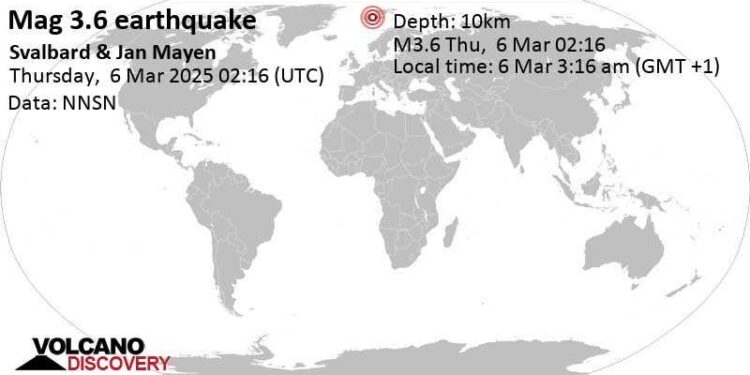
On Saturday, september 7, 2024, at precisely 01:57 PM local time in Longyearbyen, the Svalbard region was shaken by a moderate magnitude 4.0 earthquake. This seismic event has drawn attention from scientists and residents alike, given the region’s unique geological activity and its implications for local infrastructure and the surroundings. Located in the high Arctic, Svalbard is renowned for its stunning landscapes and biodiversity, but it is indeed also susceptible to natural phenomena that can disrupt daily life.As experts from volcanodiscovery and other geological institutions analyze the earthquake’s impact and potential aftershocks, this incident raises crucial questions about seismic safety and the robustness of monitoring systems in remote territories. here, we delve into the details surrounding this latest event, its geological context, and the broader implications for the Svalbard community.
Impact and Implications of the Svalbard region Earthquake
the moderate earthquake that struck the Svalbard region has raised questions regarding its geological implications and the potential for further seismic activity in this unique Arctic environment. svalbard, situated on the boundary of the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates, has a history of seismic events, yet a magnitude 4.0 quake is significant enough to warrant a closer examination of its potential impact on the region’s geological stability. Researchers have identified several key areas of concern, including:
- Infrastructure Vulnerability: The earthquake’s magnitude could affect critical infrastructures, such as research stations and transportation links, particularly in the populous town of Longyearbyen.
- Environmental Changes: The seismic activity may lead to landslides or other geological shifts, causing changes to local ecosystems and habitats.
- Increased Monitoring: Following this event, seismic monitoring may intensify to ensure preparedness against future quakes.
The effects of this seismic event extend beyond immediate geological risks. The potential implications for maritime activity must also be considered, as the Svalbard archipelago is strategically located along critical shipping routes in the Arctic. Authorities may need to reassess navigational safety protocols and the impact of ice dynamics in the area, which could be exacerbated by seismic influences. Furthermore, the earthquake’s occurrence can stimulate interest and funding in scientific research aimed at understanding and mitigating the effects of climate change in polar regions. Key considerations for stakeholders include:
- Assessment of Shipping Routes: analyzing how seismic shifts might affect established maritime pathways.
- Research Funding: Potential increases in financial backing for scientific studies focused on geological and environmental interactions.
- Disaster Preparedness: Implementing measures to develop robust response plans for both residents and visitors in the event of earthquake aftershocks.

Geological context: Understanding the Tectonic Activity of Svalbard
The tectonic setting of Svalbard is shaped by its position along the boundary of the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates. This relatively remote Arctic archipelago is frequently enough studied for its unique geological structure,characterized by a combination of compressional and extensional forces. The region experiences significant seismic activity due to the movement of these plates, resulting in phenomena such as earthquakes and the formation of geological features like fjords and mountainous terrain. In particular, the Greenland Sea Rift to the west and the Spitsbergen Arch to the east exemplify the dynamic interactions within the earth’s crust that contribute to Svalbard’s geological diversity.
Recent events, including the magnitude 4.0 earthquake on September 7, 2024, further highlight the ongoing tectonic processes in the area. This seismic event is part of a broader pattern of activity that can be attributed to several key factors:
- Plate tectonics: Constant shifts lead to stress accumulation and release along fault lines.
- Glacial rebound: With the ongoing melting of glaciers, pressure is relieved, impacting local seismicity.
- Volcanic activity: The potential for volcanic systems adds another layer of complexity and hazard.
Understanding these factors provides insight not only into the immediate effects of earthquakes but also into the long-term geological evolution of Svalbard.

Emergency Preparedness: What Residents Should Know
Residents in the Svalbard region should remain vigilant and well-informed, especially after a moderate magnitude 4.0 earthquake that struck on September 7, 2024. It is crucial to have a complete understanding of potential risks and preventative measures. Here are essential steps to ensure safety:
- stay Informed: Keep track of local news and seismic alerts.
- Emergency Kit: Prepare a kit with medical supplies, food, and water sufficient for at least 72 hours.
- Evacuation Plan: Designate safe meeting spots and evacuation routes known to all family members.
- Insurance Review: Check property insurance and update coverage to include earthquake damage if necessary.
In addition to preparation, understanding how to respond during and after an earthquake can considerably reduce risks and promote safety.Consider the following guidelines:
| Action | When | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Drop, Cover, and Hold On | During the quake | Protects you from falling debris and minimizes injuries. |
| Check for Injuries | After the quake | Assess and provide frist aid to those in need. |
| Avoid Bridges | Instantly after | Bridges may be compromised; ensure their safety before crossing. |

Potential Aftershocks and Monitoring Efforts
In the aftermath of the moderate magnitude 4.0 earthquake that struck the Svalbard region, seismic experts indicate that the potential for aftershocks remains a significant concern. These aftershocks can range in intensity and may occur days, weeks, or even months following the initial quake. Key factors influencing the likelihood of aftershocks include:
- Depth of the initial quake: Shallower earthquakes typically generate more frequent aftershocks.
- Fault line activity: The characteristics of the geological fault involved can dictate aftershock patterns.
- Regional tectonics: Nearby tectonic activity may increase stress in the surrounding area, possibly leading to subsequent tremors.
Monitoring efforts are being ramped up in response to this seismic event. Seismologists are employing advanced technology to detect and analyze any aftershock activity. This includes the use of:
- Seismic networks: Enhanced networks provide real-time data on ground motions.
- Satellite imagery: Aerial surveys can help assess any structural damage and geological shifts.
- Community reporting: Local residents are encouraged to report any tremors felt, aiding in data collection.
| Monitoring Tools | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Seismic Sensors | Detect ground motion |
| GPS Stations | Measure land displacement |
| Field Surveys | Assess damage and geological changes |
Scientific Insights: The Role of VolcanoDiscovery in Earthquake Analysis
In the realm of geological sciences, VolcanoDiscovery plays a pivotal role in enhancing our understanding of seismic activity, particularly when it comes to analyzing earthquakes like the recent event in the svalbard Region. With its extensive database and real-time monitoring capabilities, the platform provides invaluable data for researchers and the public alike. By compiling facts from various geological sources,VolcanoDiscovery offers insights into the patterns and causes of seismic events,helping us to comprehend the intricate dynamics of tectonic movements.
This particular earthquake,registering a moderate magnitude of 4.0, allows scientists to investigate several factors:
- Location Analysis: The geographical positioning of the Svalbard Region and its geological features.
- Tectonic Implications: Insights into plate movements and strain accumulation in this arctic region.
- Ancient Context: Comparing this event with past seismic activities to identify trends and changes in earthquake behavior.
Integrating real-time data with historical analysis, VolcanoDiscovery not only aids in immediate assessments but also fosters a deeper understanding of long-term geological processes. This combination proves essential for developing more effective strategies for monitoring and preparing for future seismic events.

Safety Recommendations for Residents and Tourists in Earthquake-Prone Areas
Residents and visitors in earthquake-prone regions must stay informed and prepared for seismic events. Here are some essential tips to enhance your safety during an earthquake:
- identify Safe Spots: Recognize safe areas in your home, workplace, or hotel, such as under sturdy furniture or against an interior wall.
- Have an Emergency Kit: Prepare a kit containing essentials like water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, and a first aid kit.
- Practice Drills: Regularly conduct earthquake drills to ensure everyone understands evacuation routes and safety protocols.
- stay Informed: Follow local news and alerts for real-time updates. Download emergency apps for notifications on seismic activities.
In the unfortunate event of an earthquake,follow these crucial steps:
- Drop,Cover,and Hold On: Drop down to your hands and knees,take cover under sturdy furniture,and hold on until the shaking stops.
- Move with caution: After the quake,check for hazards before moving. Be cautious of potential aftershocks.
- Help Others: Assist those in need, such as the elderly or disabled, while prioritizing your safety.
- Seek Shelter:** If outdoors, stay away from buildings, trees, streetlights, and utility wires.
In Retrospect
the moderate magnitude 4.0 earthquake that struck the Svalbard region on September 7, 2024, at 01:57 pm Longyearbyen time serves as a reminder of the geological activity beneath this Arctic archipelago. While no significant damage or injuries have been reported,the event highlights the importance of ongoing monitoring of seismic activity in this remote region. Researchers and local authorities will continue to assess the aftereffects and ensure readiness for potential future seismic events. As climate change influences geological formations and contributes to altered landscapes, the need for comprehensive studies on the impact of such earthquakes in polar regions becomes increasingly vital. For residents and researchers alike, this event underscores the intricate connection between the Earth’s processes and human habitation, reinforcing the ongoing importance of preparedness and scientific inquiry in a world marked by change.











Unexpected Allies: The G.O.P.’s Unlikely Embrace of Putin’s Russia