Introduction:
As health authorities continue to monitor infectious diseases, recent reports highlight a concerning increase in chickenpox cases across various regions. the 3FM health desk has gathered critical insights into the factors contributing to the spread of this highly contagious virus, which primarily affects children but can also pose risks to adults without prior immunity. With vaccination rates fluctuating adn public awareness about the disease varying,health experts are calling for renewed attention to preventive measures and community awareness. This article delves into the current state of chickenpox outbreaks, examining its transmission dynamics, the importance of vaccination, and what communities can do to mitigate the spread of this viral infection.
Understanding Chickenpox and Its Transmission
Chickenpox is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, resulting in an itchy, blister-like rash, mild fever, and fatigue. The virus primarily spreads through close contact with an infected person’s skin lesions or through respiratory droplets when they cough or sneeze. This means that even brief interactions can lead to transmission, especially in crowded places or among individuals who are not vaccinated. Understanding the transmission routes can definitely help mitigate outbreaks and ensure that those at risk, notably young children and individuals with weakened immune systems, are protected.
Ther are several key factors that influence how easily chickenpox spreads:
- infectious Period: A person infected with chickenpox is contagious from about 1 to 2 days before the rash appears untill all the blisters have crusted over.
- Vaccination Status: Vaccinated individuals have a significantly lower risk of contracting the virus, and if infected, frequently enough experience a milder form of the disease.
- Surroundings: The likelihood of transmission increases in enclosed environments such as schools and daycare centers where individuals are in close quarters.
| Transmission Route | Details |
|---|---|
| Direct Contact | Touching or interacting with an infected individual’s skin lesions. |
| Airborne | Virus particles in the air from respiratory droplets. |
| Indirect Contact | Touching surfaces contaminated with the virus. |
Identifying Symptoms and Early Signs of Infection
Recognizing the onset of chickenpox is vital for effective management and prevention. Symptoms typically appear 10-21 days after exposure to the virus. Early indicators often include:
- Fever: Usually mild, this may persist for a few days.
- Fatigue: An overall feeling of tiredness or malaise.
- Loss of appetite: A noticeable decrease in hunger.
- Headache: Mild to moderate intensity.
- Itchy skin: The most prominent sign, often starting as small red spots.
As the infection progresses, these spots develop into blisters, which can be highly contagious. Early intervention is essential to limit the spread; therefore,parents and caregivers shoudl be vigilant. Watch for:
| Signs to Watch For | Action Steps |
|---|---|
| Rapid appearance of spots | Isolate the affected individual |
| Increasing itchiness | Consult a physician for advice |
| Signs of infection in blisters | Seek immediate medical attention |
The Impact of Chickenpox on Public Health
Chickenpox, caused by the varicella-zoster virus, has historically posed significant challenges to public health systems. While it is indeed usually considered a mild childhood illness, outbreaks can lead to substantial morbidity and occasionally mortality, particularly among vulnerable populations. The complications associated with chickenpox can include pneumonia, encephalitis, and secondary bacterial infections. this highlights the importance of vaccination in reducing the spread of the virus.
Vaccination programs have dramatically reduced the incidence of chickenpox in many regions.The introduction of the varicella vaccine has led to a notable decline in both cases and hospitalizations. Public health authorities advocate for widespread immunization, emphasizing the benefits such as:
- Herd immunity, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated.
- Reduced healthcare costs associated with treating complications.
- Diminished disease transmission, leading to lower overall prevalence.
To illustrate the impact of vaccination, the following table compares the incidence rates of chickenpox before and after the introduction of the varicella vaccine in selected states:
| Year | Cases per 100,000 Population (Pre-Vaccine) | Cases per 100,000 Population (Post-Vaccine) |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 110 | N/A |
| 2000 | N/A | 66 |
| 2010 | N/A | 12 |
The data above emphasizes the transformative effect of vaccination efforts, reaffirming the necessity of continued public health campaigns to ensure high vaccination rates. The overall impact on community health is profound, showcasing how proactive measures can mitigate the risks associated with common infectious diseases.
Risk Factors Contributing to Increased Spread
the spread of chickenpox is influenced by several risk factors that can significantly increase transmission rates. One of the primary contributors is vaccination coverage. Areas with low vaccination rates create a larger susceptible population, facilitating outbreaks. Additionally,the seasonal variations observed in viral transmission patterns can play a crucial role; for instance,the risk tends to heighten in colder months when people congregate indoors,fostering an environment for the virus to thrive. Furthermore, individuals who are immunocompromised or not previously infected are at a higher risk, underscoring the need for vigilant health measures in such populations.
Another contributing factor is population density. Urban environments with higher populations can exacerbate the transmission of chickenpox, as close contact among individuals facilitates the spread of the virus. Social dynamics, including increased travel during holiday seasons, also heighten the risk by introducing the virus into new communities.The role of schools and daycare centers cannot be overlooked; these institutions often serve as hotspots for outbreaks due to the close interactions among children. Below are some additional risk factors outlined in a brief table format:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Low vaccination Rates | Higher susceptibility increases outbreak potential. |
| Cold Seasons | Indoor crowding raises transmission risks. |
| Immunocompromised Individuals | More vulnerable to severe cases and spread. |
| Urban Density | Closer proximity facilitates easier transmission. |
| School Environments | Increased close contact among children. |
The Role of Vaccination in Preventing Outbreaks
The importance of vaccination in controlling and preventing disease outbreaks cannot be overstated. Vaccines serve as a frontline defense, creating immunity within populations and reducing the likelihood of disease transmission. By immunizing individuals, particularly children who are most vulnerable, we can significantly diminish the number of cases, minimizing the potential for severe complications and hospitalizations. The widespread acceptance and application of vaccines have proven effective in curbing outbreaks not only of chickenpox but also of other infectious diseases.
when enough individuals within a community are vaccinated, a state of herd immunity is achieved, protecting those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. this collective immunity helps disrupt the chain of infection, leading to fewer outbreaks and safeguarding the health of the community.Consider the following highlights on the impact of vaccination on disease prevention:
- Reduction in Cases: A substantial decline in chickenpox cases has been observed in vaccinated populations.
- Economic Savings: Prevention of outbreaks reduces healthcare costs and loss of productivity.
- Public Health Safety: Vaccination campaigns ensure community resilience against potential outbreaks.
| Year | Cases of Chickenpox | Vaccination Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 250,000 | 85 |
| 2015 | 100,000 | 92 |
| 2020 | 30,000 | 95 |
vaccination stands as a critical tool in public health strategy, with the ability to significantly limit the spread of chickenpox and other infectious diseases when practiced widely. By engaging in proactive vaccination programs and encouraging community participation, we can continue to protect our society from the potential devastation of outbreak scenarios.
Recommended Health Practices to Minimize Transmission
To reduce the risk of chickenpox transmission, individuals should adopt a series of key health practices.Vaccination remains one of the most effective preventive measures. The chickenpox vaccine is typically administered in two doses, beginning in childhood, and offers robust protection against the virus. Along with vaccination, it is indeed crucial to maintain good hygiene by frequently washing hands with soap and water, especially after interacting with infected individuals. This simple practice can significantly lower the chances of spreading the virus.
Moreover, when an outbreak occurs, it is significant to isolate affected individuals until all blisters have crusted over, typically about a week after the first rash appears.In crowded settings such as schools and daycare centers, encouraging respiratory etiquette—including covering coughs and sneezes with a tissue or elbow—can help curtail the spread of the virus. Consider implementing a health education program that emphasizes these practices, making it clear how easy it is to prevent transmission among peers.
| Recommended Practices | impact on Transmission |
|---|---|
| Vaccination | Significantly lowers chance of infection |
| Hand Washing | Minimizes virus spread and contact |
| Isolation of Infected | Reduces risk of outbreaks |
| Respiratory Etiquette | Prevents airborne transmission |
The Importance of Isolation During an Outbreak
During an outbreak, particularly one as contagious as chickenpox, isolation plays a crucial role in controlling the spread of the virus. When individuals who are infected remain at home, they significantly reduce the chances of transmission to others in schools, workplaces, and public spaces. This proactive measure not only protects those who are susceptible—such as infants and immunocompromised individuals—but also helps to ensure that healthcare systems do not become overwhelmed. By recognizing the signs of the disease and adhering to precautionary guidelines, communities can work together to minimize impact.
The essence of isolation goes beyond just keeping the sick at home; it cultivates a culture of communal duty. Here are some key aspects that highlight the importance of isolation during such outbreaks:
- Prevention of further infections: Isolating infected individuals prevents them from interacting with others.
- Reduction of asymptomatic spread: Some individuals may not show symptoms but can still transmit the disease.
- Education on hygiene practices: Isolation emphasizes the importance of cleanliness and personal hygiene to curb virus spread.
| key benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced Transmission | Minimizes contact with vulnerable populations,thereby lowering infection rates. |
| Awareness and Preparedness | Encourages communities to stay informed and ready to respond effectively. |
Educating the Community on Chickenpox Awareness
Awareness is the first step towards prevention. Community education about chickenpox is crucial as cases are on the rise. Understanding the disease can definitely help to curb its spread. Here are some key points to remember:
- Vaccination: Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent chickenpox. ensuring that children and adults are vaccinated is essential.
- Symptoms: Familiarize yourself with the symptoms, which include an itchy rash, fever, and fatigue. Early detection helps in timely treatment.
- Transmission: Chickenpox is highly contagious. it spreads through respiratory droplets or direct contact with the rash.
- Isolation: Infected individuals should stay home until the blisters have crusted over to minimize spreading the virus.
Furthermore,understanding the complications associated with chickenpox can safeguard vulnerable populations. Although most cases resolve without serious issues,certain groups like infants,pregnant women,and immunocompromised individuals are at greater risk. A brief overview of potential complications is outlined below:
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
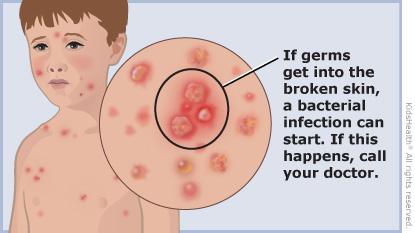
| Secondary Infections | Infections of the skin or lungs due to bacteria entering blisters. |
| Pneumonia | Can occur in people with weakened immune systems. |
| Encephalitis | In rare cases, inflammation of the brain may occur. |
addressing Misconceptions About Chickenpox
Chickenpox is often viewed as a harmless childhood illness, but this common misconception can lead to a lack of understanding about its real implications. While it’s true that many children recover with few complications, some individuals can experience severe symptoms or health issues. These may include:
- Secondary Infections: scratching the blisters can lead to bacterial infections.
- Pneumonia: Adults and immunocompromised individuals are at a higher risk.
- Neurological Problems: In rare cases, chickenpox can lead to encephalitis.
Moreover,it’s essential to debunk the belief that chickenpox only occurs in childhood. Adults can contract the virus, frequently enough experiencing more severe symptoms.Additionally, the misguided notion that once you have chickenpox, you are immune for life fails to account for the potential reactivation of the virus as shingles later in life. To further emphasize these differences,the following table clarifies the key points regarding chickenpox transmission and immunity:
| Aspect | Chickenpox | Shingles |
|---|---|---|
| Age of Onset | Common in children | Occurs in adults or post-chickenpox |
| Severity | Typically mild | Can be severe,especially in older adults |
| Immunity | lifetime immunity post-infection | Can recur as shingles |
Advice for Parents on Managing chickenpox in Children
Managing chickenpox in children can be challenging,but with proper care,recovery can be smooth. Monitor symptoms closely and keep a record of your child’s temperature and overall condition. It’s essential to avoid letting them scratch the blisters,as this can lead to infection. Here are a few tips to help alleviate discomfort:
- Keep nails trimmed to prevent scratching.
- Use calamine lotion or over-the-counter antihistamines for itching relief.
- Ensure hydration by encouraging plenty of fluids to drink.
- Dress lightly in loose, breathable clothing to minimize irritation.
While chickenpox is typically a mild illness, understanding when to seek further medical advice is crucial. If your child experiences any of the following, it’s important to contact your healthcare provider promptly:
| Symptoms | Action |
|---|---|
| High fever (above 102°F or 39°C) | Contact a doctor for advice. |
| Difficulties breathing | Seek immediate medical attention. |
| Signs of infection (increased redness, pus) | Consult a healthcare professional. |
Keeping to these guidelines and staying alert for any changes in your child’s condition can help ensure a quicker and more agreeable recovery from chickenpox.
Navigating Chickenpox in School Settings
As chickenpox outbreaks can spread quickly in school environments, understanding the disease and implementing effective prevention strategies is crucial. It’s essential for schools to foster a culture of awareness about the symptoms and transmission of chickenpox. Parents and educators should be informed about the signs to watch for,such as:
- Itchy rash – Begins as small red spots that develop into blisters.
- Fever – Frequently enough mild but can be higher at times.
- Fatigue – A general feeling of tiredness may be present.
- Loss of appetite – Children may show less interest in food.
Furthermore,schools should take proactive measures to contain outbreaks. This can include initiating clear dialog protocols for reporting suspected cases, encouraging vaccinations among students, and implementing isolation procedures to prevent further spread. Here’s a simple overview of recommended actions:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Vaccination | Ensure all eligible students are vaccinated against chickenpox. |
| Notification | Inform parents and guardians promptly about any outbreaks to monitor for symptoms. |
| Isolation | Isolate infected individuals at home until they are no longer contagious. |
| Education | Hold informational sessions on chickenpox for staff and parents. |
Collaborating with Healthcare providers for Effective Prevention
Effective prevention of chickenpox hinges on a collaborative effort between health organizations and frontline healthcare providers. By strengthening these partnerships, we can implement extensive vaccination programs and educational initiatives that emphasize the importance of immunization.Regular communication is key; updates on emerging data regarding vaccine efficacy and safety can empower providers to engage parents and patients with confidence. Additionally, leveraging technology in data sharing allows healthcare professionals to identify outbreak patterns and respond swiftly to potential cases, ensuring that communities are well informed.
Another essential component is involving community leaders to promote awareness and prevention strategies. By organizing workshops or outreach programs in schools and community centers, healthcare providers can reach a broader audience to spread crucial facts regarding chickenpox symptoms and preventative measures. Furthermore,creating a feedback loop where health providers can report the outcomes of these initiatives can help refine and adapt strategies in real-time. The table below summarizes some key activities for collaboration:
| Activity | Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| vaccination Drives | Organizing community vaccination days | Increased immunization rates |
| Educational Workshops | Hosting sessions in schools | Enhanced awareness among parents |
| Surveillance Programs | tracking outbreak reports | timely response to cases |
Monitoring and Reporting Outbreaks: What You Should Know
Monitoring outbreaks of chickenpox, particularly in communities, is crucial for public health. Health authorities and parents alike should be vigilant in recognizing symptoms, which include a distinctive itchy rash, fever, and fatigue. Here are a few key points to consider:
- Reporting Symptoms: Early identification allows for timely reporting to health agencies.
- Quarantine Measures: Infected individuals should stay home to prevent further spread.
- Vaccination Status: Confirming vaccination status can help assess community risk.
Effective communication between schools, healthcare providers, and parents is essential for managing chickenpox outbreaks.Here’s a rapid overview of recommended practice:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Notify Parents | Inform about the outbreak and encourage monitoring for symptoms. |
| Consult Healthcare Providers | For vaccination recommendations and treatment options. |
| Follow Up | Keep track of new cases to adapt response strategies. |
Looking Ahead: The Future of Chickenpox Management
As we move forward, the management of chickenpox is highly likely to evolve significantly, driven by advancements in medical research and public health strategies.The implementation of vaccines has already transformed the landscape, reducing incidence rates dramatically. In the coming years, we can anticipate the following trends:
- Innovative Vaccines: Continued development of more effective vaccines that provide longer-lasting immunity.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Enhanced efforts to educate communities about the importance of vaccinations and recognizing symptoms early.
- Global Collaboration: Increased partnerships between health organizations worldwide to monitor outbreaks and share data.
Furthermore,as new therapeutic options emerge,healthcare providers may adopt personalized treatment methods tailored to individual patient needs.This can lead to improved management of symptoms and reduction in complications.A potential focus of future research is:
| Research Focus | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Antiviral Medications | Quicker recovery times and fewer complications. |
| genetic Studies | Understanding susceptibility and immunity variations. |
| Community Health Initiatives | Reducing spread during outbreaks through targeted interventions. |
The conclusion
As we conclude our examination of the recent increase in chickenpox cases reported by 3FM, it is imperative to emphasize the importance of awareness and vaccination in controlling the spread of this contagious disease. Health officials urge parents and caregivers to ensure that children are up-to-date with their vaccinations, as this remains the most effective method to prevent outbreaks. With a growing number of cases, it is indeed crucial for communities to stay informed and vigilant. By understanding the signs and symptoms of chickenpox and recognizing the significance of immunization, we can collectively mitigate the risk of transmission and protect those who are most vulnerable.Stay tuned for further updates and health advisories as we continue to monitor this evolving situation.