In a decisive move to combat the escalating threat of foot-and-mouth disease, Slovakia has officially declared an “emergency situation” across the nation. This declaration comes in response to a growing number of confirmed cases that pose meaningful risks to the agricultural sector and livestock health. With the potential for widespread economic repercussions, the Slovak government is implementing stringent measures aimed at containment and prevention. This article delves into the implications of this emergency declaration, the specific actions being taken by authorities, and the broader context of foot-and-mouth disease management in the region. As Slovakia seeks to safeguard its agriculture and ensure food security, the situation continues to evolve, prompting close monitoring and strategic interventions.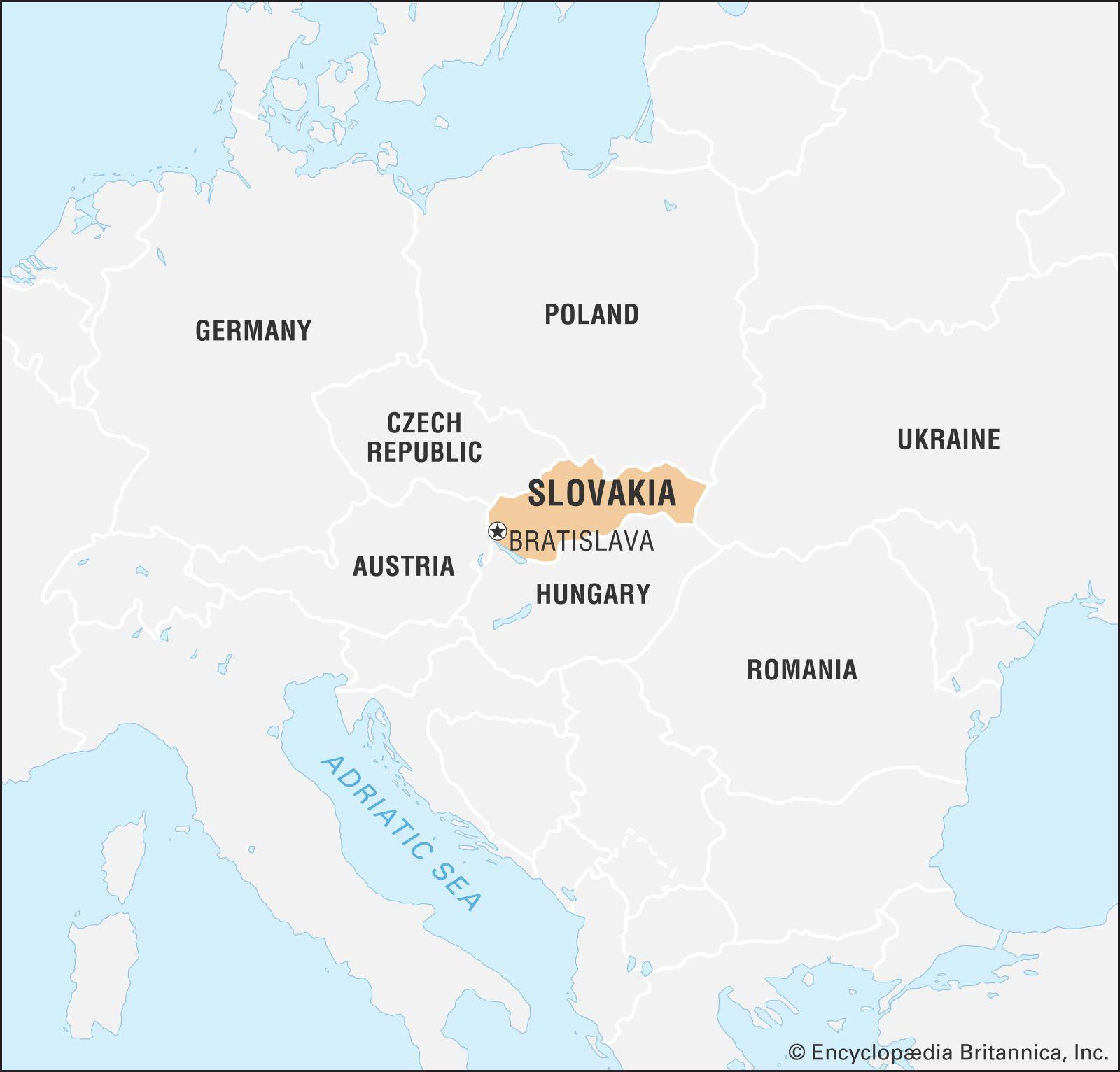
Emergency Situation Declared in Slovakia to Combat Foot-and-Mouth Disease Outbreak
In a decisive move to contain an outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease, Slovakia has officially declared an emergency situation. This drastic measure comes in response to a rise in reported cases, prompting health and agricultural authorities to take immediate action. The government has outlined a series of protocols aimed at controlling the spread of the virus among livestock, which is crucial for protecting both agricultural livelihoods and public health.
The emergency response includes:
- Quarantine Measures: Affected areas will face strict quarantines to prevent movement of animals.
- Health Checks: Livestock will undergo complete health examinations to identify and isolate infected animals.
- Public Awareness campaigns: Heightened educational efforts to inform farmers and the general public about symptoms and preventive measures.
- International Collaboration: Cooperation with neighboring countries and international health organizations to monitor and manage the situation.
| Key Focus Areas | Actions Taken |
|---|---|
| Animal Movement Control | strict restrictions in outbreak zones |
| Vaccine Implementation | Emergency vaccination plans are being discussed |
| Monitoring and Reporting | Increased surveillance for early detection |

Understanding the Impact of Foot-and-Mouth Disease on Livestock and Agricultural economy
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) poses a significant threat to livestock health and, consequently, the agricultural economy. Characterized by high contagion and rapid spread among cloven-hoofed animals, FMD can lead to severe animal welfare issues and significant economic losses. Farmers relying on cattle, pigs, sheep, and goats face not only the costs associated with treatment but also the potential for mass culling to control outbreaks. The immediate effects include:
- Reduced livestock productivity: Infected animals experience decreased milk production and poor weight gain.
- Trade restrictions: Countries often impose bans on livestock imports or exports from affected regions, further straining economies.
- Increased veterinary costs: Farmers must spend substantially on disease management and preventive measures.
The impact of FMD extends beyond the farm gate, influencing the broader agricultural landscape. Rural economies reliant on livestock contribute to communities through employment and local business. As disease outbreaks ensue, the ripple effect can lead to:
- Unemployment: Workers in associated industries, such as feed production and veterinary services, may face job losses.
- Price volatility: Supply chain disruptions can lead to increased prices for consumers and decreased margins for producers.
- Long-term economic decline: Prolonged FMD crises can deter investment in agriculture and lead to shifts away from livestock farming.
| economic Impact | Short-term Effects | Long-term Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Farmers | Disease control costs | Loss of future livestock |
| Local Economy | Reduced sales | Employment decline |
| Overall Market | Price increases | Investment hesitance |
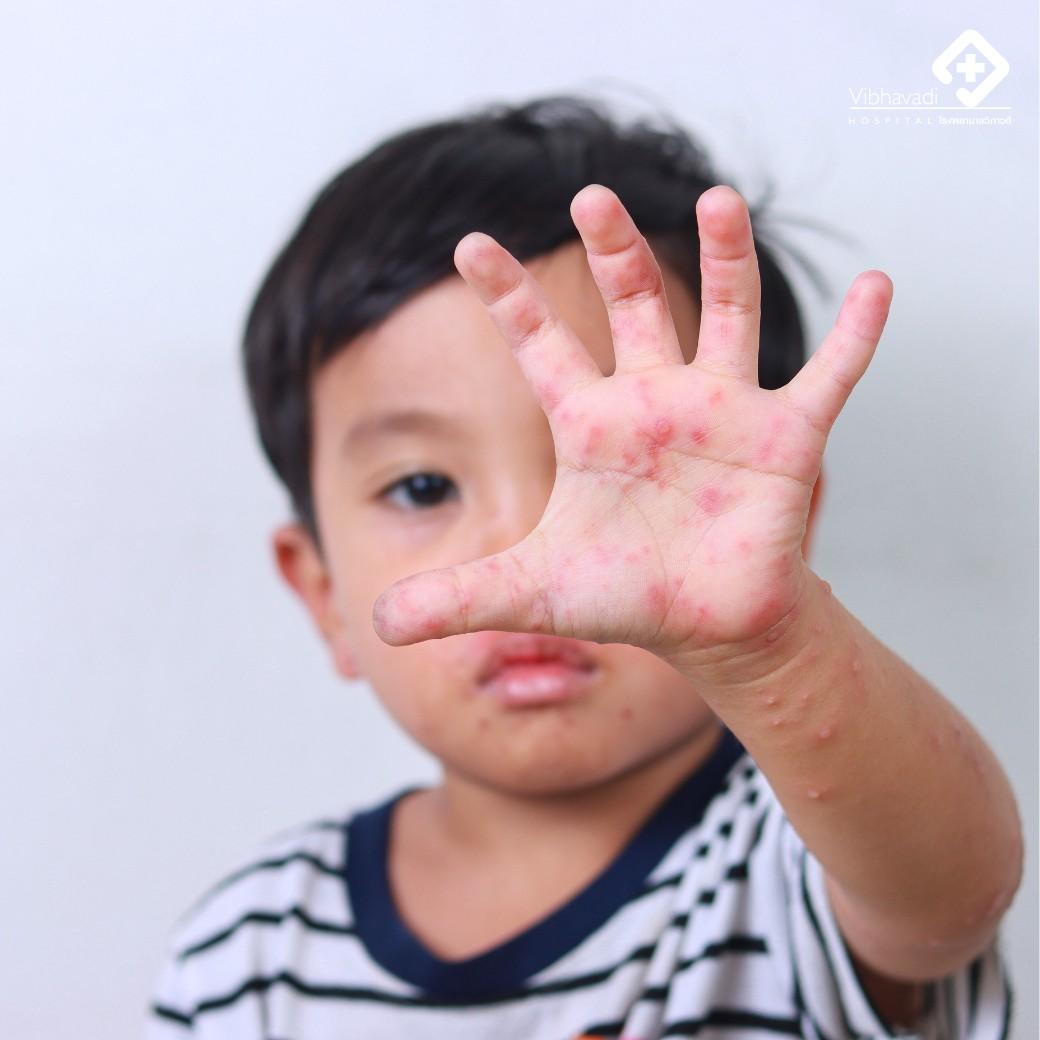

Government Responses and Measures to Contain the Spread of Foot-and-Mouth Disease
In response to the escalating cases of foot-and-mouth disease, the Slovak government has implemented a series of stringent measures aimed at curbing the outbreak and protecting livestock health.This includes immediate restrictions on the movement of animals, particularly in areas showing signs of infection. Authorities have initiated a comprehensive surveillance strategy to monitor livestock populations, ensuring that any potential outbreaks are detected and managed swiftly.Additionally, the government is promoting biosecurity protocols among farmers through targeted educational campaigns. Key actions include:
- Animal Movement Bans: Restrictions on the transportation of livestock to prevent further spread.
- Increased Surveillance: Regular inspections and health checks in farms and markets.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Informing the public and farmers about preventive measures against the disease.
Moreover, the state has allocated funding for vital resources to aid in the containment efforts, such as vaccinations and diagnostic tools for early detection. Coordination with veterinary services has become paramount, focusing on rapid response teams that can swiftly implement control measures in affected areas. In tandem with domestic efforts,Slovakia is also working in collaboration with neighboring countries to establish a united front against cross-border transmission of the disease.A table illustrating key response areas and allocated resources is shown below:
| Measure | Details | Allocated Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Movement Bans | Prohibition in affected zones | €1 million |
| Vaccination Programs | Mass immunization in high-risk areas | €500,000 |
| Public Awareness | Workshops and facts distribution | €250,000 |

Recommendations for Farmers and Livestock Owners Amid the emergency Situation
In light of the recent emergency declaration in Slovakia aimed at curbing the spread of foot-and-mouth disease, farmers and livestock owners must adopt proactive measures to protect their herds and operations. Essential steps include:
- Enhanced Biosecurity Measures: Implement strict biosecurity protocols on farms to prevent any contamination, including disinfection of equipment and clothing.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Regularly monitor livestock health and report any symptoms instantly to veterinary authorities for swift action.
- Restricting Movements: Limit animal movements to reduce the risk of spreading the virus,including avoiding fairs and markets until the situation stabilizes.
- Vaccination Programs: Consult with veterinary services about the possibility of vaccinating livestock as a preventative measure against infection.
Additionally, staying informed through reliable sources is crucial during this emergency. Local agricultural boards and veterinary services can provide timely updates and guidance. Farmers should consider:
- Establishing Communication: Create a communication line among local farmers to share updates and strategies related to the emergency.
- Financial Planning: Be prepared for potential economic impacts by reviewing financial plans and exploring available government support programs for affected businesses.
- Education and Training: Invest in training for farm staff on disease recognition and response to be better prepared for any potential outbreaks in the future.

The role of Public Health and Safety in Addressing Animal Disease Threats
The recent declaration of an ’emergency situation’ in Slovakia highlights the critical importance of public health and safety in mitigating animal disease threats. In the face of foot-and-mouth disease, which poses significant risks not only to livestock but also to public health and economic stability, swift and coordinated actions are essential. Effective management involves a multifaceted approach that includes monitoring, vaccination, and strict biosecurity measures. Key components of this approach include:
- Surveillance and Response: Continuous monitoring of animal health to identify outbreaks early.
- Public Awareness campaigns: Educating farmers and the public about disease symptoms and prevention methods.
- Collaboration with Veterinarians: partnering with professionals to implement vaccination programs and health checks.
Moreover, public health entities must adapt their strategies to address the evolving nature of these threats. By establishing a strong framework for communication between government bodies, agricultural sectors, and local communities, they can enhance their responsiveness to outbreaks. The integration of technology in tracking disease spread and its impact on animal and human health has become increasingly significant. Below is a simplified structure of essential strategies that can be employed:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Vaccination Programs | Administering vaccines to livestock to build herd immunity against specific diseases. |
| Biosecurity Measures | Implementing strict hygiene protocols to prevent disease transmission on farms. |
| Public Collaboration | Engaging local communities in awareness and prevention efforts. |

Future Implications for Slovakian Trade and Market Stability Following the Outbreak
The recent declaration of an emergency situation in Slovakia due to foot-and-mouth disease has raised significant concerns regarding the nation’s trade relations and market stability.as a primary producer of agricultural products,particularly in the livestock sector,slovakia’s economy heavily relies on the export of these goods. The outbreak poses several challenges that could reshape both domestic and international trade dynamics:
- Export Restrictions: Immediate restrictions on livestock exports can be expected, leading to a surplus in the domestic market and a consequent drop in prices.
- Reputational Damage: Incidents of disease outbreaks frequently enough lead to long-lasting impacts on a country’s reputation as a reliable trading partner, affecting future trade agreements.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: livestock and associated products moving through the supply chain could face delays, increasing costs for producers and consumers alike.
To assess and strategize future responses, the Slovak government may consider implementing measures that mitigate the outbreak’s impact on trade. These could include:
| Proposed Measures | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Biosecurity Protocols | Reducing the risk of further outbreaks and restoring trade confidence. |
| Compensation Programs for Affected Farmers | Support for local businesses to prevent closures and maintain employment. |
| Market Diversification Initiatives | Encouraging exports in less-affected sectors to stabilize economic contributions. |
Responding proactively to the crisis is crucial for Slovakia not only to safeguard its current economic standing but also to position itself favorably for a future return to stability and growth in the agricultural export market.

To Wrap It Up
Slovakia’s declaration of an emergency situation to combat the spread of foot-and-mouth disease marks a significant step in safeguarding its agricultural sector and livestock health.This proactive measure underscores the government’s commitment to mitigating the risks associated with this highly contagious virus, which could have dire economic implications if left unchecked. As authorities implement strict monitoring and biosecurity protocols, farmers and veterinarians are urged to remain vigilant in reporting any potential outbreaks. The situation will be continuously assessed as Slovakia navigates this challenge, and updates will be crucial for stakeholders across the agricultural community. With cooperation and swift action, Slovakia aims to contain the spread of foot-and-mouth disease, ensuring the resilience of its livestock industry in the face of emerging threats.







JD Vance says US and UK ‘working very hard’ on trade deal and will come to a ‘great agreement’ – Sky News