On a day that will be etched in the memory of residents across the North Atlantic, Jan Mayen Island, a remote territory of Norway, was shaken by a powerful 6.5 magnitude earthquake. Occurring at approximately 10:00 AM local time, the seismic event sent shockwaves across the region, with tremors reported as far away as Iceland and Greenland. This article delves into the details surrounding the earthquake, including its epicenter, impact on the island’s inhabitants, and reactions from geological experts. As scientists study the implications of this significant event in an area already known for its volatile geology, the wider community grapples with the lasting effects of nature’s unpredictable force.
Impact of the 6.5 Magnitude Earthquake on Jan Mayen Island
The 6.5 magnitude earthquake that struck Jan Mayen Island has left a considerable mark on the remote territory, prompting officials to assess the impact on both infrastructure and the local environment. The tremors, which reverberated beyond the island’s shores, were significant enough to be felt as far away as Iceland and Greenland. Local authorities reported minimal infrastructure damage; however, concerns about potential aftershocks remain. Key points of concern include:
- Initial structural assessments indicating no major hazards in residential areas
- Damage to interaction facilities, causing temporary disruptions
- Increased geological monitoring to detect any subsequent seismic activity
Moreover, the earthquake has raised questions regarding the safety protocols in place for the island’s residents, particularly given its strategic position for scientific research and military operations. As the region grapples with the implications of this seismic event,the necessity for preparedness against future natural disasters has become more prominent. An emergency meeting was convened to discuss contingency plans, highlighting the need for resilient infrastructure and community awareness. Considerations from the meeting included:
| Consideration | Detail |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure Assessment | Regular checks on buildings and critical systems |
| Community Awareness | Workshops on earthquake safety and preparedness |
| Geological Monitoring | Enhanced surveillance of tectonic activity |

Historical context of Earthquakes in jan Mayen and Surrounding Regions
The geological activity in the jan Mayen region is largely attributed to its position along the boundary of the Eurasian and North American tectonic plates. This convergence results in a complex interplay of geological forces that can lead to seismic events. Historically, Jan Mayen and its surrounding areas—including parts of Iceland and Greenland—have experienced significant tectonic activity.The following factors play a crucial role in the earthquake dynamics of this region:
- Tectonic Plate Interactions: The movement of plates can generate considerable tension, resulting in earthquakes of varying magnitudes.
- Volcanic Activity: The presence of active volcanoes in nearby Iceland contributes not only to seismic events but also to the potential for further volcanic eruptions.
- Historical Seismic Records: Previous earthquakes in the region, including those documented in the 20th century, help scientists gauge potential future activity.
To provide further insight, below is a concise table illustrating significant seismic events in the vicinity of Jan Mayen:
| Date | Magnitude | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1985 | 5.8 | Iceland |
| 2000 | 6.1 | Iceland |
| 2021 | 6.3 | |
| 2023 | 6.5 | jan Mayen |
Understanding the historical context of earthquakes in this volatile region is essential for preparedness and safety measures.Ongoing geological studies aim to improve the predictability of such events, providing critical information for both residents and researchers alike.
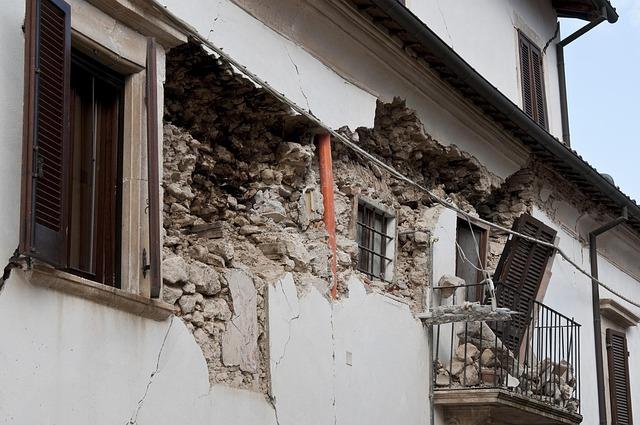

Reactions and Preparedness: How Residents and Authorities Responded
The recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake that shook Jan Mayen Island not only startled its residents but also garnered swift reactions from local authorities and neighboring regions. In the immediate aftermath, the island’s emergency services were activated, ensuring the safety of all inhabitants. Authorities issued alerts to remain vigilant against potential aftershocks, and organized a series of public briefings to disseminate critical information. Residents reported feeling strong tremors that rattled windows and set alarm systems off, prompting many to gather in communal areas to discuss safety measures and share their experiences. As a precaution, local officials advised on the importance of earthquake preparedness, which includes having basic supplies ready and knowing the safest evacuation routes.
In Iceland and greenland, where tremors were felt, emergency management agencies quickly assessed the situation to determine any impact on their own territories. many residents instinctively moved to open areas, fearing further seismic activity. Reports highlighted the calm demeanor of most,but officials still stressed the need for readiness. Agencies conducted informational sessions focusing on earthquake preparedness,emphasizing the importance of having an emergency kit and understanding safe building practices. Tabletop exercises were also initiated to practice responses to seismic events, enhancing readiness across the board. As these communities navigate through the unease caused by the quake, collaboration among neighbors and government bodies helps reinforce resilience in the face of natural disasters.
| Region | Response Measures |
|---|---|
| Jan Mayen Island |
|
| Iceland |
|
| Greenland |
|
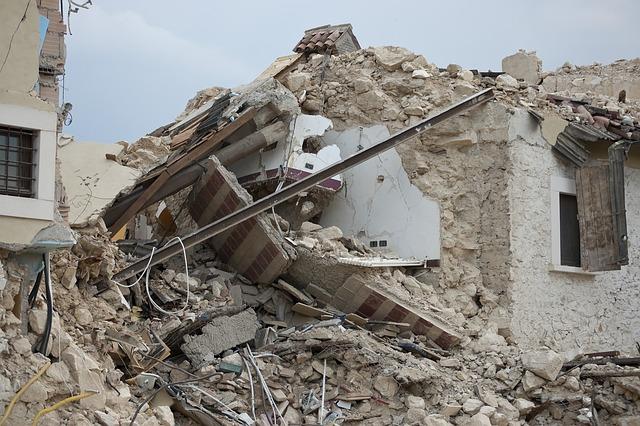

Geological Insights: Understanding the Dynamics of the Area
the recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake that struck Jan Mayen Island serves as a stark reminder of the geophysical dynamics at play in this northern region. Situated along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Jan Mayen is part of a complex system of tectonic plates that interact perilously beneath the Earth’s surface. The collision of the North American and Eurasian plates not only gives rise to volcanic activity but also creates significant fault lines that can result in powerful seismic events. The intricate geological framework includes various rock types, with basalt being predominant, shaped over millennia by volcanic eruptions and tectonic movements.
The impacts of the earthquake were distinctly felt across nearby regions, including Iceland and Greenland, highlighting the interconnectedness of geological systems in the Arctic. Citizens reported tremors and unleashed fears rooted in the volatile nature of the area,further illustrating the need for comprehensive understanding and monitoring. In light of this event, researchers stress the importance of knowledge-sharing and preparedness due to the potential for future quakes. Key points in assessing local geological risks include:
- Tectonic plate interactions and their implications for seismic activity.
- Monitoring geological changes in response to volcanic and earthquake activity.
- Community preparedness strategies to mitigate risks associated with seismic events.

safety Tips for Travelers in Earthquake-prone Regions
When visiting places susceptible to seismic activity, being prepared can considerably enhance your safety. Stay informed about the region’s seismic history and current alerts. Before embarking on your journey, familiarize yourself with local emergency contact numbers and evacuation routes. Pack a small emergency kit that includes essentials such as water, first aid supplies, and a flashlight. When in a building during a quake, remember to Drop, Cover, and Hold On — finding shelter under sturdy furniture or against an interior wall can help protect you from falling objects.
Additionally, understanding the typical symptoms of aftershocks is crucial, as they often follow significant earthquakes. In the event you are outdoors when a tremor strikes, stay away from buildings, trees, and power lines, as these can collapse or cause injury. For those exploring the wilderness, take note of your surroundings and be aware of potential landslides. Consider the following checklist to enhance your earthquake preparedness:
- Research local seismic history.
- Prepare an emergency kit.
- Know evacuation routes.
- Familiarize yourself with local emergency contacts.
- Practice earthquake drills.
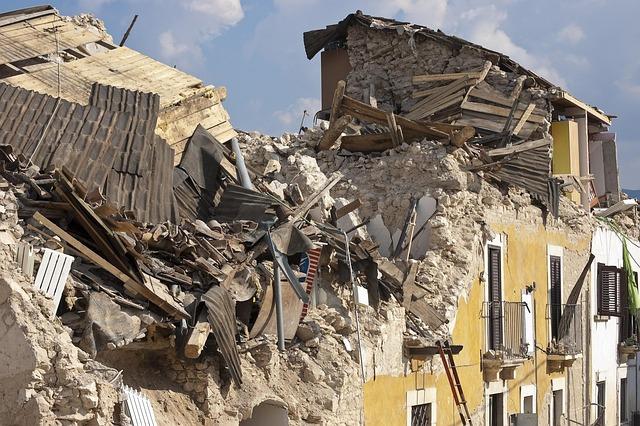

Future Monitoring: The Importance of seismic Awareness in northern Europe
As seismic activity becomes increasingly relevant to regions historically considered stable, the recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake that struck Jan Mayen Island sends a clarion call for enhanced seismic awareness in Northern Europe. Countries like Norway, Iceland, and Greenland, which sit on the edges of tectonic plates, must prioritize monitoring systems and public education around seismic risks. Preparedness and awareness are crucial as such events can happen without warning, demanding that residents understand safety measures and emergency protocols.
Investing in seismic research and advanced technology can definitely help predict and mitigate the impact of earthquakes. Here are some key aspects to focus on:
- Real-time monitoring: Implementing state-of-the-art devices to detect tremors as they occur.
- Public Education: Promoting understanding of earthquake preparedness and response strategies.
- Collaboration Between Countries: Establishing partnerships for information sharing and resource allocation can enhance regional resilience.
| country | Seismic Risk Level | Preparedness Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Norway | Moderate | Earthquake drills in schools |
| Iceland | High | Continuous seismic monitoring |
| Greenland | Low | Community awareness programs |

concluding Remarks
the recent 6.5 magnitude earthquake that struck Jan Mayen island serves as a stark reminder of the dynamic geological forces at play in the region. although the remote location of the island minimized the immediate risks to human life and infrastructure,the tremors reverberated through surrounding areas,including Iceland and Greenland,underscoring the interconnectedness of earth’s seismic activity. As scientists continue to monitor the situation and analyze the earthquake’s potential implications, the event highlights the importance of preparedness in seismically active regions. The resilience of local communities and the ongoing advancements in earthquake research will be crucial as we seek to better understand and respond to such natural phenomena.