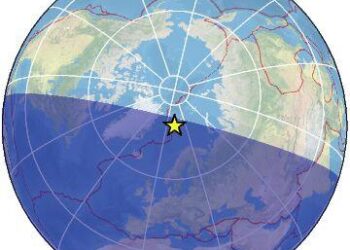
On June 9, 2024, at 06:41 AM GMT+1, a moderate earthquake registering a magnitude of 4.5 struck a remote region approximately 263 kilometers southwest of Longyearbyen, teh largest settlement on the archipelago of Svalbard and Jan Mayen. According to VolcanoDiscovery, the tremor highlights the ongoing seismic activity in this geologically dynamic area, which is known for its volcanic landscapes and dramatic geological features. While such earthquakes are not uncommon in the Arctic region,the impact and potential implications for local infrastructure,wildlife,and ongoing geological studies warrant attention. This incident serves as a reminder of the ever-present natural forces that shape our planet,particularly in areas where tectonic activity continues to evolve.
Moderate earthquake Strikes Near Longyearbyen: An Overview of the Event
A moderate earthquake registering a magnitude of 4.5 occurred on June 9, 2024, at 06:41 AM (GMT +1), approximately 263 km southwest of Longyearbyen. The tremor’s depth and location suggest it was generated by tectonic activity typical of this region, known for its geological dynamism. Residents of Longyearbyen reported feeling light to moderate shaking, but no immediate damage has been documented. The remote nature of the epicenter likely mitigated any potential hazards, but emergency services remain on standby to assess any situations that may arise.
Key details about the seismic event include:
- Magnitude: 4.5
- Magnitude Type: Local
- Depth: 10 km
- Coordinates: 78.7°N, 14.1°E
Despite the earthquake’s moderate strength, geological research indicates that the area has experienced similar seismic occurrences in the past. Monitoring agencies, including the norwegian Meteorological Institute, continue to track aftershocks and assess the quake’s implications on local infrastructure. Preparedness initiatives are already in place, ensuring that the longyearbyen community can respond effectively to such natural events.

Seismic Activity in the Arctic: Understanding the Implications for Svalbard
the recent earthquake, registering a magnitude of 4.5 and occurring 263 km southwest of Longyearbyen,highlights the growing seismic activity in the Arctic region. this event, which took place on June 9, 2024, at 06:41 am GMT +1, serves as a reminder that Svalbard is not immune to geological forces. Understanding the implications of such seismic events is crucial for both residents and policymakers in the area. While earthquakes of this magnitude are common in tectonically active regions, thier frequency and proximity to populated areas warrant a closer examination of their potential impacts on infrastructure, the habitat, and the local economy.
seismic activity in the Arctic can lead to a number of important consequences.These may include:
- Infrastructure Risk: increased potential for damage to buildings, roads, and essential services.
- Environmental Concerns: Potential disturbances in local ecosystems and the release of methane from permafrost.
- Tourism Impact: Changes in visitor patterns and concerns over safety can affect the local economy, which heavily relies on tourism.
Furthermore, there is a need for enhanced monitoring and research initiatives that focus on seismic patterns in the Arctic. Establishing comprehensive data collection systems can help in predicting future events and ensuring public safety. A collaborative effort between scientists, government officials, and local communities is essential to mitigate the risks posed by seismic activities in this fragile and rapidly changing region.

Potential Impact on Local Infrastructure: How prepared is Longyearbyen?
The recent earthquake occurring 263 km southwest of Longyearbyen highlights the seismic vulnerabilities of the Arctic region, underscoring the urgent need for robust infrastructure preparedness. In a location where natural resources and tourism are pivotal to the economy, the resilience of local structures becomes increasingly critical. Key infrastructures, including essential services and residential buildings, must be evaluated to ensure they can withstand seismic activity. Several factors contribute to the region’s readiness, including:
- Engineering Standards: Local building codes must incorporate earthquake-resistant designs.
- emergency Response Plans: Coordinated efforts among emergency services to address potential fallout from seismic events.
- Community Awareness: Regular drills can help residents react effectively in the event of a quake.
Assessing the potential impact of seismic activity also involves understanding infrastructural vulnerabilities that may arise due to Longyearbyen’s unique geographical challenges. Key infrastructure components, such as roads and utilities, may face significant strain during seismic events. A preliminary assessment indicates the following concerns:
| Infrastructure Component | Risk Level | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Roads | High | Regular monitoring and reinforcement |
| water Supply | Medium | Backup systems and routine checks |
| Power Grid | High | Seismic bracing of utility poles |

Emergency Response: Recommendations for Residents and Tourists
When faced with an earthquake, it is indeed crucial for both residents and tourists to remain calm and follow recommended safety procedures. Stay indoors if you are already inside a building, as going outside can expose you to falling debris.Drop, Cover, and Hold On should be your immediate instinct; get down on your hands and knees, take cover under a sturdy piece of furniture, and hold on until the shaking stops. For those outdoors, move away from buildings, streetlights, and utility wires to avoid potential hazards, and find an open space until the tremors cease.
Readiness is key to ensuring safety during and after seismic events. Consider taking the following steps to better equip yourself and your family for such emergencies:
- Create an emergency kit containing essentials like food, water, first aid supplies, and a flashlight.
- Develop a family interaction plan that outlines meeting points and contact information for all members.
- Familiarize yourself with local emergency services and evacuation routes in your area.
- Attend community workshops on earthquake preparedness for additional resources and training.
Additionally, participating in local preparedness drills can enhance your readiness for future seismic activities.Below is a quick reference table detailing essential emergency contact numbers that can be helpful in the aftermath of an earthquake:
| Emergency Service | Contact Number |
|---|---|
| Police | 112 |
| Fire Department | 113 |
| Medical Assistance | 114 |
| Local Emergency Management Office | [Your local Number] |

Future Monitoring and Research: Importance of Continued Observation in the Region
Continued observation in regions susceptible to seismic activity is essential for understanding the dynamics of tectonic movements and their potential impacts. Following the recent earthquake near Longyearbyen, researchers emphasize the need for comprehensive monitoring to assess both immediate consequences and longer-term geological changes. Key reasons for ongoing surveillance include:
- Data Collection: Enhanced data gathering can inform models of seismic behavior.
- Community Safety: Consistent monitoring helps ensure that local populations are prepared for future seismic events.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Understanding how seismic activity affects surrounding ecosystems can guide conservation efforts.
The unique geological features of the Svalbard archipelago make it a prime location for studying the relationship between environmental geology and seismic activity. As researchers continue to analyse data from the recent earthquake, establishing a systematic approach to future geological surveys becomes increasingly critical. This includes:
| Research Focus | objective |
|---|---|
| Seismic Activity Trends | To identify patterns and predict future occurrences |
| Infrastructure Resilience | To enhance building standards that can withstand earthquakes |
| Climate Change Effects | To study the interplay between climate phenomena and tectonic stability |

Lessons Learned: Insights from Previous Earthquake Events in the arctic
The occurrence of a moderate magnitude 4.5 earthquake near Longyearbyen serves as a reminder of the unique geological challenges faced in the Arctic region. Previous earthquake events have demonstrated several critical insights that can inform preparedness and response strategies in this remote area.Notable lessons from past seismic activities include:
- seismic Monitoring: Enhanced monitoring systems are crucial for timely alerts, allowing communities to respond quickly.
- Infrastructure Resilience: building design must incorporate seismic considerations due to the area’s geological instability.
- Public Awareness: Continuous education programs for residents can promote individual safety measures and community preparedness.
Analysis of historical data reveals patterns that can lead to improved responses. For instance, the recurrence intervals and magnitudes of past earthquakes in similar geological settings suggest that:
| Magnitude | frequency (Years) | Response Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0 – 4.9 | 5-10 | Evacuations and damage assessment |
| 5.0 – 5.9 | 10-20 | Infrastructure repair and resources mobilization |
| 6.0+ | 20+ | Long-term recovery and rebuilding efforts |
Understanding these trends can aid in improving emergency protocols and resource allocation, ensuring that Arctic communities are better protected against future seismic events.

The Way Forward
the magnitude 4.5 earthquake that struck 263 km southwest of Longyearbyen, Svalbard and Jan Mayen, serves as a reminder of the dynamic geological activity occurring in this remote region.Occurring at 06:41 AM GMT +1 on June 9, 2024, the tremor was felt across the area but did not prompt any immediate reports of damage or injury. As researchers continue to monitor seismic activity in the Arctic,such events highlight the importance of preparedness and understanding of the natural forces at play. While the region is not known for extreme seismic events, the occurrence of this earthquake emphasizes the ongoing need for vigilance and scientific investigation in order to better predict and respond to potential seismic threats in the future. As we await further analysis from geological experts, the resilience of the Svalbard community, coupled with ongoing monitoring efforts, remains crucial in ensuring safety in this stunning yet volatile corner of the world.