North American plates. Researchers are closely observing the frequency and intensity of these earthquakes to understand better the dynamic processes shaping the archipelago’s geology.
Significant observations from recent monitoring efforts include:
- Increased Seismic activity: A pattern of low-magnitude earthquakes has been noted,suggesting possible volcanic activity or shifting tectonic plates.
- Potential Volcanic Implications: The region’s volcanic history indicates that even minor quakes can precede larger seismic events.
- Monitoring Technology: Stations equipped with advanced seismological tools provide real-time data crucial for understanding earthquake behavior in this fragile ecosystem.
| Earthquake Details | Magnitude | Date | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weak Earthquake | 2.5 | April 9, 2024 | Nordaustlandet, Svalbard |

Safety Recommendations for Residents and Travelers in Earthquake-Prone Areas
In earthquake-prone areas,safety must be a priority for both residents and travelers. It is essential to familiarize yourself with the local emergency plans and procedures, as these can vary substantially from one region to another. Stay informed by keeping track of seismic activity through reliable sources and local authorities. Always have an emergency kit ready, which should include critical items such as:
- Water and non-perishable food for at least 72 hours.
- First-aid supplies for treating injuries.
- Flashlights and extra batteries.
- Whistle to signal for help.
- Portable phone charger to maintain interaction.
Understanding the best practices for when an earthquake strikes can also save lives. Drop, Cover, and Hold On are crucial steps to remember. If you are indoors, get down on your hands and knees, take cover under a sturdy piece of furniture, and hold on until the shaking stops. if you are outdoors, move to an open area away from buildings, trees, streetlights, and utility wires. For those in vehicles,safely pull over and remain inside until the shaking ceases. Regularly participating in earthquake drills can prepare everyone, including children and visitors, for the unexpected.

Exploring the Geophysical Significance of Earthquakes in Arctic Regions
The recent seismic activity in the Svalbard archipelago, specifically the magnitude 2.5 earthquake recorded near Nordaustlandet, underscores the complex geological dynamics at play in Arctic regions. Earthquakes, even those of lower magnitude, can offer critical insights into the tectonic stress and movement beneath the surface. The polar environment presents unique conditions, with permafrost and glacial movements influencing the geophysical landscape. This event highlights not only the potential for larger seismic events but also the necessity for ongoing monitoring to understand the region’s geological health. Scientists are particularly interested in the way these seismic occurrences correlate with melting ice and the potential implications for global sea levels and ecosystem stability.
Understanding the geophysical significance of such earthquakes involves a multi-disciplinary approach, combining geological sciences, glaciology, and environmental studies. The data gathered from seismic activities contributes to a broader awareness of several factors, including:
- Tectonic Plate Movements: Analysis of fault lines and stress distributions in the Earth’s crust.
- Climate Change Impact: The relationship between increased meltwater and seismic frequency.
- Ecological Consequences: Impacts on local wildlife and habitat structures resulting from shifting landforms.
Through rigorous research and technological advancements, scientists endeavor to unravel these complex interactions, making it critical to continue observing these regions to prepare for and mitigate future geological hazards.

Closing Remarks
the recent weak magnitude 2.5 earthquake that struck Nordaustlandet on April 9, 2024, at 02:51 am Longyearbyen time serves as a reminder of the geological activity present in the svalbard and Jan Mayen region. While the tremor was relatively mild and unlikely to have caused significant impact,it showcases the importance of continuous monitoring and research in this seismically active area. As scientists and researchers delve deeper into understanding the dynamics of such events, the data collected will contribute to our broader comprehension of tectonic processes at play in the Arctic. For residents and visitors alike, staying informed about seismic activity is essential in ensuring safety in this unique and breathtaking environment. As we look ahead, further observations and studies will continue to play a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of the natural forces that shape this remote region.