In a remarkable geological event, a volcano in Iceland that has remained dormant for nearly 800 years has erupted, sending ash and molten lava into the air and drawing the attention of scientists and locals alike. This eruption, wich began with an notable display of natural power, marks a significant moment in the region’s volcanic history and raises questions about the underlying geological processes at play. As experts rush to study the phenomenon and assess its potential impact on the surrounding environment and communities, the eruption serves as a vivid reminder of Iceland’s dynamic landscape, shaped by the forces of nature. ABC News delves into the details of this remarkable eruption, its implications, and the historical context surrounding this ancient volcano’s sudden revival.
Icelandic Volcano Erupts After Eight Centuries of Dormancy
After eight centuries of silence, the eruption of one of Iceland’s long-dormant volcanoes is a dramatic reminder of the dynamic geological nature of our planet. citizens and scientists alike have witnessed the impressive display of nature’s power, as lava flows and volcanic ash create mesmerizing yet hazardous landscapes. The eruption, which began unexpectedly, has raised concerns about air travel disruptions and local safety while together attracting tourism interest. Residents in the surrounding areas have been advised to stay alert and prepared for potential evacuations.
The Icelandic Meteorological Office has reported an increase in seismic activity leading up to the eruption, which served as an early warning sign for geologists. The volcanic activity brings to light several key considerations:
- Environmental Impact: Ash clouds may affect air quality and wildlife.
- Travel Advisory: Airports in the region have issued warnings and potential flight cancellations.
- Tourism Boost: Tour operators are preparing for an increase in visitors eager to witness the eruption.
Local authorities have mobilized resources to monitor the situation closely. Emergency response plans are being put into place, ensuring the safety of both residents and tourists. Mapping the eruption’s progression is crucial for understanding not only this event but also the wider implications of volcanic activity in the region, where the landscape has continuously been shaped by geological forces.

Geological Insights into the Volcanic Activity in iceland
The recent eruption of an Icelandic volcano that has been dormant for 800 years serves as a powerful reminder of the island’s geological dynamism. Situated on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Iceland is uniquely positioned over a hotspot of volcanic activity due to its location on tectonic plate boundaries. The nation experiences a regular cycle of eruptions and eruptions are part of a natural process of rejuvenation for the earth’s crust.Understanding the underlying geological mechanisms can provide crucial insights into this stunning phenomenon:
- Rifting Zones: As the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates diverge, magma rises through fissures, leading to volcanic activity.
- Magma Composition: The basaltic magma found in Iceland is typically low in viscosity, allowing it to flow relatively easily and creating short and explosive bursts.
- Historic Patterns: Previous eruptions in Iceland have followed cyclical patterns, suggesting that monitoring current activity may provide clues to future events.
A closer look at past eruptions highlights the potential impact and hazards associated with volcanic activity. Rather than being isolated incidents,these eruptions contribute to the broader landscape and atmosphere of Iceland.They play a vital role in shaping its geography and ecology, delivering necessary nutrients to the soil and contributing to the formation of new lands:
| Eruption Year | Volcano Name | Type of Eruption | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 934 AD | Hekla | Explosive | Destruction of farmland |
| 1783-1784 | Laki | Fissure | Tremendous climate effects, livestock deaths |
| 2010 | Eyjafjallajökull | Plinian | Air travel disruption across Europe |
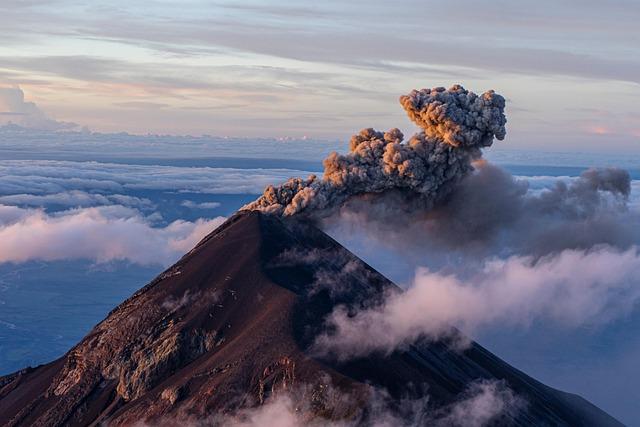

Impact of Eruptions on Local Communities and Ecosystems
The recent eruption of an Icelandic volcano that had lain dormant for 800 years is poised to have profound effects on both the local communities and the surrounding ecosystems. Residents in nearby areas face immediate challenges, such as evacuation and property damage. the ash and gases emitted can disrupt air travel, impacting tourism and local economies that rely on it. Emergency services are activated, and public health concerns arise due to the potential for air quality deterioration.Essential infrastructures, such as roads and hospitals, could also be hindered by volcanic activity, complicating governmental responses and community resilience efforts.
ecologically, the consequences of such eruptions are multifaceted.On one hand, the introduction of ash can enrich soils, leading to fertile ground that fosters new plant growth in the long term.Conversely, the immediate impact can be devastating for local wildlife, disrupting habitats and food sources. Key concerns for ecosystems include the following:
- Displacement of fauna due to ash accumulation
- Acid rain affecting water quality
- Alteration of landscape and natural habitats
To better understand these effects, the table below summarizes potential repercussions on local communities versus ecosystems during volcanic events:
| Aspect | Local Communities | Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Air Quality | Affected by ash and gases | Chemical changes in flora |
| Economy | Tourism decline | Potential long-term fertility increases |
| Health Risks | Respiratory issues | Habitat destruction |
The balance between short-term chaos and long-term ecological benefits will inevitably shape the future of both the affected communities and their diverse environments.

Safety Measures and Evacuation Protocols for Residents
As the threat of volcanic activity increases, it is indeed crucial for residents in the surrounding areas to remain vigilant and well-informed about safety measures. Residents should adhere to the following guidelines to ensure their safety:
- Stay Informed: Regularly check updates from local authorities and the Icelandic Meteorological Office regarding volcanic activity.
- Emergency Kit: Prepare an emergency kit that includes essentials such as water,food,medications,and a flashlight.
- Evacuation Routes: Familiarize yourself with designated evacuation routes and ensure your vehicle is prepared for sudden departure.
- Communications Plan: Establish a communications strategy with family and friends to stay connected during emergencies.
In the event of an evacuation,swift adherence to protocols can save lives. Local emergency services will provide specific instructions, but residents should also be ready to act independently. below is a simple guide to follow during an evacuation:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Activate Emergency Alert | Listen for alarms and follow directives from local authorities. |
| Gather Essentials | Pack important documents and necessary items quickly. |
| leave Early | Avoid waiting until the last minute. Depart quickly. |
| Stay Updated | Monitor news outlets and official channels for real-time updates. |
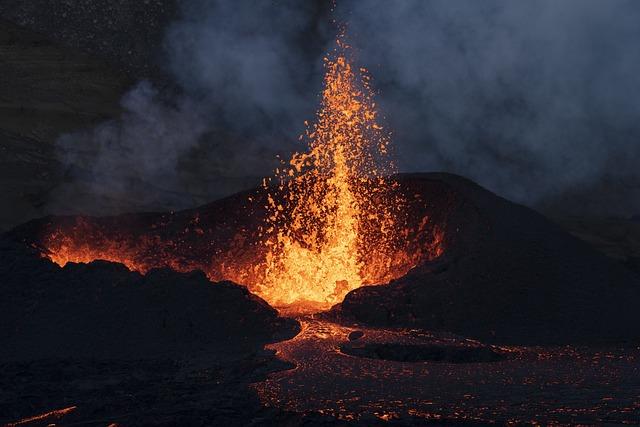

Tourism and Economic Implications of Renewed Volcanic Activity
The recent eruption of a volcano in Iceland that had lain dormant for over 800 years is set to impact the local economy profoundly. The surge in volcanic activity could attract a wave of tourists eager to witness the natural spectacle,presenting both opportunities and challenges. Local businesses, including hotels, restaurants, and tour operators, are likely to benefit from the influx of visitors, perhaps leading to increased revenue and job creation. Though, the infrastructure may face strain due to the heightened demand, leading to concerns over safety and environmental sustainability in the region.
Additionally, while the elements of tourism are ofen an economic boon, the government and stakeholders must also consider the implications of such natural events. The potential for disruptions from ash clouds and lava flows could affect air travel in and out of the country, leading to economic losses in sectors reliant on international tourism. By balancing the economic benefits with responsible disaster management, stakeholders can navigate this dual-edged sword effectively. Here’s a brief overview of potential impacts:
| Impact | Positive Effects | Negative Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Tourism Growth | Increased business for hotels and tours | Risk of overcrowding |
| Infrastructure Strain | Job creation in hospitality | Reduced quality of service |
| Air Travel | Increased flights and interest | Possible flight cancellations |
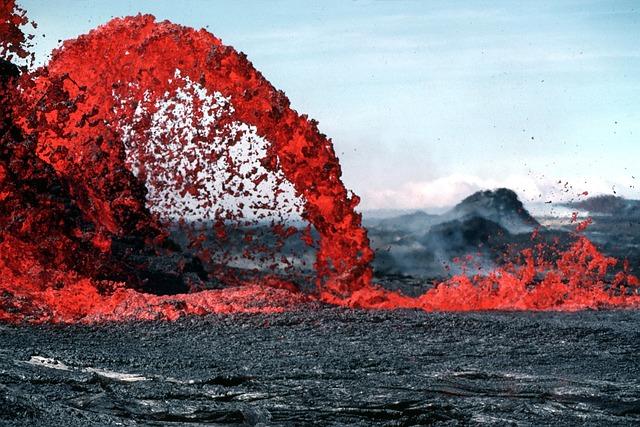

Monitoring and Research Efforts to Understand Future Eruptions
Recent seismic activity in Iceland has sparked a renewed focus on monitoring and research efforts aimed at predicting future volcanic eruptions. Scientists have deployed advanced technologies, including satellite imagery, ground deformation measurements, and real-time gas emission monitoring, to closely observe the newly active volcano. These methods allow researchers to gather invaluable data, including:
- Ground movement patterns, which can indicate magma accumulation.
- Gas emissions, such as sulfur dioxide, that serve as precursors to eruptions.
- Seismic activity, providing insights into underground processes and potential eruption triggers.
Collaboration between local authorities and international research groups has been paramount in enhancing predictive capabilities. A specialized interdisciplinary team continuously analyzes data to create models that offer insights on potential eruption timelines and impacts. This effort includes:
| Research Focus | Methodology | key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Magma Dynamics | Geophysical Surveys | Understanding magma pathways |
| Gas Emissions | Air Quality Monitoring | Forecasting eruption likelihood |
This multifaceted approach not only improves our understanding of the current eruption but also equips scientists with the knowledge to predict and mitigate risks associated with future volcanic activity, thus safeguarding both communities and ecosystems in the region.
To Conclude
the recent eruption of Iceland’s long-dormant volcano has not only captivated the attention of scientists and observers alike but also highlighted the dynamic and unpredictable nature of our planet’s geological activity. Following 800 years of dormancy, this eruption serves as a potent reminder of the forces that shape our world and the importance of ongoing monitoring and research in volcanic regions. As authorities continue to assess the situation and its implications for both local communities and global climate patterns, the event underscores the need for preparedness and understanding of volcanic behavior. ABC News will continue to provide updates on this developing story, keeping you informed about both the immediate effects and the broader geological meaning of this remarkable eruption.