On June 11, 2024, at precisely 09:54 PM GMT, a minor seismic event was recorded just north of Svalbard, a remote archipelago situated between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The earthquake measured a magnitude of 2.4, a relatively weak tremor that typically goes unnoticed by the general population. However, this occurrence is noteworthy due to Svalbard’s geological activity and its implications for the surrounding regions. As scientists and researchers continue to monitor seismic trends in the Arctic, understanding such events becomes crucial in assessing the broader tectonic landscape of the area. This article delves into the details of the recent earthquake,its potential causes,and the significance of seismic activity in a region often characterized by its rugged terrain and icy expanses.
Weak Earthquake Strikes North of Svalbard: What we certainly know So Far

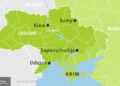
A magnitude 2.4 earthquake was recorded just north of Svalbard on Tuesday, June 11, 2024, at 09:54 PM (GMT +0). The quake’s epicenter was located approximately 30 kilometers from the archipelago’s northern tip, an area that, while not densely populated, has drawn attention due to its unique geological activity. Seismologists have categorized this as a weak earthquake, which typically does not pose any notable threat to the region or its residents. Earthquakes of this magnitude are common in parts of the Arctic, though they can occasionally stir concern among locals and researchers alike.
The seismic event has prompted reactions from both scientists and local authorities, who have assured the public that there is no immediate cause for alarm. Key points of interest include:
- Time of Occurrence: 09:54 PM (GMT +0)
- Magnitude: 2.4
- Depth: Estimated at 5 kilometers
- Location: North of Svalbard, approximately 30 km from land
While larger earthquakes can have devastating effects, monitoring agencies emphasize that this incident is part of ongoing seismic activity typical of the region. Generally, the Svalbard area experiences low-level tremors with little to no damage reported. Residents are encouraged to stay informed via local news and to report any unusual seismic activity should it occur in the future.
Seismological Insights: Understanding the Context of the June 11 tremor

The weak magnitude 2.4 earthquake that struck north of Svalbard on June 11, 2024, at 09:54 PM (GMT +0) serves as a reminder of the dynamic geological processes at play in this remote northern region. While such low-magnitude events are often beneath the threshold of human perception, their occurrence contributes to our broader understanding of seismic activity in the area. The Svalbard archipelago and Jan Mayen lie within a elaborate tectonic setting influenced by both the mid-Atlantic ridge and local fault systems, making it a point of interest for seismologists and volcanologists alike.
Such tremors can be attributed to a variety of factors, including:
- Fault Movement: Activities along local faults can release built-up stress in the Earth’s crust.
- Glacial Isostatic Adjustment: The ongoing rebound of the land from glacial melting contributes to seismicity.
- Volcanic Activity: Nearby volcanic systems may play a role in the earthquake dynamics, although this specific event is classified as too weak to indicate a volcanic eruption.
The history of seismic events in the region illustrates sporadic activity that contributes to the area’s geological narrative. Below is a summary of notable seismic activity recorded in the vicinity over recent years:
| Date | Magnitude | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Jun 11, 2024 | 2.4 | North of Svalbard |
| Mar 3, 2023 | 2.7 | Svalbard Archipelago |
| Jan 15, 2022 | 3.0 | Jan Mayen Island |
Potential Impacts on the Arctic Environment and Local Communities

A mild earthquake like the one reported north of Svalbard can serve as a pivotal reminder of the geological volatility that underlies the arctic region.the effects of such seismic activity can have profound implications for the delicate arctic environment. Coastal erosion may be exacerbated by shifts in the earth, leading to increased vulnerability of shorelines that are already under stress from rising sea levels. Additionally, permafrost destabilization caused by seismic events can lead to the release of stored greenhouse gases, further accelerating climate change. This could disrupt local ecosystems, which rely on a fragile balance of temperatures and habitats.
Local communities in the Svalbard archipelago face unique challenges as a result of seismic events. The infrastructure that supports habitation and tourism—such as roads, buildings, and research facilities—may be at risk from both the immediate impacts of an earthquake and the long-term effects of ground shifts. Communities dependent on fishing and hunting may find traditional migratory paths of local wildlife altered, further stressing food sources. Moreover, the social fabric of these communities could be threatened as residents adapt to changing landscapes and increased risks, creating a need for strategic planning and resilience-building measures in an era of unpredictable geological activity.
Preparedness and Response: Recommendations for Residents in Seismically Active Regions

Residents in seismically active regions, such as Svalbard and Jan Mayen, must prioritize earthquake preparedness to mitigate risks associated with seismic activity.Developing an emergency plan is crucial. This plan should include communication strategies, designated meeting points, and an inventory of essential supplies. Residents should also enhance their homes by securing heavy furniture, installing earthquake straps, and identifying safe zones within their residences where occupants can take cover during an earthquake.
Engaging with local community resources is equally critically important. Participate in earthquake drills and stay informed about local emergency services and procedures. Residents should consider creating a family emergency kit that contains non-perishable foods, water, flashlights, batteries, and first-aid supplies. @media only screen and (max-width: 600px) { table { font-size: smaller; } }
| Emergency Kit Essentials |
| Water (1 gallon per person per day) |
| Non-perishable food (at least a 3-day supply) |
| first-aid kit |
| Flashlight and batteries |
| Emergency blanket |
Ensuring that these preparations are regularly updated will greatly improve safety and resilience in the face of unexpected seismic events.
Future Monitoring: The Role of VolcanoDiscovery in Tracking Earthquake Activity

Monitoring seismic activity is crucial for understanding geological processes and mitigating risks associated with earthquakes. In this effort, volcanodiscovery plays a pivotal role by providing real-time data and analysis on events such as the recent weak magnitude 2.4 earthquake that occurred north of Svalbard. This event, recorded on June 11, 2024, at 09:54 PM (GMT +0), highlights the importance of continuous surveillance in regions where tectonic activity can lead to more significant geological events.
Thru a combination of sophisticated technology and expert analysis,VolcanoDiscovery enables researchers and the public to access critical information about seismic events. Key components of their monitoring system include:
- Seismic Stations: A network of sensors that detect and record earthquake activity.
- Data Visualization: dynamic maps and charts that display real-time seismic activity and historical trends.
- Alerts and Updates: Timely notifications regarding significant seismic events and potential impacts.
- Research Contributions: Collaboration with scientists to enhance the understanding of earthquake mechanics and risks.
The Way Forward
the magnitude 2.4 earthquake that struck north of Svalbard on June 11,2024,at 09:54 PM (GMT +0) serves as a reminder of the dynamic geological processes at play in this remote and often overlooked region of the Arctic. While the tremor’s low magnitude suggests minimal impact on local residents and infrastructure, it underscores the active seismic conditions that characterize the Svalbard archipelago. Continuous monitoring and research are crucial for understanding these natural phenomena, notably in an age of climate change and increasing human activity in the Arctic. As we further explore the implications of seismic activity in such an ecologically sensitive area, it becomes ever more critically important to remain vigilant and informed about these geological events. For updates on future seismic occurrences and their potential effects, stay connected with volcanodiscovery and related geological monitoring agencies.