On Thursday, march 6, 2025, at 03:16 AM (GMT +1), a low-magnitude earthquake measuring 3.6 on teh Richter scale struck the remote regions of Svalbard and Jan Mayen, drawing attention from geologists and seismology enthusiasts alike. Positioned deep within the Arctic Circle, these isolated Norwegian territories are no strangers to seismic activity, yet this recent tremor emphasizes the dynamic geological processes occurring beneath the surface.while the earthquake’s relatively minor intensity suggests limited immediate risks, such events serve as a reminder of the Earth’s ever-changing nature and the importance of ongoing monitoring in these fragile ecosystems. As experts analyze the implications of this quake, insights into the region’s tectonic behavior and potential volcanic activity will become increasingly vital in understanding the complexities of this unique Arctic surroundings.
Light Magnitude Earthquake Strikes Svalbard and jan Mayen Region
A mild tremor with a magnitude of 3.6 was recorded in the Svalbard and Jan Mayen region early Thursday morning. The earthquake struck at 03:16 am (GMT +1) and, while significant enough to be noted, it caused minimal disruption due to its relatively low magnitude.Seismologists indicate that the area is no stranger to such activity, attributing these minor quakes to the geological dynamics that characterize the region.
In the aftermath of the quake, no reports of substantial damage or injury have surfaced, allowing residents to carry on with their daily routines unscathed. The geological monitoring networks continue to observe the seismic activity closely. In response to this event, the public has been urged to stay informed about potential aftershocks and the region’s seismic history.Key points of interest include:
- Date & Time: March 6, 2025, 03:16 am (GMT +1)
- Magnitude: 3.6
- Location: Svalbard & Jan Mayen region
- Impact: No significant damage reported
Impact Assessment of the March 6 Earthquake in Arctic Territory
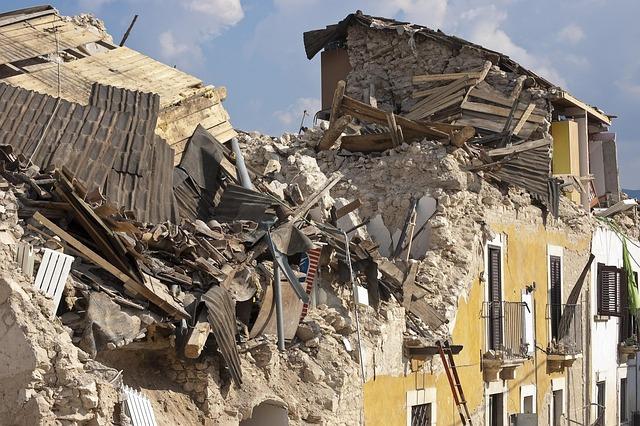

The magnitude 3.6 earthquake that struck the Arctic territory on March 6, 2025, has generated significant interest and concern among scientists and residents alike. While earthquakes of this magnitude may be relatively minor compared to those experienced in more seismically active regions, the unique geological and environmental context of Svalbard and Jan Mayen makes the impact worth assessing. Key considerations include:
- Seismic Activity Patterns: This quake is noteworthy as it adds to the understanding of the seismic patterns prevalent in this remote area, which has shown increased activity over the past decade.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Local infrastructure, including research stations and community structures, will be evaluated for their resilience to seismic events and any potential need for reinforcement.
- Ecological Consequences: Potential impacts on the delicate Arctic ecosystem,including shifts in habitat conditions for wildlife,demand monitoring and research to safeguard biodiversity.
Initial reports indicate that there were no immediate casualties or extensive property damage. Though, further assessments will be critical in understanding the broader implications of this seismic event.A detailed risk evaluation is underway, focusing on:
| Aspect | Current Status | Follow-Up Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Inspection | Ongoing | Thorough structural assessments scheduled |
| Ecological Monitoring | Proposed | Launch of long-term ecological studies |
| Community Preparedness | High | Drills and awareness programs to enhance seismic readiness |
Understanding Seismic Activity in svalbard: Historical Context and Trends

Seismic activity in Svalbard has been a focal point of geophysical research, especially given the region’s unique geological framework. Historically, the archipelago has experienced a range of seismic events, from minor tremors to more significant earthquakes. The recent light magnitude 3.6 earthquake recorded on March 6, 2025, exemplifies the ongoing tectonic activity. These earthquakes are often linked to the movement of sedimentary basins and fault lines shaped by both climatic and geological factors throughout the Quaternary period. Notably, land uplift and glacial dynamics contribute to the pressures that trigger seismic events in this Arctic environment.
Over the years, monitoring efforts have revealed certain trends regarding the frequency and intensity of earthquakes in the area. While large-scale earthquakes remain infrequent, the smaller tremors have shown a steady pattern in occurrence.Factors influencing these trends may include:
- Seismic History: A deeper understanding of past earthquakes informs predictions of future activity.
- Climate Change: Melting glaciers can alter stress distributions and contribute to enhanced seismicity.
- Human Activities: Exploration and resource extraction may also influence geological stability.
As researchers continue to analyze the data from seismic recordings, the integration of local geological studies with broader patterns of global seismic activity remains crucial in developing effective risk assessments and responses.
What Residents Need to Know: Safety Measures and Preparedness Tips
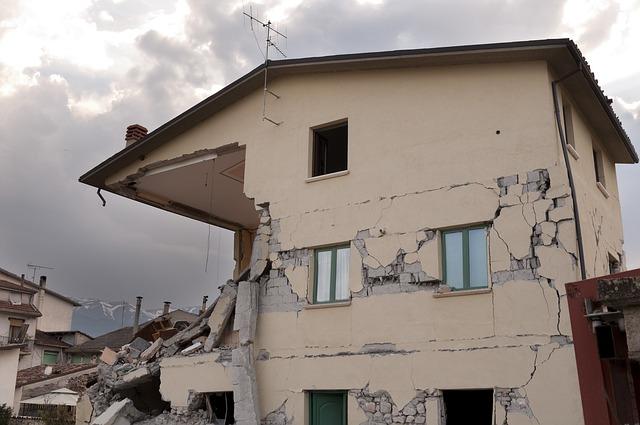

In light of the recent light magnitude 3.6 earthquake that struck Svalbard & Jan Mayen, it is indeed crucial for residents to familiarize themselves with safety measures and preparedness strategies. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind:
- Stay Informed: Regularly check local news and weather channels for updates on seismic activities.
- create an Emergency Plan: Ensure all family members know the safest areas in your home and have an agreed-upon meeting point outside.
- Secure Heavy Items: Fasten shelves and heavy furniture to walls to minimize the risk of falling during tremors.
- Prepare an emergency Kit: Stock supplies such as water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, and first-aid materials.
Understanding how to respond effectively during and after an earthquake can save lives. Remember to:
- Drop,Cover,and Hold On: Protect yourself from falling debris by dropping to your hands and knees,covering your head and neck,and taking cover under sturdy furniture.
- Stay Indoors: If you are inside during an earthquake, remain there until the shaking stops; going outside can expose you to falling objects.
- Be cautious After Shocks: Prepare for potential aftershocks, which can occur in the minutes to hours following the main event.
Keeping the above points in mind can substantially enhance your safety and preparedness in the face of natural events. For more details on creating a comprehensive emergency plan, refer to local authorities for specific guidelines tailored to your region.
Response and recovery Efforts Post-Earthquake: A community Overview
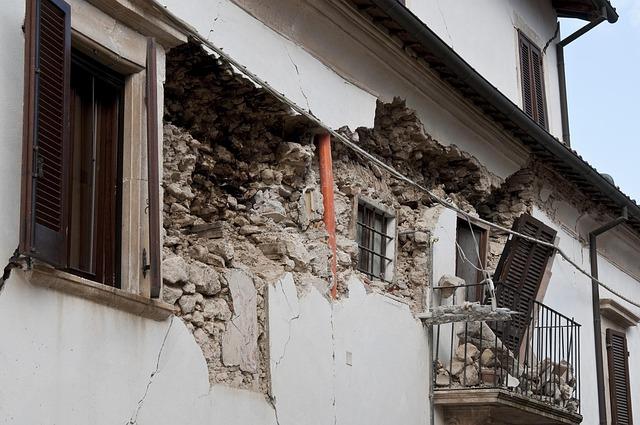

The recent light magnitude 3.6 earthquake that struck Svalbard and Jan Mayen has mobilized a swift and comprehensive response from local authorities and community members alike. Emergency services were promptly activated to assess damage and ensure the safety of residents.initial reports indicate that there were no significant injuries, but precautionary evacuations took place in vulnerable areas. Key response actions included:
- Deployment of search and rescue teams.
- Establishment of emergency shelters for affected residents.
- Immediate communication updates through local media and social platforms.
As the dust settles, recovery efforts are now underway to restore normalcy in the impacted areas. Community leaders are coordinating with government agencies to facilitate rapid assessments and repair initiatives. Local businesses are offering support through donations and services, fostering a spirit of camaraderie among residents. Significant recovery actions are being prioritized, which include:
- Evaluation of infrastructure integrity, particularly in critical services like hospitals and schools.
- Psychological support services for individuals affected by the quake.
- Collaborative meetings focused on disaster preparedness for future events.
The Role of Monitoring Agencies in Earthquake Prediction and Public Awareness

monitoring agencies play a crucial role in the ongoing efforts to understand and predict seismic events, such as the recent magnitude 3.6 earthquake near Svalbard and Jan Mayen. These organizations utilize advanced technologies and methodologies to collect data on seismic activity, which is essential for risk assessment and public safety. Through the analysis of patterns in ground movement,scientists can identify potential earthquake-prone areas and provide early warning to communities that may be at risk. Key functions of these agencies include:
- Real-time data collection: Utilizing seismographs and satellite technology to monitor tremors and respond swiftly to seismic events.
- Public education: Developing outreach programs to inform citizens about earthquake preparedness and safety protocols.
- Collaboration: Partnering with global organizations and researchers to share findings and improve prediction models.
the importance of public awareness in this context cannot be overstated.Monitoring agencies not only analyze seismic data but also strive to communicate findings effectively to the general public. By providing timely forecasts and updates on seismic activity, they empower individuals and communities to take proactive measures in the face of potential risks. This involves not only disseminating information about the recent earthquake but also emphasizing the need for preparedness plans and emergency responses. Some of the strategies agencies employ include:
- social media engagement: Using platforms to alert communities about seismic events and share safety tips.
- Workshops and drills: Organizing educational sessions that teach communities how to respond in case of an earthquake.
- Accessible resources: Providing easy access to information on earthquake safety through websites and mobile applications.
Wrapping Up
the light magnitude 3.6 earthquake that struck Svalbard and Jan Mayen early on March 6, 2025, serves as a reminder of the dynamic geological activity in this remote region of the Arctic. While the tremor, occurring at 03:16 AM GMT+1, was not significant enough to cause widespread damage or disruption, it nevertheless highlights the importance of ongoing monitoring and research in understanding the seismic landscape of these islands. As scientists continue to study the tectonic processes at play, this event underscores the intricate relationship between the earth’s movements and the unique environment of the Arctic. Monitoring organizations like VolcanoDiscovery will continue to provide updates and insights into seismic activity, ensuring that residents and researchers are well-informed about the potential risks and developments in this fascinating area.







