In a significant display of diplomatic solidarity, the European Union (EU) has reaffirmed its support for Denmark amidst mounting pressure from the United States regarding Greenland, the world’s largest island. This development highlights the complex geopolitical landscape in the Arctic region, where natural resources, strategic interests, and international relationships intersect.As the U.S.intensifies its focus on Greenland—primarily driven by its vast mineral wealth and strategic location—Denmark’s position as the sovereign authority has come under scrutiny.The EU’s backing underscores the bloc’s commitment to multilateralism and the importance of respecting national sovereignty in the face of external pressures. This article delves into the implications of this evolving situation, the reactions from both Copenhagen and Washington, and the broader context of Arctic geopolitics.
EUs Commitment to Danish Sovereignty in the Face of US Pressure

The European Union has reaffirmed its commitment to supporting Denmark amidst mounting pressure from the United States concerning Greenland. As discussions around natural resources and geopolitical strategy intensify,EU officials have emphasized the importance of respecting Denmark’s autonomy over its territories. EU leaders argue that any attempts to undermine Danish sovereignty jeopardize stability not just in the Arctic region but also within the broader framework of international diplomacy. The EU’s stance serves as a reminder of its dedication to multilateralism and respect for territorial integrity,particularly in a time characterized by shifting power dynamics.
Central to this support is the recognition that Greenland, while an autonomous territory of denmark, holds significant strategic importance due to its abundant natural resources and potential military significance. The EU is also taking steps to enhance collaboration with Denmark in areas such as scientific research and environmental sustainability. To illustrate this commitment, key points include:
- Joint EU-Denmark initiatives on sustainability in Arctic fisheries.
- Increased funding for scientific exploration and climate studies in Greenland.
- Support for local governance in Greenland, allowing its residents to make decisions that affect their future.
| Key Areas of EU Support | Description |
|---|---|
| Strategic Partnerships | Collaborating on security and environmental issues. |
| economic Investment | Funding projects to boost local economies. |
| Cultural Exchange | Promoting Greenlandic culture within the EU framework. |
Strategic Importance of Greenland: Geopolitical Dynamics at Play
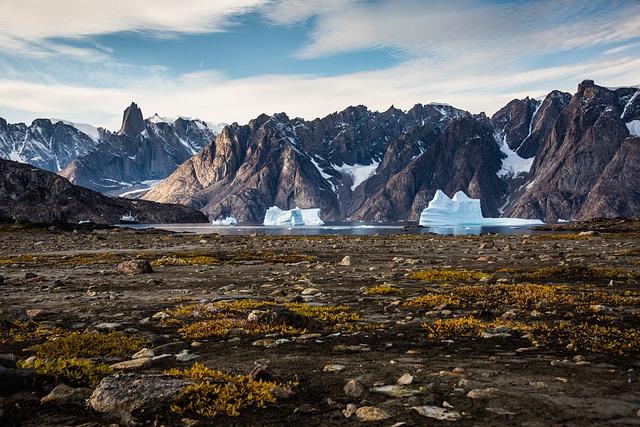

Greenland has emerged as a focal point in the ongoing global power struggle, particularly reflecting the interests of both the United States and the European Union. As Arctic ice melts and new shipping routes open, the geopolitical significance of this vast territory grows. Several factors contribute to its strategic importance:
- Resource Wealth: Greenland is rich in natural resources, including rare earth minerals, oil, and gas, making it a target for global powers keen on securing energy supplies.
- Military Strategy: Its geographical position allows for enhanced military presence,essential for monitoring Arctic activities as tensions rise in the region.
- Climate Change Impact: The island’s changing landscape poses challenges and opportunities for shipping and extraction, drawing attention from nations across the globe.
The dynamics surrounding Greenland are not just limited to military and economic factors; they also highlight the importance of diplomatic ties. Denmark’s relationship with the EU has become a cornerstone for maintaining stability in the region amid rising American pressure.The involvement of the EU brings additional support and resources to Denmark, reinforcing their stance against unilateral actions by the U.S. A brief overview of recent developments includes:
| Date | Event | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| 2023-10-01 | EU diplomatic support for Greenland | strengthening Denmark’s position |
| 2023-09-15 | U.S. military base discussions | Potential shifts in regional power dynamics |
| 2023-08-21 | International summit on Arctic policy | Collaborative approaches towards climate and resource management |
Economic Implications of US Interest in Greenlands Resources

The increasing interest from the United States in Greenland’s vast natural resources, particularly rare earth minerals and potential oil reserves, presents an array of economic implications both for Greenland and its relationships with Denmark and the european Union. As discussions intensify, the U.S. aims to secure access to resources critical for advanced technologies and renewable energy initiatives. This growing competition for greenland’s assets could result in a boost for local economies through job creation and infrastructural development, but also risk fostering dependency on external powers.
- Resource Extraction: Increased mining and drilling could lead to short-term economic gains for Greenland.
- Foreign Investment: The potential for U.S. economic foothold may attract other international investors.
- environmental Concerns: Rapid resource exploitation raises serious ecological and social issues, challenging local governance.
In contrast, this pressure also compels the European Union to reinforce its support for Denmark as it navigates the complexities of national sovereignty intertwined with the allure of lucrative deals. The ramifications are not just economic; they extend into the geopolitical landscape, where the potential for U.S. military presence in Greenland heightens tensions. The following table summarizes the juxtaposition of potential benefits and concerns:
| Economic Benefits | Concerns |
|---|---|
| Increased Job Opportunities | Environmental Degradation |
| infrastructure Development | Political Tensions |
| Boost in Local Revenues | Dependency on Foreign Entities |
Recommendations for Strengthening Danish-EU Collaboration

To enhance collaboration between Denmark and the european Union considering geopolitical pressures, several strategic initiatives should be considered. Strengthening cross-border ties through enhanced trade relations can foster economic resilience.Specific actions may include:
- Developing joint initiatives focused on enduring development in Greenland that align with the EU’s Green Deal.
- Establishing collaborative defense measures to bolster maritime security, ensuring protection against any external pressures.
- Promoting cultural exchange programs that deepen mutual understanding and cooperation among citizens.
Additionally, a concerted effort to prioritize research and innovation can position both Denmark and the EU as leaders in global environmental strategies. Implementing programs that facilitate shared research endeavors and investment in green technologies can yield substantial benefits. Proposed actions to support this goal include:
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Innovative Funding programs | Encourage private and public partnerships to invest in renewable energy projects. |
| Collaborative Research Centers | Establish joint research facilities focusing on climate resilience in arctic regions. |
| Workforce Development | Offer training programs to enhance skills in green technology sectors. |
The Role of Greenlands Indigenous Population in Geopolitical Strategies
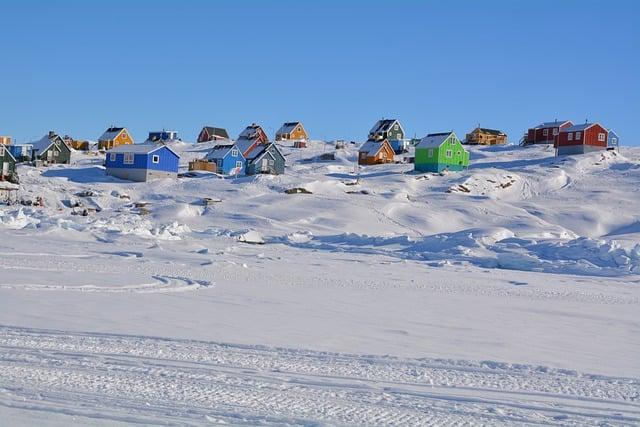

The geopolitical landscape surrounding Greenland has been increasingly shaped by the interests and influences of global powers, particularly the United States and the European Union. Central to these dynamics is the indigenous population of Greenland, whose rich cultural heritage and customary knowledge provide critical insight into the region’s sustainable development and ecological resources. their perspectives on land use, climate change, and resource management underscore the importance of involving local voices in international discussions. This engagement significantly alters the geopolitical calculus,as indigenous rights and sovereignty come to the forefront of negotiations over Greenland’s future.
Furthermore, the indigenous community stands at the crossroads of tradition and modernity, influencing geopolitical strategies in several ways:
- Advocacy for Sovereignty: Indigenous groups are increasingly vocal in asserting their rights, pushing for greater autonomy and decision-making powers.
- environmental Stewardship: Their knowledge of sustainable practices plays a crucial role in discussions about resource extraction and its environmental impacts.
- Strategic Alliances: Collaborations with both the Danish goverment and international entities can bolster their influence in negotiations regarding military and economic interests in the region.
As the EU reaffirms its support for Denmark amidst rising U.S. pressure, the role of Greenland’s indigenous population cannot be overlooked. Their participation in dialogues can possibly redefine the strategic framework, ensuring that their concerns are integrated into broader geopolitical strategies while promoting sustainable practices that reflect both their heritage and the needs of the modern world.
Future Prospects for Greenland: balancing Global Interests and Local Autonomy
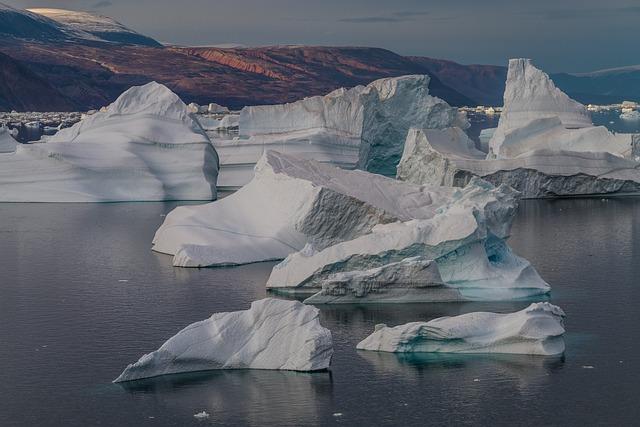

The evolving landscape of Greenland’s political and economic prospects highlights a complex interplay between global interests and local governance. As environmental changes unlock new resources and trade routes, various nations—including the United States and members of the European Union—are keenly eyeing Greenland’s potential. This interest not only affects the economic future of the territory but also raises significant questions about the degree of autonomy Greenlanders will have as they navigate the pressures from larger powers. Local leaders are in a pivotal position to advocate for self-determination while ensuring that they are not merely pawns in a geopolitical chess game.
Key considerations for Greenland’s future will likely revolve around economic development, environmental protection, and cultural preservation. Stakeholders must work collaboratively to secure:
- Sustainable resource management: To balance economic benefits with environmental integrity.
- Investment in infrastructure: To enhance local livelihoods while accommodating international interests.
- Strengthening local governance: To empower communities to make decisions that affect their land and culture.
The task at hand is to ensure that Greenland’s wealth serves its people, rather than merely fueling external ambitions. As global players bring new dynamics into play, the emphasis must remain on empowering local voices and upholding the principles of autonomy and self-governance.
To Conclude
the european Union’s steadfast support for Denmark amidst escalating tensions with the United States over Greenland underscores a significant geopolitical dynamic at play. As the U.S. intensifies its focus on the Arctic and seeks to strengthen its influence in the region, denmark’s position as an autonomous entity within the Kingdom carries considerable weight. the EU’s backing not only highlights its commitment to safeguarding the interests of its member states but also emphasizes the importance of solidarity in navigating complex international relationships. As discussions of resource management, climate change, and strategic security evolve, the implications of these developments will likely resonate far beyond the Arctic, impacting transatlantic relations and the broader geopolitical landscape. Moving forward,it will be crucial to monitor how Denmark balances its ties with both the EU and the U.S., and also how this situation shapes the future of Arctic governance and international cooperation.