On [insert date], the remote island of Jan Mayen, located in the Arctic Ocean and part of Norway, experienced a significant seismic event as a strong M6.5 earthquake struck the region. The tremor, which hit at [insert time], sent shockwaves felt across the sparsely populated island, raising concerns among local residents and scientists alike. Jan Mayen, known for its unique volcanic landscape and ecological meaning, has now drawn the attention of seismologists as they assess the earthquake’s impact and potential aftershocks. This event not only highlights the geological activity of the North Atlantic but also underscores the importance of disaster preparedness in vulnerable regions. In this article, we delve into the details of the earthquake, its effects on the island, and what it signifies for the broader context of seismic activity in Northern Europe.
Impact and Aftermath of the M6.5 Earthquake on Jan Mayen
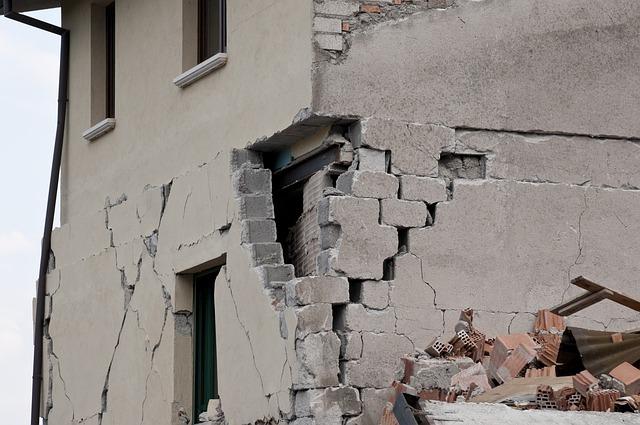

The M6.5 earthquake that struck Jan Mayen has left an indelible mark on the small island’s fragile ecosystem and its sparse human settlement. Although the island is largely uninhabited, the earthquake triggered landslides and aftershocks that posed immediate risks to any potential wildlife and vegetation in the vicinity. Preliminary assessments indicate that the quake may have caused some damage to the limited infrastructure, including research stations which are crucial for scientific study in this remote habitat. The geological upheaval will require ongoing monitoring to understand its long-term effects on the island’s geology and biodiversity.
In the aftermath, responses from local and international agencies have begun to materialize. Emergency teams are assessing the situation and providing aid where necesary, focusing primarily on two main areas:
| Response Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Assessment | Surveys to monitor landslide impact and environmental changes. |
| Infrastructure Re-evaluation | Inspections of research facilities for structural integrity. |
As scientists predict further seismic activity may occur in the coming weeks, preparedness measures are being prioritized to mitigate future risks. The earthquake has not only sparked conversations about the island’s geological vulnerability but also highlighted the importance of international collaboration in disaster response efforts in remote regions.
Geological Insights: Understanding the Tectonic Activity in the Region

The recent M6.5 earthquake that struck jan mayen serves as a stark reminder of the dynamic geological forces at play beneath the Earth’s surface. This isolated archipelago, situated between Greenland and Norway, is part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary. The region is characterized by its unique geology, influenced by both the underlying basaltic formations and volcanic activity.As tectonic plates shift, they release immense energy, causing seismic events that can dramatically alter the landscape and remind us of the planet’s restless nature.
The significance of such tectonic activity extends beyond mere geological curiosity; it impacts local ecosystems, human settlements, and even global weather patterns. Key factors driving the tectonic processes in this area include:
- Plate Movements: The North American and Eurasian plates are slowly diverging.
- Volcanic Activity: Ongoing eruptions from submerged volcanoes contribute to the landscape.
- Seismic Monitoring: Stations on Jan Mayen help track earthquake activity and provide critical data.
Understanding these factors is crucial for researchers and policymakers alike, as they inform not only geological studies but also emergency preparedness and response strategies in the region.
Emergency Response: Assessing Preparedness and Recovery Efforts

The recent seismic event measuring M6.5 that struck Jan Mayen has prompted an immediate assessment of local preparedness and response mechanisms. In the aftermath of this earthquake, various stakeholders, including government agencies, emergency services, and local communities, are mobilizing to evaluate the effectiveness of their emergency plans. Key areas of focus include:
- Infrastructure resilience: Examining the structural integrity of buildings and roads.
- Emergency communication: Ensuring that all communication systems are operational and effective.
- Public awareness: Assessing how well the community understands emergency protocols.
- resource allocation: Identifying available resources such as frist aid supplies and personnel.
Recovery efforts are already being integrated, with local authorities coordinating rehabilitation strategies that prioritize rapid assistance to those affected. Collaboration with national and international organizations is crucial to providing the necessary support. critically important components of the recovery plan consist of:
- Immediate relief: Distribution of food, water, and medical supplies.
- Psychological support: Offering mental health services for trauma victims.
- Reconstruction plans: Developing a blueprint for rebuilding safer infrastructure.
| Aspect | Status |
|---|---|
| Communications | Operational |
| Infrastructure Assessment | Ongoing |
| Emergency Supplies | Available |
| Recovery Timeline | TBD |
Safety Recommendations for Residents and Visitors in Earthquake-Prone Areas

Residents and visitors in earthquake-prone regions, like Jan Mayen, must remain vigilant and prepared for seismic activity. To enhance personal safety during such events, consider the following essential recommendations:
- Create an emergency kit: Include water, non-perishable food, a flashlight, batteries, and first aid supplies.
- Develop a family emergency plan: Ensure all family members know how to react during an earthquake and establish a communication protocol.
- Secure heavy items: Anchor shelves, pictures, and large furniture to walls to minimize hazards during shaking.
- Stay informed: Keep up with local alerts and seismic activity reports to be prepared for aftershocks.
During an earthquake, knowing how to react can significantly reduce the risk of injury. Follow these critical guidelines:
- Drop, Cover, and Hold On: Find a sturdy piece of furniture to take cover under and hold on until the shaking stops.
- Stay indoors: If you are indoors, stay put; do not run outside during the shaking to avoid falling debris.
- Avoid doorways: Contrary to popular belief, doorways are not the safest place to be. Stay away from windows and heavy objects.
- Listen to local authorities: Authorities will provide vital updates and instructions; follow their guidance closely.
Long-term Implications for Seismology and Monitoring in Norway
The recent magnitude 6.5 earthquake that struck Jan Mayen serves as a critical reminder of the inherent geophysical volatility in Norway’s northern regions. This seismic event has significant long-term ramifications for seismology and monitoring practices, particularly in an area known for its geological complexity. Enhanced awareness and understanding of tectonic processes are essential for improving predictive capabilities, which may entail:
- Investment in Advanced Monitoring Systems: upgrading existing seismic networks with state-of-the-art technology can aid in real-time data gathering and processing.
- Collaboration with International Research Entities: Partnerships with global seismic research organizations can lead to knowledge sharing and improvements in monitoring techniques.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: initiating educational programs about earthquake preparedness can reduce risks associated with future seismic activities.
In addition, the earthquake’s occurrence highlights the need for continuous research into Norway’s complex geological setting.Future studies might focus on characterizing local fault lines and assessing their likelihood of causing significant seismic events. This research drive can foster a deeper understanding that not only enhances preparedness but also assists in shaping urban planning strategies. Key areas of focus could include:
| Research Focus Area | Significance |
|---|---|
| Fault Line Mapping | Identifies potential seismic hazards. |
| Past Seismic Activity | Informs probability models for future events. |
| Public policy Recommendations | Enhances community resilience strategies. |
Community resilience: Lessons Learned from the Jan Mayen Event

The recent M6.5 earthquake that struck Jan Mayen serves as a stark reminder of the volatile nature of Earth’s tectonic movements and the importance of community preparedness.In the aftermath of the event, several key lessons emerged regarding resilience-building strategies that communities can implement to better withstand similar natural disasters in the future. Notably, a focus on emergency response training, infrastructure resilience, and community engagement proved invaluable. Local authorities highlighted the significance of regular drills and simulations,which help residents understand evacuation routes and emergency protocols,ensuring a quicker and more organized response during crises.
Furthermore, the event underscored the need for a robust communication plan, warding off misinformation that often spreads during disasters. Establishing clear channels—such as social media updates, text alerts, and community meetings—can significantly reduce panic and promote coordinated responses. The collaboration between local government,emergency services,and community organizations played a crucial role in the swift assessment and repair of infrastructure post-quake,which is critical for restoring normalcy. The experiences garnered from this incident highlight that building a resilient community is an ongoing process that requires constant evaluation, adaptation, and commitment.
Wrapping Up
the M6.5 earthquake that struck Jan Mayen, Norway, serves as a stark reminder of the dynamic and often unpredictable nature of our planet. monitoring organizations and geologists will continue to analyze the seismic data to better understand the implications of this event and to prepare for potential aftershocks. While the remote location of Jan Mayen mitigates the risk to populated areas,the incident emphasizes the importance of readiness and awareness regarding seismic activity in all regions,particularly in tectonically active zones. As communities and researchers remain vigilant, continued advancements in earthquake prediction and monitoring will be vital in safeguarding lives and infrastructure against future seismic events. For now, residents and officials in the area are advised to stay informed and proceed with caution as they assess the full impact of this powerful earthquake.












Unexpected Allies: The G.O.P.’s Unlikely Embrace of Putin’s Russia