In a significant shift in energy policy, the European Union has stepped back from its recent call to investigate the potential revival of Russian gas supplies for Slovakia, a move that underscores the intricate balance between energy security and geopolitical considerations in the region.As europe grapples with ongoing tensions stemming from the war in Ukraine and the urgent need to transition to alternative energy sources, the decision reflects heightened concerns over reliance on Russian gas amidst an evolving landscape of energy diplomacy. This article delves into the implications of the EU’s retreat from exploring Russian gas options for Slovakia, examining the factors that contributed to this decision and its potential impact on the nation’s energy strategy and broader European energy landscape.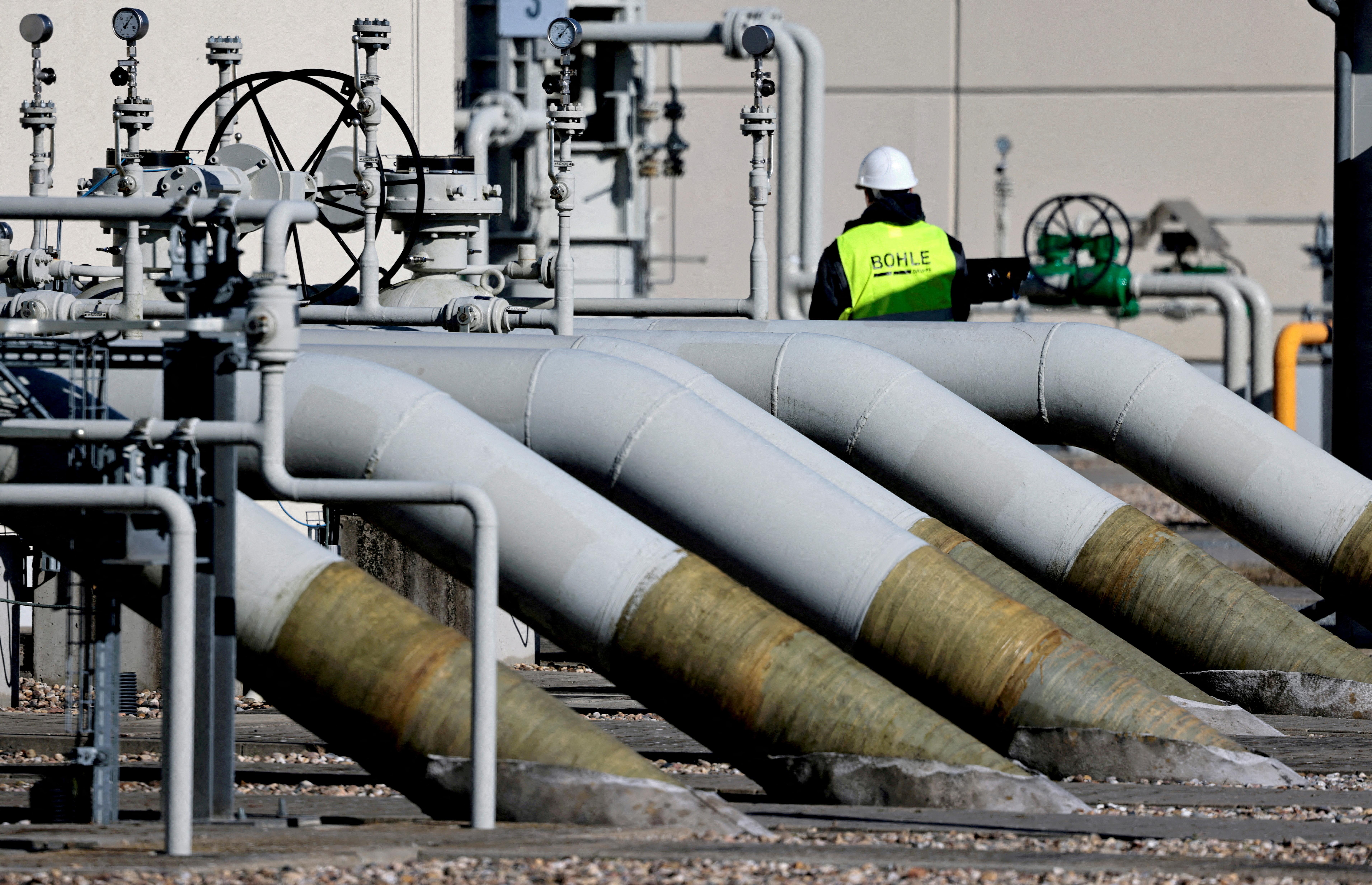
EU Reevaluates Stance on Russian Gas Supply for Slovakia
The European Union is undergoing a significant policy shift regarding the importation of Russian gas for Slovakia, as recent discussions have revealed a growing hesitance among member states. Formerly, the bloc’s strategy emphasized diversification of energy sources in light of the ongoing geopolitical tensions. Now, internal debates suggest a renewed exploration of existing contracts with Russian gas suppliers, acknowledging the delicate balance between energy security and political considerations. Key factors influencing this reevaluation include:
- slovakia’s Energy Dependence: The nation has traditionally relied heavily on russian gas, prompting concerns about potential energy shortages during colder months.
- Market Volatility: Recent fluctuations in energy prices have made Russian gas potentially attractive again, raising questions about long-term sustainability.
- Alternative Sources Limitations: Challenges in securing reliable alternatives have become more apparent, emphasizing the difficulty in achieving energy independence.
This shift in outlook, while controversial, underscores the complexities of energy politics within the EU. Member states must navigate not only economic realities but also the potential repercussions of altering their stance towards Russia. As Slovakia continues to advocate for a tailored approach to its gas supply, further negotiations may set a precedent for how the EU copes with its intricate energy landscape in the near future. A recent roundtable highlighted several points of contention, emphasizing the need for a coordinated response:
| Consideration | Current Status | future Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Security | Critical dependence on imports | Potential for supply interruptions |
| Political Relations | Tense with Russia | Likely to impact negotiations |
| Market Prices | Increased fluctuations | Impact on economic stability |

Implications of Reduced Energy Dependence on Russian Gas
The recent decision by EU officials to step back from exploring a revival of Russian gas supply for Slovakia underscores a significant shift in energy policy that could have far-reaching consequences. As European nations increasingly prioritize energy independence, this pivot reflects a broader strategic aim to mitigate reliance on contentious suppliers. The implications of reducing energy dependence on Russian gas can be seen in several key areas:
- Energy Security: Countries are likely to develop local resources and diversify energy sources, enhancing their energy security.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: With diminished reliance on Russian gas, geopolitical ties may shift, affecting the balance of power in Eastern Europe.
- Investment in Renewables: A focus on lasting energy alternatives may accelerate investments in renewable technologies, pushing for broader infrastructure changes.
- economic Impact: Transitioning away from Russian gas could lead to fluctuations in energy prices, affecting consumers and industries alike.
Moreover, the move prompts a reevaluation of existing energy partnerships and encourages EU member states to look beyond customary suppliers. Considering this,a more interconnected energy market could emerge,characterized by:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Resilience | More suppliers create a buffer against supply disruptions. |
| Price stability | Diversification may lead to competitive pricing and reduced volatility. |
| Innovative Partnerships | New collaborative efforts may drive technological advancements and energy efficiency. |

Economic and Environmental Considerations in Energy Policy Shift
The recent decision by the EU to recoil from its previous consideration of restarting Russian gas imports for slovakia emphasizes a significant pivot in energy policy, reflecting both economic and environmental imperatives. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine and subsequent sanctions against Russia have necessitated a comprehensive reassessment of energy dependencies. In an era marked by rising energy prices, the EU is exploring a blend of energy diversification and sustainability initiatives, aiming to secure energy supplies while simultaneously addressing climate change obligations. Stakeholders are increasingly advocating for investment in local renewable energy sources, which could mitigate the risks associated with over-reliance on external suppliers.
This strategic shift unveils a complicated economic landscape where energy security and environmental sustainability must coexist. policymakers are grappling with the challenge of transitioning from fossil fuels to greener alternatives, necessitating careful consideration of the financial and environmental trade-offs. Key areas of focus include:
- Investment in Renewable Energy: Redirecting funds towards solar, wind, and hydroelectric power systems.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Ensuring a mix of energy options to reduce reliance on any single supplier.
- Energy efficiency Programs: Enhancing energy conservation measures to decrease overall consumption.
To understand the region’s evolving energy landscape, consider the following table that contrasts various energy sources in Slovakia post-policy shift:
| Energy Source | Current Status | Future Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Gas | Decreasing reliance on imports | Transition towards hybrids |
| Renewables | Expanding investments | Goal for 40% share by 2030 |
| Coal | Phasing out | Minimal in future plans |

Strategic Alternatives for slovakias Energy Security
Considering the EU’s recent hesitance to consider reviving Russian gas supplies for Slovakia, the nation must explore alternative energy sources to ensure its resilience and energy independence. A multifaceted approach is necessary to navigate the shifting geopolitical landscape and secure stable energy supply lines. Potential strategic alternatives could include:
- Investment in Renewable Energy: Harnessing wind,solar,and hydroelectric power can significantly reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels.
- Strengthening Energy Efficiency: Upgrading infrastructure and promoting energy-saving technologies within homes and businesses can lower overall demand.
- Diversifying Energy Sources: Exploring partnerships with neighboring countries for alternative gas supplies and investing in liquefied natural gas (LNG) infrastructure.
- Expanding Nuclear Energy: Increasing the share of nuclear power in Slovakia’s energy mix could provide a stable and low-carbon energy source.
As slovakia evaluates these options, it is indeed crucial to establish a comprehensive energy security strategy that incorporates both short-term and long-term solutions. An assessment of potential partners, their reliability, and market conditions must guide investments. The following table summarizes potential strategic partners and their respective energy contributions:
| Country | Energy Type | potential Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Germany | Renewable Energy | High |
| Austria | Hydroelectric Power | Medium |
| USA | Liquefied Natural Gas | Increasing |
| France | Nuclear Energy | Stable |

Recommendations for Diversifying Energy Sources in Europe
In light of the recent shift regarding Russian gas imports, it is indeed essential for European nations to broaden their energy portfolios. Leveraging a mix of renewable sources, nuclear power, and innovative technologies can facilitate greater energy independence and sustainability. Key strategies include:
- Enhancing Wind and Solar Infrastructure: Investing in offshore and onshore wind farms, as well as solar panels, to harness natural resources and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Expanding Energy storage: Developing advanced battery technologies and facilities for energy storage to manage supply fluctuations from renewable sources.
- Fostering Bioenergy: Utilizing agricultural and organic waste to produce biogas and biomass energy as a transition fuel.
- Promoting Interconnectivity: Building cross-border electric grids that link different countries’ energy systems, allowing for better distribution and efficiency of energy resources.
Furthermore, investment in hydrogen technology could revolutionize the energy landscape in Europe. Utilizing green hydrogen—produced thru electrolysis using renewable energy—offers a potent fuel alternative. A clear roadmap for collaborative research initiatives across EU member states can amplify progress. Here’s a concise overview of potential investments:
| Investment Area | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Renewables Expansion | Increased energy self-sufficiency |
| Hydrogen Research | New technology breakthroughs |
| Energy Interconnectors | enhanced grid stability |
| Storage Solutions | More reliable energy supply |

The Future of EU-Russia Energy Relations Amid ongoing Tensions
The recent decision by the European Union to retract its previous call for exploring a revival of Russian gas supplies to Slovakia underscores the complex dynamics of energy relations in the context of ongoing geopolitical tensions.As Europe seeks to balance energy security with political principles, this development reflects a broader strategy to reduce dependence on Russian hydrocarbons. The EU’s alignment with Slovakia’s desire for stable energy sources juxtaposed with its commitment to sanctions against russia illustrates the intricate dance of diplomacy and energy economics. Key factors influencing this pivot include:
- Inflationary Pressures: Rising energy costs are placing a significant strain on the European economy,prompting a cautious approach towards energy sourcing.
- Energy Diversification: The EU is investing in alternative energy partners, and also developing renewable energy sources to bolster its energy independence.
- Geopolitical Strategy: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine diminishes the EU’s willingness to re-engage with Russian energy, prioritizing solidarity with Ukraine and the principle of energy sovereignty.
Moreover, this retraction indicates a redefined energy strategy that may lead to increased investments in infrastructure and technology focused on sustainable energy solutions. As member states navigate the implications of a fractured energy market, they are weighing short-term needs against long-term goals. One potential development could involve a strengthening of regional energy cooperation among EU countries, aimed at creating a more resilient energy framework. An overview of potential actions to address energy security includes:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Investment in Renewables | Increasing funding for solar, wind, and other renewable sources across member states. |
| Diversify Supply Chains | Establishing new supply agreements with non-Russian suppliers, including Norway and the United States. |
| Energy Efficiency Initiatives | Promoting programs to reduce energy consumption at both the industrial and residential levels. |
Final Thoughts
the EU’s decision to retract its suggestion to explore the revival of Russian gas imports in Slovakia underscores the complexities and sensitivities surrounding energy security in a post-conflict europe.This shift reflects a broader strategic pivot as EU member states seek to reduce dependence on Russian energy sources amidst ongoing geopolitical tensions.Slovakia, grappling with energy supply challenges and the need for stability, finds itself at a crossroads. As the EU continues to navigate the intricate balance between energy diversification and regional energy security, the implications of this decision will resonate beyond Slovakia, potentially influencing future policy directions across the continent. As Europe strives for a sustainable energy future, the path taken will undoubtedly shape the region’s economic and political landscape in the years to come.