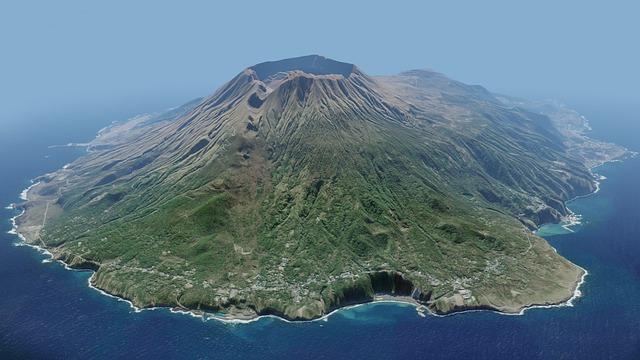
In a notable geological event that has drawn attention from scientists and residents alike, a 6.5 magnitude earthquake struck Jan Mayen Island, located in the Arctic Ocean, early on [insert date]. This remote volcanic island, governed by Norway, is situated approximately halfway between Greenland and Norway and is known for its rugged terrain and unique ecological characteristics. The earthquake, which occurred at a depth of [insert depth], generated tremors felt across the surrounding region, prompting immediate responses from local authorities and monitoring agencies. While details regarding damage and casualties remain limited, experts are closely analyzing the seismic activity as they work to assess the implications of this event on the island’s landscape and its potential impact on the broader tectonic environment of the Arctic.
Impact Assessment of the 6.5 Magnitude Earthquake on Jan Mayen Island
The recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake that struck Jan Mayen Island has raised significant concerns regarding its effects on both the local environment and the island’s infrastructure. Preliminary assessments indicate the following key impacts:
- Infrastructure Damage: Initial reports suggest damage to old lookout towers and some research facilities, though critical infrastructure remains largely intact.
- environmental Effects: Geological surveys indicate potential shifts in local tectonic structures,which may have long-term implications for the island’s unique ecosystems.
- Safety Precautions: Emergency protocols are being evaluated, with updated guidelines for residents and research personnel to ensure safety in case of aftershocks.
Local authorities and geological experts are closely monitoring seismic activity in the region to better understand the earthquake’s ramifications.The following table summarizes the current status of the assessments conducted:
| Category | Status |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Minor Damage |
| Environmental Monitoring | Ongoing |
| Public Safety | Advisories Issued |

Geological Insights: Understanding the Seismic Activity in the Arctic Region
The recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake that shook Jan Mayen island has raised significant questions about the geological dynamics of the Arctic region. Situated along the boundary of the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates, Jan Mayen is an area characterized by a complex interplay of geological forces. In this part of the world, seismic activity is not merely a curiosity; it is indicative of the ever-changing landscape shaped by plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and the unique environmental conditions of the polar region.Understanding these factors is crucial, as they contribute to both the natural processes occurring beneath the surface and the potential risks posed to human activity in the area.
Key elements influencing seismicity in the Arctic include:
- Tectonic Plate interactions: The movement of plates can cause stress accumulation,leading to earthquakes.
- Volcanic Activity: The interaction of molten rock with the earth’s crust can trigger tremors.
- Climate Change: Melting ice can affect the weight on tectonic plates, possibly influencing their movement.
The monitoring of seismic activity in this vulnerable region is essential for ensuring the safety of research stations and any future commercial interests. Below is a table illustrating recent seismic events in and around the Arctic Circle, highlighting the need for continued observation.
| Date | Magnitude | Location | Depth (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| August 15, 2023 | 5.3 | Greenland Sea | 10 |
| July 22, 2023 | 4.8 | Norwegian Sea | 12 |
| June 10, 2023 | 6.0 | Jan Mayen | 8 |

Emergency Response Strategies for Natural Disasters in Remote Areas
In the aftermath of seismic events such as the recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake near Jan Mayen Island, having a robust emergency response framework is crucial for safeguarding lives and minimizing devastation. The geographical isolation of remote areas presents unique challenges that necessitate tailored strategies. Effective communication is paramount; establishing reliable channels that can function during emergencies ensures that vital information flows seamlessly to affected populations. Additionally, pre-emptive measures, such as community training programs and disaster drills, can considerably enhance the readiness of residents and local responders.
To further bolster response efforts, local authorities and organizations should consider implementing the following strategies:
- Mobile Response Units: Deployment of teams equipped with essential supplies and medical assistance ready to reach isolated areas.
- Local Partnerships: Collaboration with NGOs and local volunteers to streamline logistics and distribution of aid.
- Remote Monitoring Technology: Utilization of drones and satellite imagery to monitor affected areas and assess damage effectively.
- Community Resilience Programs: initiatives that focus on infrastructure enhancement and resource management to prepare residents for potential future disasters.
Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance the resilience and preparedness of remote communities, allowing them to navigate the complexities of natural disasters more effectively. As the situation develops, continuous assessment and adaptation of these approaches will be essential in safeguarding the vulnerable populations residing in such challenging environments.

Lessons Learned from Previous Earthquakes: Preparing for Future Events
Each seismic event carries valuable insights that can enhance our understanding and preparedness for future quakes. Studies of past earthquakes have shown the significance of timely education and community drills in reducing casualties and improving response times. Regions that implemented regular emergency preparedness training were consistently better equipped to handle aftershocks or emergencies that followed an initial quake. Additionally, investing in infrastructure improvements is crucial; buildings designed or retrofitted to withstand seismic forces have proven to save lives during catastrophic events.
Moreover,analyzing data from previous earthquakes highlights the critical need for robust communication systems. Establishing reliable channels for disseminating alerts and information can significantly enhance community resilience. A focus on real-time data monitoring and sharing for immediate public access can empower individuals and businesses to make informed decisions during a crisis. The table below illustrates several key lessons learned from past seismic activities:
| Lesson | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Drills | Conduct community drills to prepare for potential emergencies. |
| Infrastructure Upgrades | Ensure buildings are designed to withstand seismic activity. |
| Communication Systems | Develop reliable systems for disseminating emergency information. |
| Public Awareness | Educate the public on earthquake signs and safety measures. |

Scientific Community Response and Ongoing Research after the Quake
the recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake that struck Jan Mayen Island has prompted an immediate and robust response from the scientific community. Researchers and seismologists worldwide are rallying to analyze the seismic data collected during and after the quake. Various institutions are dedicating resources to monitor aftershocks, investigate the tectonic implications of this unique location, and study the potential impact on local ecosystems. Key areas of focus include:
- Seismic Data Analysis: Enhanced network of sensors to capture detailed readings.
- Tectonic Studies: Evaluating the tectonic plates’ interactions that may have contributed to the quake.
- Ecosystem Impact Research: Investigating any geological or ecological changes resulting from the seismic activity.
Moreover,international collaboration is evident as universities and research institutions set up joint initiatives to explore the broader implications of the earthquake. Preliminary assessments suggest that Jan Mayen’s position between the north American and Eurasian plates makes it a vital site for understanding earthquake behaviour in subpolar regions. To facilitate ongoing research, a series of workshops and symposiums are being planned, where scientists will share findings and strategies moving forward. A timeline for the planned initiatives is outlined below:
| date | Event | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| November 2023 | Data Collection Review | Seismic Analysis |
| December 2023 | international Symposium | Tectonic Interactions |
| January 2024 | Workshop on Ecosystem Changes | Environmental Impact |

recommendations for Resilience Building in Earthquake-Prone Regions
Building resilience in regions susceptible to seismic activity is crucial for minimizing the impact of earthquakes on communities. A multi-faceted approach is essential, including:
- Enhanced Building Codes: Implementing and strictly enforcing building codes that account for seismic risks can significantly reduce structural damage during earthquakes.
- Community Awareness Programs: Education initiatives should be launched to inform residents about earthquake preparedness, including evacuation routes and emergency kits.
- Regular Drills: Conducting regular earthquake drills within schools, workplaces, and communities will help people respond swiftly and effectively in the event of a quake.
- Emergency Response Plans: Developing thorough emergency response plans that involve local governments, emergency services, and community organizations can facilitate coordinated responses during an earthquake.
Additionally, investment in research and technology plays a pivotal role in resilience building. this includes:
- Seismographic Monitoring Systems: Establishing a network of advanced seismographs can provide real-time data and early warning systems to mitigate damage and save lives.
- Community Resilience Funds: Creating funds dedicated to disaster recovery can help communities rebuild and recover more effectively after an earthquake.
- Infrastructure Upgrades: Strengthening critical infrastructure such as bridges and communication systems is vital to ensure functionality during and after seismic events.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Engaging the private sector in resilience initiatives can lead to innovative solutions and additional resources to support earthquake preparedness.
To Conclude
the recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake that struck Jan Mayen Island in the Arctic Ocean serves as a stark reminder of the geological volatility present in this remote region. While immediate reports indicate minimal damage and no known casualties, the event highlights the need for ongoing monitoring and research in seismically active zones. As scientists continue to study the implications of such earthquakes, understanding their potential impact on both local ecosystems and human activities remains critical. As we keep an eye on further developments, this incident underscores the importance of preparedness in areas vulnerable to natural disasters, even in some of the world’s least populated regions.