In recent months, Latvia has found itself at the center of a contentious national debate regarding the potential introduction of conscription for women. As the baltic nation grapples with evolving security concerns and regional tensions, the discussion around gender equality in military service has taken on new urgency. Advocates argue that extending conscription to women is a vital step towards equal responsibilities in national defense, while opponents raise concerns about the implications for gender roles and societal norms. This article delves into the intricacies of the debate, exploring the perspectives of policymakers, military officials, and citizens, as Latvia navigates this pivotal moment in its defense policy and social fabric.
Exploring the Historical Context of Conscription in Latvia
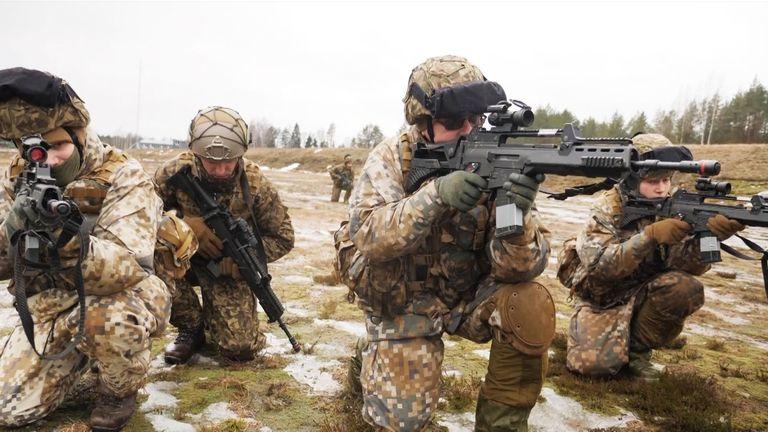

Latvia’s relationship with conscription has evolved dramatically over the past century, influenced by the country’s tumultuous history of independence, occupation, and geopolitical pressures. Following its declaration of independence in 1918, latvia established a national army, which included conscription for men, as a means to defend its sovereignty. However, during the Soviet period, Latvia’s military identity was subsumed under the larger Soviet military framework, and local conscription practices were deeply impacted by Moscow’s centralized control. The re-establishment of independence in 1990 reignited discussions about national defense,leading to a renewed focus on military service,including efforts to introduce a more modern form of conscription that would be reflective of contemporary societal values.
In recent decades, Latvia has seen a growing debate surrounding the inclusion of women in conscription, marking a significant shift in public perception of military service. This dialogue touches upon several key points:
- Gender Equality: Advocates argue that equal responsibilities in national defense are paramount in achieving true gender equality.
- Military Preparedness: Expanding conscription to include women could enhance the operational capabilities of the Latvian Armed forces, ensuring a more diverse and skilled military.
- Cultural Shifts: The discussion reflects broader changes in societal attitudes toward women’s roles, both in the military and in civic duties.
As discussions continue, some see a potential legislative shift as pivotal in shaping the future of national defense. This includes considerations of how women’s conscription could redefine customary notions of duty and service within the Latvian context.
Arguments For and Against Womens Conscription in Contemporary Society

The debate surrounding women’s conscription in Latvia has sparked a variety of arguments both for and against the policy. proponents argue that gender equality should extend to all aspects of society, including military service. They assert that including women in conscription can enhance national security by increasing the pool of available personnel. Moreover, supporters believe it could challenge traditional gender roles, showcasing women’s capabilities in various fields, including combat and leadership. Other arguments for conscription include:
- Inclusivity: Ensuring everyone contributes to national defense.
- Skill Advancement: Offering training and education that benefits individuals and society.
- Promotion of National unity: Fostering a sense of shared duty among citizens.
Conversely, critics of women’s conscription present compelling concerns regarding its implementation. Detractors argue that conscripting women may reinforce outdated notions of military service as primarily a male domain. They also cite potential physical and psychological differences that could affect performance in rigorous military environments. Furthermore, some believe that mandatory service should not be imposed on women, emphasizing personal choice over enforced duty. Key counterarguments include:
- Effectiveness: Questioning whether it genuinely enhances military capability.
- Ethics of Conscription: Scrutinizing the morality of compelled service.
- Workforce Impact: Concerns around disruption to education and careers.
The Impact of Gender Equality Initiatives on Military Policies

the ongoing debate in Latvia about the introduction of conscription for women sheds light on the broader implications of gender equality initiatives within military policies. As nations around the world strive for inclusivity in their armed forces, the incorporation of women into conscription discussions signals a significant shift in societal norms and governmental approaches. this initiative reflects a commitment to recognizing the capabilities and potential contributions of women in defense roles, paving the way for a more balanced representation in military ranks. Proponents argue that gender equality in conscription not only enhances military effectiveness but also promotes social cohesion and empowers women by granting them equal responsibilities and rights.
In exploring the impacts of such policies, several key considerations emerge:
- Operational Readiness: Integrating women into conscription can lead to a more diverse and prepared military force.
- Societal Perception: Changing views on women’s roles in the military may encourage broader acceptance of female leadership across various sectors.
- Policy Frameworks: Establishing clear guidelines and support systems is essential to ensure successful implementation and retention of women in military service.
| Proponents’ Arguments | Critics’ Concerns |
|---|---|
| Equality in service opportunities | readiness and effectiveness concerns |
| enhanced military capabilities | Potential backlash from traditionalists |
| Gender-sensitive military culture | Implementation challenges |
Public Opinion Trends on Female Conscription in Latvia
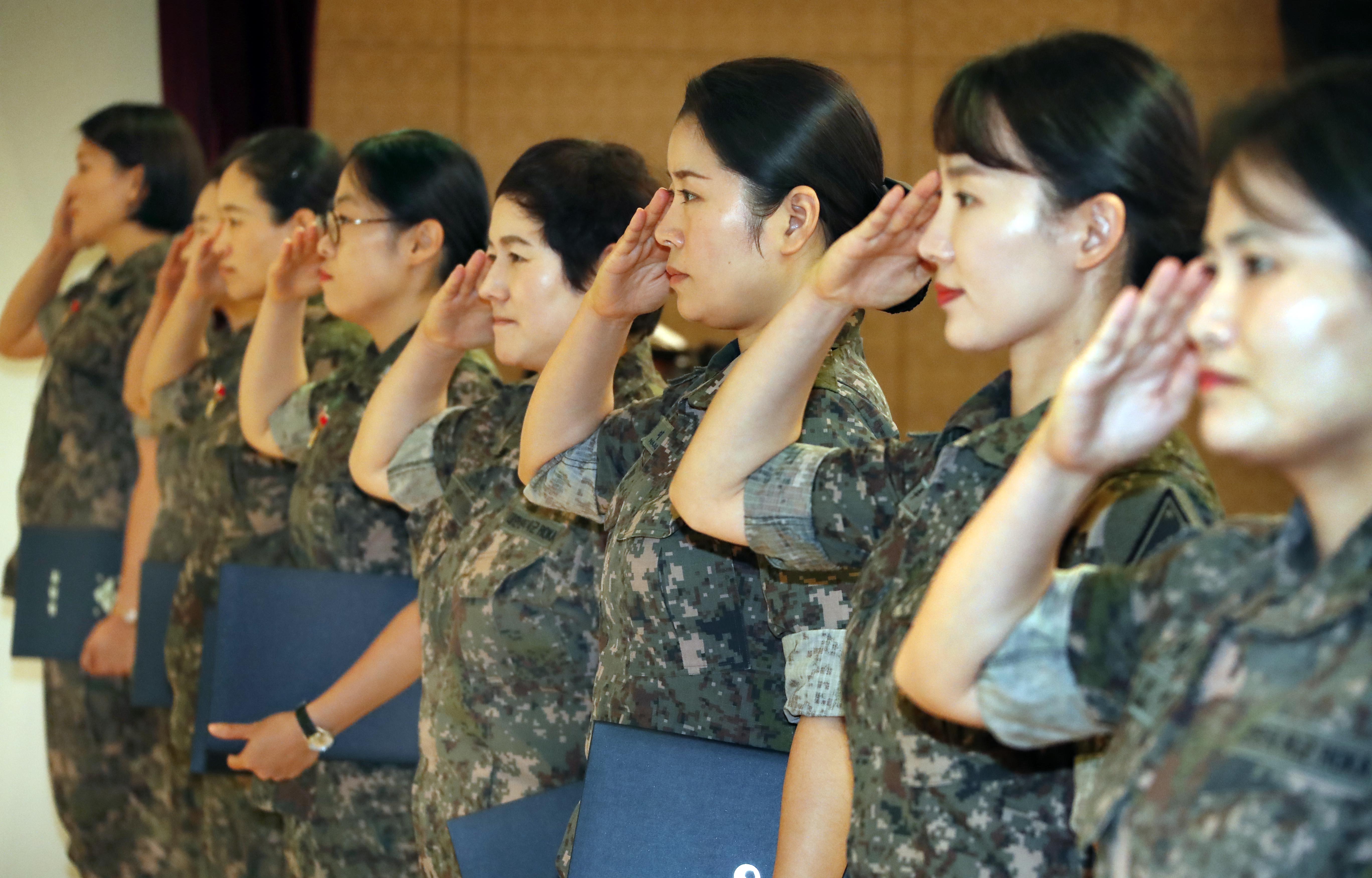

Recent discussions in Latvia regarding the potential introduction of female conscription have highlighted significant shifts in public opinion. While traditional views often relegated military service to males, a growing number of citizens are recognizing the importance of gender equality in national defense. key factors influencing this debate include:
- Equality and Empowerment: Advocates argue that conscription for women promotes equality and empowers women to contribute equally to national security.
- Security Needs: In light of geopolitical tensions, some citizens believe that expanding the pool of eligible conscripts is crucial for enhancing military readiness.
- Cultural Shifts: The evolving roles of women in society,alongside their participation in various sectors,signify a gradual acceptance of their presence in traditionally male-dominated areas.
Opponents of female conscription raise concerns about the implications for women’s rights and societal roles. There is a palpable fear that mandatory service could impede women’s career advancements and personal freedoms. Public opinion surveys reveal the following sentiments:
| Opinion | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Support for female conscription | 45% |
| Opposition to female conscription | 35% |
| Undecided | 20% |
International Comparisons: Lessons from other Nations
As Latvia grapples with the notion of introducing conscription for women, examining international precedents can provide valuable insights. Countries such as Israel, Norway, and Sweden have already implemented gender-neutral conscription systems, offering a wealth of lessons on integration and societal impact. For instance,in Israel,military service is mandatory for both men and women,which has fostered a culture of equality and shared responsibility in defense matters. This model not only normalizes women’s roles in the military but also paves the way for greater representation in various sectors post-service.
Moreover, Norway has been at the forefront of gender equality in military service, introducing conscription for women in 2015. This policy has resulted in a diverse and capable armed forces, reflecting the nation’s commitment to inclusivity. Key outcomes from various countries’ experiences suggest that successful implementation of similar measures in Latvia could lead to:
- Enhanced national security – A broader recruitment pool may strengthen defense capabilities.
- Empowerment of women – Contributing to national service can boost women’s roles in society.
- Societal cohesion – Shared experiences among citizens promote unity and understanding.
In the context of Latvia’s debate, a comparison shows varying degrees of public support and cultural acceptance across these nations.Below is a simplified table summarizing the approaches to conscription in these countries:
| Country | Conscription Status | gender Neutrality |
|---|---|---|
| Israel | Mandatory | Yes |
| Norway | Mandatory | Yes |
| sweden | Optional (Reloaded system) | Yes |
These international comparisons can help Latvian policymakers understand the potential benefits and challenges of introducing a similar system and how it may shape the future of their military and society.
Recommendations for Policy Makers on Gender Inclusivity in Defense Forces

To enhance gender inclusivity within defense forces, policy makers should prioritize complete training and awareness programs that emphasize the value of diversity and equality. By fostering an surroundings that recognizes the contributions of all service members, the following initiatives can be implemented:
- Targeted Recruitment Campaigns: Develop outreach strategies that encourage women to consider military careers, showcasing role models and success stories.
- Supportive Policies: Establish policies that promote work-life balance, including flexible scheduling and parental leave, to support service members with families.
- Mentorship Programs: Implement mentorship initiatives that connect women with seasoned leaders in the defense forces, enhancing their professional development and retention.
Furthermore, it is essential to continually assess and adapt policies to ensure that they are not only inclusive but also effective in promoting a culture of respect and equity. An effective approach might include:
| Action Item | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Regular Climate Surveys | Identify areas for improvement and gauge member satisfaction. |
| Feedback Mechanisms | enable service members to voice concerns and suggest improvements. |
| performance Metrics | Assess the effectiveness of gender inclusivity initiatives over time. |
In Summary
the ongoing debate in Latvia regarding the potential introduction of conscription for women reflects broader societal discussions about gender roles, national defense, and equality. As the country grapples with the implications of such a policy shift, opinions remain divided among lawmakers, military officials, and citizens alike. With rising security challenges in the region,the decision to perhaps implement conscription for women will not only impact military readiness but also resonate deeply within the fabric of Latvian society. As the discourse continues, it will be crucial for stakeholders to consider both the strategic needs of the nation and the principles of equality and inclusivity that underpin modern democratic values. The outcome of this debate may well set a precedent for other nations in the region,highlighting the evolving nature of defense responsibilities in contemporary warfare and the role of women therein.