Understanding the Journey of European Eel Larvae Through the Strait of Gibraltar
As the world grapples wiht the complexities of climate change and biodiversity loss, the delicate interplay between oceanic currents and the life cycles of marine species remains a significant area of research. one such species is the European eel (Anguilla anguilla), a engaging and enigmatic creature whose lifecycle traverses thousands of kilometers, from the depths of the Sargasso Sea to the freshwater rivers and lakes of Europe. Recent findings shed light on a crucial aspect of this journey: the transport of European eel larvae through the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean sea. This article delves into the intricate dynamics of this migration, exploring the environmental factors that influence larval dispersal and the implications for the species’ survival. As we learn more about this critical phase of the European eel’s life, we uncover not only the challenges facing this ancient fish but also the broader ecological ramifications in a rapidly changing world.
Transport Mechanisms of European Eel Larvae through the Strait of Gibraltar
The transport of European eel larvae, known as glass eels, through the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea is a phenomenon influenced by a combination of natural currents, seasonal changes, and biological adaptations. The larvae embark on a remarkable journey from their spawning grounds in the Sargasso Sea, propelled by the Atlantic Ocean’s eastward currents. these currents create a natural highway that helps the larvae navigate effectively towards the Mediterranean. Key factors affecting their transport include:
- ocean Currents: Predominant currents such as the Canary Current and the Alboran Sea Current facilitate the movement of eels.
- Wind Patterns: Seasonal winds like the Trade Winds influence surface currents, aiding in larval dispersal.
- Salinity Gradients: larvae are also responsive to changes in salinity that help guide their ascent toward brackish waters.
Research indicates that the timing of the glass eels’ arrival significantly correlates with environmental patterns, especially in spring and autumn. This adaptability not only plays a crucial role in their survival but also impacts local ecosystems where they eventually settle. Studies suggest several mechanisms through which larvae maintain their position within the water column, including:
- Buoyancy Control: Eel larvae possess the ability to adjust their swim bladder volume to maintain buoyancy.
- Behavioral Adaptations: Vertical migrations allow larvae to exploit favorable currents for transport.
- Predator Avoidance: By staying suspended in the water column, they reduce predation risks.
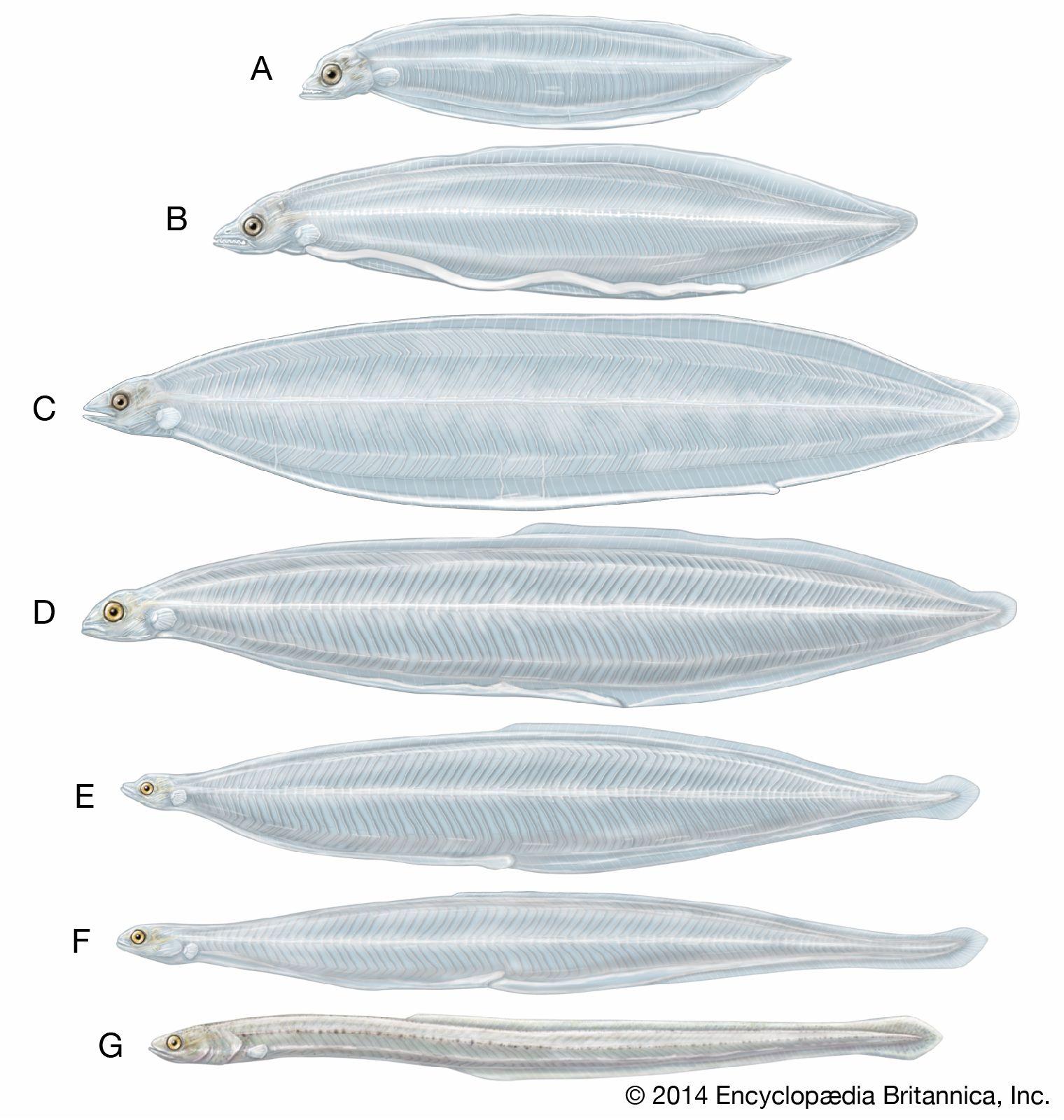

Ecological Implications of Mediterranean Influx on Eel Populations
The influx of European eel larvae from the Atlantic through the Strait of gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea raises significant ecological concerns and implications for the already vulnerable eel populations. As these larvae settle into the distinct habitats of the Mediterranean, they may compete with native species for resources, leading to shifts in local biodiversity. The introduction of new genetic material through these larvae could also disrupt existing mating patterns, perhaps affecting the resilience of eel populations to environmental changes.
Moreover, the shifting dynamics in the Mediterranean ecosystem may have cascading effects on fisheries and local economies that rely on eels as a critical resource. some potential implications include:
- Changes in predator-prey relationships: The arrival of new larvae may alter the food web, affecting not just eels but various species that interact with them.
- Increased disease transmission: New populations can introduce pathogens or parasites that may impact native species.
- Commercial fishing challenges: Fishers may need to adapt to changing eel populations and market demands.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for conservation efforts, as it highlights the need for thorough monitoring and management strategies. A study on the impact of this influx could benefit from a clear overview of the potential changes in the ecosystem:
| ecological impacts | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|
| Species Competition | Decline in native eel populations |
| Biodiversity Shifts | Altered community structures |
| Economic Effects | Changes in fishery yields |
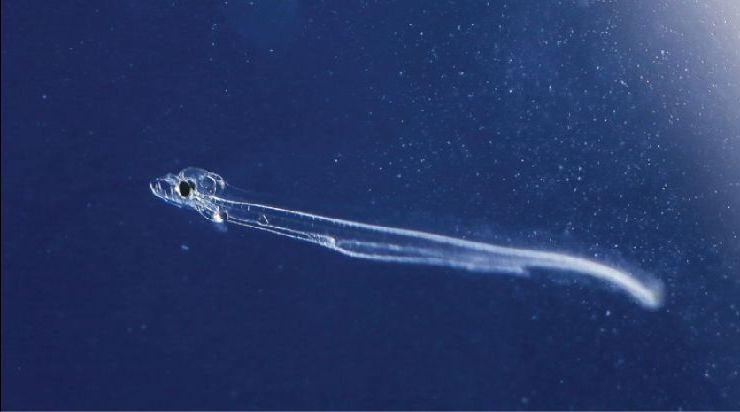

Challenges Facing European Eels in Their Migration Journey
The journey of European eels from their spawning grounds in the Sargasso Sea to the European freshwater and coastal waters is fraught with peril. As these larvae traverse extensive distances, they encounter numerous challenges that threaten their survival.Among the most significant obstacles are climate change, which disrupts ocean currents and alters migration patterns, and pollution, contaminating their habitats and impairing their developmental stages. Moreover,overfishing and habitat degradation hinder their population replenishment,making it increasingly difficult for eels to navigate their path to maturity.
Additionally, human activities pose a considerable risk to the eel migration process. The construction of dams and barriers on rivers obstruct the natural routes that eels take to reach freshwater spawning areas, while urban growth along coastlines further reduces available habitats. The introduction of invasive species also adds competitive pressure on native eel populations, complicating their ability to adapt and thrive. Compounding these issues are the ongoing challenges related to poor management practices and a lack of coordinated conservation efforts across nations, which are critical for safeguarding the future of this remarkable species.

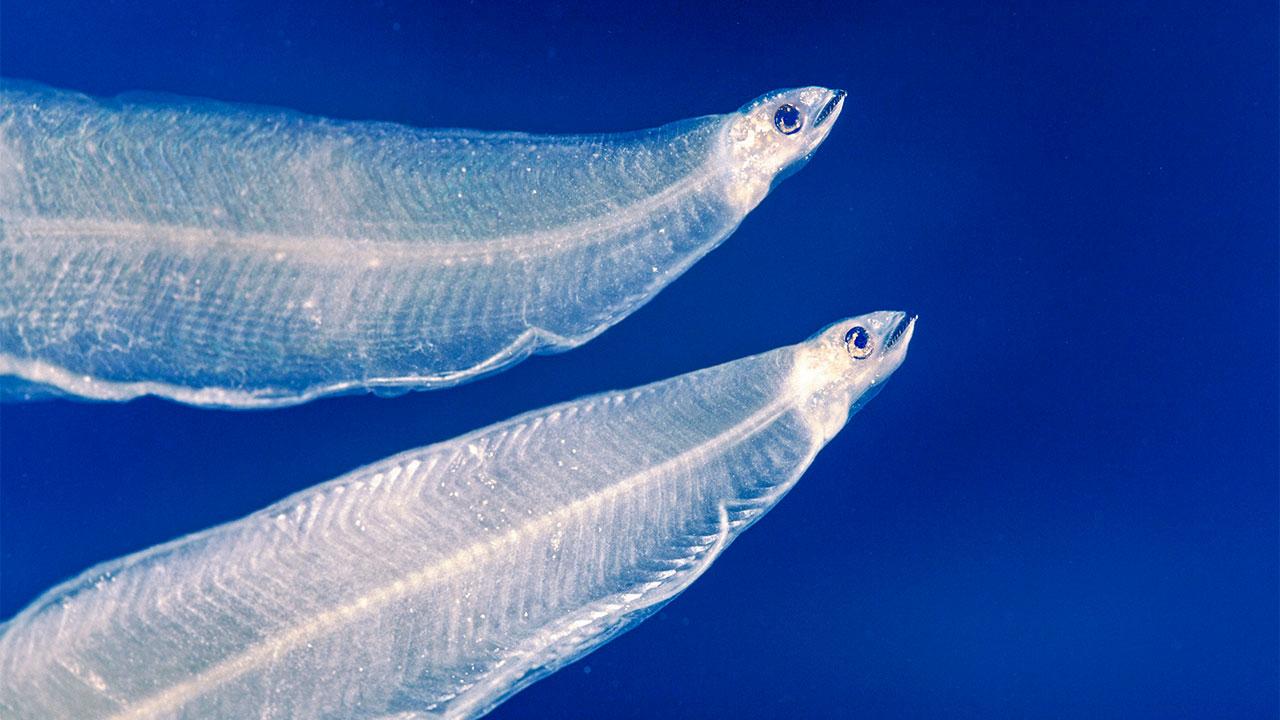
recent Research Findings on Larval Resilience and Behavior
Recent studies highlight the remarkable adaptability of European eel larvae, particularly during their perilous journey through the Strait of Gibraltar. Researchers observed that these larvae exhibit increased buoyancy and enhanced swimming capabilities, crucial for navigating the turbulent waters of this significant marine passage. Key findings indicate that the larvae can alter their behavioral patterns based on environmental cues, enabling them to optimize their transport into the mediterranean.This resilience is not merely a response to physical challenges but also reflects an evolutionary advantage, allowing them to thrive across a wide range of habitats.
The research also delves into the behavioral patterns of eel larvae post-transit, revealing critically important insights into their predation risks and habitat selection. Key behaviors where categorized as follows:
| Behavioral Pattern | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Aggregation | Reduces predation risk |
| Diel Vertical Migration | Aids in foraging and energy conservation |
| Directional Swimming | Enhances navigation efficiency |
As these findings unfold, they underscore the importance of understanding larval behavior in relation to environmental factors—a crucial step in the broader efforts to conserve this species amidst the challenges of climate change and habitat loss.
Conservation strategies for Protecting Eel Larvae during Their Transit
The transitory journey of European eel larvae,or leptocephali,through the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea presents unique challenges that necessitate focused conservation strategies. Coastal habitat preservation is paramount, as these areas serve as vital nursery grounds. Efforts should include limiting pollution, restoring natural habitats, and implementing effective fishing regulations to reduce bycatch.additionally, creating marine protected areas (MPAs) can provide safe zones where the larvae can grow and thrive without the threat of human disturbances.
To further enhance the survival rates of eel larvae during their transit, monitoring programs that track environmental conditions such as water temperature, salinity, and currents are crucial. Implementing public awareness campaigns can engage local communities in conservation efforts, emphasizing the importance of eels in the ecosystem.Collaboration between researchers, governmental bodies, and non-governmental organizations will facilitate a more holistic approach to conservation, allowing for real-time data collection and adaptive management of strategies to protect these vulnerable life stages of the European eel.

Future Directions for Eel Migration Studies in Marine Environments
Eel migration studies are poised to expand significantly, particularly in the context of marine environments influenced by climate change and human activities.Researchers aim to utilize advanced tracking technologies, such as satellite telemetry and acoustic tagging, to gain deeper insights into the migratory patterns of European eel larvae. These methods will enhance our understanding of key migration corridors, including the complex pathways leading through the strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea. By integrating genetic analysis with environmental data, scientists can assess how varying conditions affect larval survival rates and distribution across differing habitats.
In addition, collaboration among international research institutions will play a crucial role in addressing the challenges faced by marine ecosystems. Future studies may prioritize the following areas:
- Assessment of anthropogenic impacts on eel migration routes.
- Long-term ecological monitoring of eels’ adaptation to shifting environmental conditions.
- Development of conservation strategies that include habitat restoration and protection measures.
- Public engagement and education to raise awareness of eel conservation issues.
By targeting these areas, researchers can help ensure that the European eel population remains viable in the face of ongoing environmental challenges.

In Conclusion
the remarkable journey of European eel larvae through the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea not only highlights the intricate dynamics of marine ecosystems but also raises important questions about the future of this species amid environmental challenges. The findings presented in the recent study underscore the crucial role of hydrological and ecological factors in shaping the migration patterns of these enigmatic creatures.As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of eel ecology, it becomes increasingly clear that understanding these transport mechanisms is vital for the conservation of European eels, which are currently facing significant threats from habitat loss, climate change, and overfishing. Ongoing studies will be essential for informing conservation strategies and ensuring the resilience of this species in an ever-changing environment. as we deepen our understanding of this fascinating journey, we are reminded of the delicate balance within our oceans and the imperative to safeguard its inhabitants for generations to come.







