In a meaningful growth for end-of-life legislation, the Isle of Man is poised to debate a proposed bill aimed at legalizing assisted dying, a topic that continues to ignite passionate discussions across the globe. As the Isle of Man lawmakers prepare to deliberate on this contentious issue,the potential for parliamentary “ping-pong” looms large—where the bill could bounce between the House of Keys and the Legislative Council amid differing opinions and concerns.Proponents of assisted dying argue for compassion and autonomy in death, while opponents raise ethical and moral objections, fearing the implications for vulnerable populations. This article delves into the complexities surrounding the proposed bill, examining the arguments for and against assisted dying, the cultural and political landscape of the Isle of Man, and what the future may hold for this pivotal legislative initiative.
The Controversial Landscape of Assisted Dying Legislation in the Isle of Man
As discussions around assisted dying intensify, the Isle of Man finds itself at a crossroads, caught in a web of ethical dilemmas and legal complexities. Proponents argue that the legislation would empower individuals facing terminal illnesses to make choices about their own end-of-life care, advocating for personal autonomy and dignity in death. They highlight compelling arguments, including:
- Compassionate choice: Allowing individuals to conclude their suffering on their own terms.
- Regulatory frameworks: Establishing clear guidelines to prevent abuse and ensure informed consent.
- Healthcare burden: Alleviating the emotional and financial toll on families and the healthcare system.
Conversely, opponents raise significant concerns over the potential for sanctioned euthanasia to spiral into abuse and the moral implications it entails. Critics fear that vulnerable populations, including the elderly and the disabled, may find themselves coerced into making such irreversible decisions. they emphasize the need for a thorough understanding of the societal ramifications, raising points such as:
- Slippery slope argument: Fears that initial safeguards might be eroded over time.
- Alternatives to assisted dying: Highlighting the importance of robust palliative care options.
- Potential societal impacts: The risk of normalizing death as a solution.
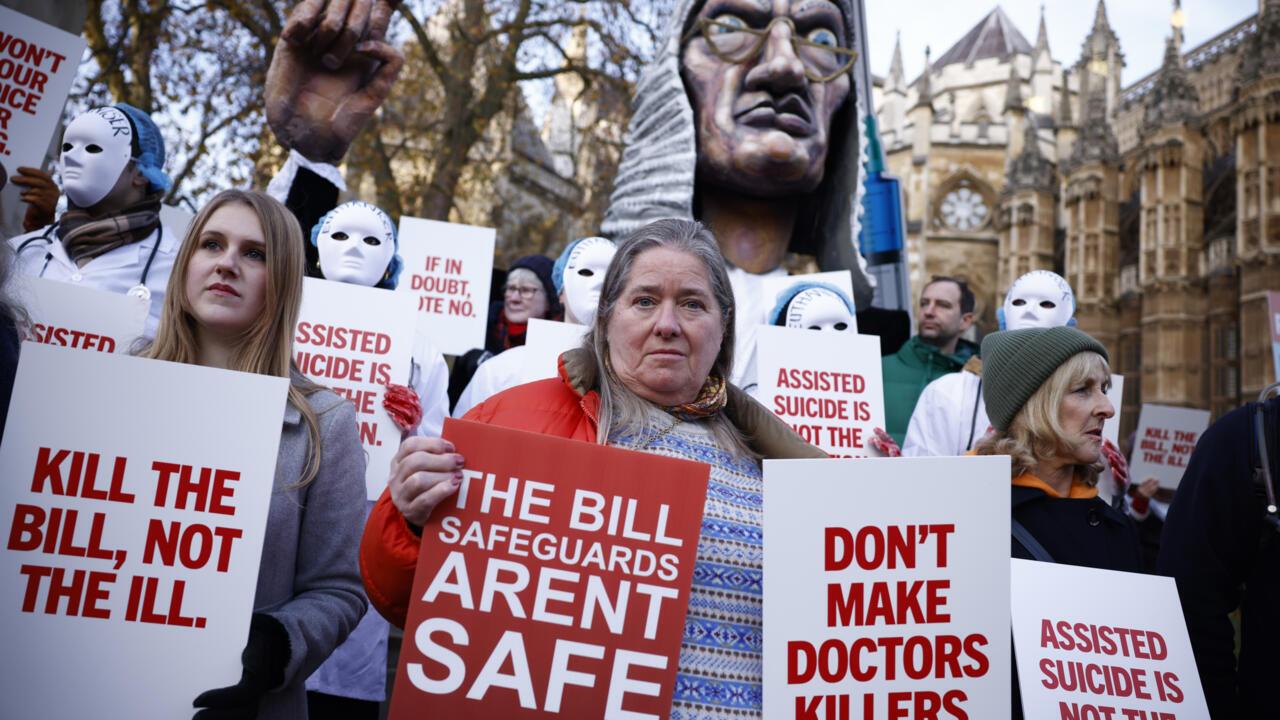

Key Provisions of the Proposed Assisted Dying Bill and Their Implications
The proposed Assisted Dying Bill outlines several key provisions designed to govern the process by which qualified individuals can seek assistance in ending their lives. Among the primary features of the bill are:
- Eligibility Criteria: Individuals must be at least 18 years old, suffering from a terminal or life-limiting condition, and experiencing unbearable pain and suffering.
- Two Physicians’ Assessments: The patient must undergo evaluations by two self-reliant physicians to confirm their eligibility and ensure informed consent.
- Waiting Period: A mandatory reflection period is established, allowing individuals time to reconsider their decision.
- Reporting and Oversight: Detailed reporting requirements are implemented to monitor how the bill is applied in practice, ensuring openness and accountability.
These provisions aim to create a framework that balances the compassionate choices for individuals facing insurmountable suffering with rigorous safeguards to prevent misuse. However, the implications of these measures extend beyond individual cases, sparking intense debate regarding ethical concerns, societal values, and the potential normalization of assisted dying. As legislators grapple with these complexities, the bill may find itself in a cycle of revisions and amendments, leading to what some commentators are calling “parliamentary ping-pong.” Below is a brief table illustrating the potential implications of the proposed bill:
| Concern | Potential Implication |
|---|---|
| Ethical Dilemmas | Discussions around the morality of assisted dying may deepen societal divides. |
| Legal Challenges | Potential for court challenges surrounding patients’ rights and definitions of suffering. |
| Healthcare Impact | Shift in focus for healthcare providers addressing end-of-life care. |
| Public Perception | Risk of changing public views on the value of life and dying with dignity. |

Public Sentiment and Stakeholder Opinions on Euthanasia in the Isle of Man
The discussion surrounding euthanasia in the Isle of Man has invoked a broad spectrum of public sentiment, reflecting deep societal values and varying personal experiences. A recent survey highlighted that 61% of the population supports assisted dying, viewing it as a compassionate option for those suffering from terminal illnesses. Though, a significant minority, approximately 27%, oppose it on moral and ethical grounds, frequently enough citing religious beliefs or concerns about potential abuses. This polarized landscape indicates that while there is a growing acceptance of assisted dying, apprehension about safeguarding vulnerable groups remains a central theme in community discussions.
Stakeholder opinions in the Isle of Man further illustrate the complexity of the issue. Healthcare professionals, including palliative care specialists, emphasize the importance of extensive end-of-life care yet recognize the need for patient autonomy.Conversely, religious groups and patient advocacy organizations frequently enough express contrasting views, promoting the sanctity of life and raising alarms about the implications of legalizing assisted dying. A recent public consultation gathered insights from various factions, revealing:
| Stakeholder Group | Outlook |
|---|---|
| Healthcare Professionals | supportive of patient autonomy; cautious about implementation. |
| Religious Organizations | Oppose euthanasia; emphasize the sanctity of life. |
| Patient Advocacy Groups | Advocate for patient rights; concerned about accessibility. |

Potential Parliamentary Challenges: Navigating the ping-Pong Process
The journey of the assisted dying bill in the Isle of Man is laden with potential hurdles, primarily illustrated by the parliamentary “ping-pong” process. This mechanism, where the House of Keys and Legislative Council alternate in reviewing amendments, can lead to significant delays and modifications.As the bill is subject to rigorous scrutiny, a few key challenges are likely to arise:
- Contentious Amendments: Diverse opinions on specifics, such as eligibility criteria or procedural safeguards, can provoke extensive debate.
- Political Dynamics: Shifts in political support or opposition within either house may introduce uncertainty, affecting the bill’s momentum.
- public Sentiment: Evolving public opinions may prompt lawmakers to reconsider their stance, leading to potential revisions in proposals.
Moreover, the ping-pong process could elongate discussions and complicate negotiations between the two houses. The need for consensus might push back the timeline considerably. The lack of a definitive deadline often adds to the inertia, meaning the bill could encounter:
- Repeated Revisions: Amendments could be made and remade, creating a cycle that frustrates advocates.
- Political Maneuvering: Strategic moves by lawmakers may stymie progress at critical moments.
- Risk of Stalemate: if the houses cannot agree, a deadlock might render the bill dormant, sidelining a crucial issue for an indefinite period.

Lessons from Other Jurisdictions: What the Isle of Man Can Learn About Assisted Dying
As discussions surrounding assisted dying gain momentum in the Isle of Man, it is essential to look beyond its shores and examine how other jurisdictions have navigated similar waters. Countries like Canada, the netherlands, and Belgium have implemented their own laws regarding euthanasia and assisted dying, providing invaluable insights into what might work or fail.As an example, Canada’s legislation emphasizes procedural safeguards, requiring individuals to undergo thorough assessments to ensure they are making informed decisions free from external pressures. Such mechanisms could serve as a model for the Isle of Man, highlighting the importance of protecting vulnerable populations while respecting individual autonomy.
Moreover, the experiences in these jurisdictions shed light on the societal and ethical implications of assisted dying. In the Netherlands, public acceptance of euthanasia has increased over the years, leading to a broader discussion on end-of-life care. However, challenges such as the possibility of slippery slopes—where the criteria for eligibility might expand over time—remain concerns worth addressing. As the Isle of Man develops its own framework, learning from the pitfalls and successes of other nations could guide lawmakers in establishing a balanced approach that considers both compassion and ethical duty. Key aspects to consider include:
- Clear eligibility criteria
- Robust oversight mechanisms
- Public engagement and debate

recommendations for a Balanced Approach to Euthanasia Legislation and Implementation
The discussion surrounding euthanasia legislation necessitates a multifaceted approach that addresses ethical, medical, and societal perspectives. Key considerations should include:
- Comprehensive Stakeholder Engagement: Involving healthcare professionals, ethicists, legal experts, and the public to ensure diverse viewpoints are considered.
- Clear Guidelines for Implementation: Establishing well-defined protocols for eligibility, consent, and oversight to prevent misuse and safeguard vulnerable populations.
- Continuous Education and Support: Offering resources and training for healthcare providers to navigate the complexities of assisted dying with empathy and professionalism.
Additionally, transparency in the legislative process is crucial to foster public trust and understanding. A proposed framework may include:
| Aspect | Advice |
|---|---|
| Monitoring and Evaluation | Regular assessments of the law’s impact on individuals and healthcare systems. |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | Educational initiatives to demystify assisted dying and reduce stigma. |
| Safeguards Against Coercion | Implementing measures to ensure decisions are made freely and without pressure. |
The Way forward
As the debate surrounding assisted dying continues to evoke strong opinions and ethical considerations, the Isle of Man finds itself at a critical juncture with its proposed legislation. The prospects of the bill navigating the complexities of parliamentary ping-pong loom large, illustrating the challenges of reaching a consensus on such a sensitive issue.As stakeholders on both sides prepare for continued discussions, the outcome remains uncertain, yet the dialogue initiated by this bill is undeniably significant. It reflects broader societal attitudes towards death and autonomy, echoing similar conversations in jurisdictions worldwide. As the Isle of Man embarks on this legislative journey, eyes will remain closely trained on the proceedings, hopeful for a resolution that acknowledges both compassion and caution in matters of life and death. the path forward may be fraught with contention, but it is through these deliberations that society can better understand the nuances of assisted dying and its implications for the future.