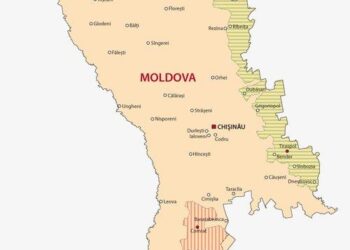
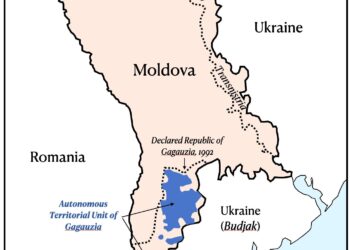
In a significant development underscoring the ongoing geopolitical tensions in Eastern Europe, the breakaway region of Transnistria, self-declared and heavily dependent on Russian support, has ceased heating and hot water services as Russian gas supplies run dry. This decision has profound implications for the approximately 470,000 residents of the region, many of whom are now bracing for a harsh winter amid dwindling resources and an uncertain political landscape. The cessation of gas flow from Russia, a key energy supplier to both Transnistria and neighboring Moldova, highlights the fragility of energy security in the region and adds another layer of complexity to the already strained relations between Moldova, its breakaway territories, and Moscow. As local authorities scramble to mitigate the burgeoning crisis, the situation poses urgent questions about the future of Transnistria and the broader impact on regional stability.
Breakaway Moldovan Region Faces Heating Crisis Amidst Russian Gas Supply Halt
The recent cessation of Russian gas supplies has plunged the breakaway region into an urgent energy crisis, prompting local authorities to take decisive measures to conserve resources. As temperatures drop, the region is grappling with the consequences, leading to the implementation of critical cutbacks in essential services. The decisions made in response to this challenge include:
- Suspension of Central Heating: Residents are now facing unheated homes as the central heating system is temporarily halted.
- Hot Water Shortages: Hot water supplies have also been restricted, affecting daily hygiene and comfort.
- Community Support Initiatives: local organizations are mobilizing to provide assistance to the most vulnerable populations, ensuring they have access to basic needs in this difficult time.
In an effort to respond to the crisis, the regional government has outlined a series of strategies to mitigate the impact on residents. These include exploring option energy sources and increasing public awareness about energy conservation techniques. A recent meeting of regional officials highlighted the situation’s urgency, with discussions centering on potential partnerships to secure emergency energy supplies from neighboring areas. The table below summarizes the ongoing efforts:
| Effort | Description |
|---|---|
| Exploration of Alternatives | Investigating renewable energy options and biomass fuel sources. |
| Community Engagement | Organizing workshops on energy-saving measures for residents. |
| Emergency Supply Talks | Negotiating with neighboring regions for temporary energy imports. |
Impact of Gas Flow Disruption on Local Communities and Infrastructure
The recent cessation of Russian gas flow to a breakaway Moldovan region has sent shockwaves throughout local communities, revealing the fragile nature of the area’s energy dependency.With heating and hot water supplies now cut, residents face a cold winter, sparking concerns over health and safety.Many families are left scrambling to find alternative heating sources, wich may not be affordable or accessible. This disruption emphasizes the significant risk of relying on a single energy supplier and underlines the urgent need for diversification in energy sourcing to combat similar future crises.
Moreover, the cessation of gas flow has cascading effects on local infrastructure, affecting not only homes but also critical services such as hospitals and schools. Facilities are struggling to maintain operations without a reliable energy source, which can lead to diminished public health and educational outcomes.Local governments are now confronted with the challenge of implementing emergency measures, which may include:
- Provision of emergency heating centers
- Public awareness campaigns on energy conservation
- Engagement with alternative energy providers
- Restoration of local heating infrastructure
In response to this crisis, local authorities are also assessing the potential long-term implications on regional development. Below is a table outlining predicted impacts:
| Impact area | Short-Term Effects | Long-Term Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Residential Heating | Increased demand for alternative sources | Potential increase in energy poverty |
| Healthcare Services | reduced operational capacity of clinics | Increased risk of health emergencies |
| Education | Disrupted school schedules | Long-term impact on student performance |
Economic Ramifications of Losing Russian Gas Supply in the Region
the cessation of Russian gas supplies has sent shockwaves through the energy landscape of the region, notably affecting the breakaway Moldovan region.With heating and hot water services cut off, residents are facing immediate and harsh winter conditions. The shift not only threatens the day-to-day comfort and safety of its inhabitants but also poses considerable economic challenges.The region’s dependency on Russian gas has been longstanding, and now it is confronted with the imperative to innovate and find alternative energy sources, which could entail significant financial investments and logistical reconfigurations.
In the wake of this abrupt halt, the broader economic implications can be profound. Regions reliant on Russian gas may experience fluctuations in energy prices, inflationary pressures, and disruptions in local industries. some potential effects include:
- Increased Energy Costs: The rapid shift toward alternative energy sources may lead to higher gas prices as markets adjust.
- Economic Instability: Local businesses could face increased operational costs, threatening their viability and possibly leading to layoffs.
- Investment Stagnation: Uncertainty regarding energy supply could deter foreign investments in the region.
To further illustrate the economic impact, the table below summarizes anticipated shifts in energy expenditure for households following the loss of Russian gas:
| Energy Source | Projected Cost Increase (%) | Time to Implementation (Months) |
|---|---|---|
| Renewables (solar, wind) | 30% | 12+ |
| LNG Alternatives | 20% | 6-8 |
| Electrification (heat pumps) | 40% | 10 |
Political Implications of Energy Dependence in the Breakaway Region
The cessation of Russian gas supplies to the breakaway Moldovan region has significant political repercussions that resonate beyond its borders. Economic instability is likely to intensify as the local government grapples with the fallout from inadequate heating and hot water. This energy crisis can lead to public unrest, questioning the authority of existing political leaders who may be blamed for failing to secure alternative energy sources. In addition, the shift in energy dynamics may strengthen movements advocating for greater autonomy, drawing attention to the region’s reliance on external power, predominantly from Russia.Moreover, rising dissatisfaction among citizens could potentially embolden opposition parties and lead to calls for independence or closer ties with the European Union as a means to break free from Russian influence.
Additionally, this energy crisis places the breakaway region at the center of geopolitical maneuvering. With energy dependence as a sensitive political tool, regional stakeholders, including Moldova and surrounding countries, may exploit the turmoil to further their agendas. as an example, EU entities might increase their efforts to provide assistance, both humanitarian and financial, to foster stronger ties and counter Russian influence. Conversely, the Kremlin could leverage the situation to assert its dominance by offering renewed energy supplies under more favorable terms, thereby further entwining the region in its orbit. The following table summarizes the potential actors involved and their likely motivations:
| Actor | Possible Motivations |
|---|---|
| Local Government | Stabilize public sentiment, secure energy alternatives |
| Opposition Parties | Capitalize on discontent, rally support for changes |
| European Union | Support regional independence, diminish Russian influence |
| Russia | Reinforce control, provide energy under conditional terms |
Urgent Measures for Ensuring Energy Security in the Region
The abrupt cessation of Russian gas supplies to the breakaway Moldovan region has triggered an immediate crisis, thrusting energy security into the spotlight. with many households now left without heating and hot water, officials are compelled to explore rapid solutions to mitigate the impact on the local population. Key actions needed include:
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Seeking alternative gas suppliers and exploring renewable energy options to lessen reliance on a single source.
- Emergency Energy Partnerships: Establishing agreements with neighboring countries for energy support and resource sharing.
- Immediate Financial Aid: Implementing government subsidies or financial assistance programs to help residents cope with increased energy costs.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Informing citizens about energy conservation strategies to alleviate demand during this crisis.
To address the long-term implications of this energy crisis, strategic planning and collaborative efforts among regional stakeholders are essential. The development of a comprehensive energy security strategy could involve:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Investment in Infrastructure | Upgrading existing energy networks to increase efficiency and resilience. |
| Renewable Energy Projects | Pursuing solar, wind, and bioenergy installations to create lasting alternatives. |
| Regional Cooperation | Forming alliances with regional entities for resource management and crisis coordination. |
| Policy Reform | Enhancing regulatory frameworks to encourage private sector investments in energy. |
Long-Term Solutions for Sustainable Heating and Energy Supply
The recent developments following the cutoff of Russian gas supply have underscored the critical need for long-term energy strategies in the region. As communities grapple with the immediate challenges of disrupted heating and hot water services, there is a growing call for the adoption of renewable energy sources. By investing in technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, and biomass heating systems, the region can enhance its energy independence and resilience against future supply shocks. These solutions not only promise sustainable energy production but also align with global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Moreover, enhancing energy efficiency in existing infrastructure can play a pivotal role in sustainable energy planning. This involves upgrading heating systems, improving insulation in buildings, and promoting the use of energy-efficient appliances. A comprehensive strategy might include:
- Establishing local energy cooperatives that empower communities to manage their energy sources.
- Implementing policy incentives to encourage investment in green technologies.
- educating citizens on energy conservation practices to reduce demand.
In order to evaluate potential solutions,a comparative analysis between different energy approaches can be illustrative:
| Energy Source | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Energy | Renewable,low operational costs | Intermittent supply,high initial setup cost |
| Wind Energy | Clean,high output in windy areas | Variable generation,impact on wildlife |
| Biomass | utilizes waste,can be carbon neutral | Requires sustainable sourcing |
Regional responses and International Support Options for Affected Citizens
The recent decision to cut off heating and hot water services in the breakaway moldovan region highlights urgent challenges faced by local residents. As Russian gas supplies deteriorate, essential services are in jeopardy, prompting not only regional despair but also a call for international intervention. In response,neighboring nations and international organizations are mobilizing resources to support affected communities. Potential initiatives include:
- Emergency heating centers: Establishing temporary shelters with heating facilities to ensure citizens have access to warmth during harsh winter months.
- Humanitarian aid shipments: Coordinating efforts for food, blankets, and medical supplies to bolster the resilience of vulnerable populations.
- International financial assistance: Encouraging developmental aid from global entities to support infrastructure repairs and long-term recovery efforts.
As international support efforts ramp up,collaboration will be crucial in addressing both immediate needs and long-term stability in the region. Regional partners, including EU nations, have emphasized their commitment to providing aid, while discussions regarding energy alternatives are underway. A potential response framework may include:
| International Body | Proposed Support | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| European Union | Financial aid for heating infrastructure | Within 3 months |
| United Nations | Humanitarian aid delivery | Promptly |
| NATO | Security and logistics support | Ongoing |
Analyzing the Future of Energy Relations Between Moldova and Russia
The recent cessation of Russian gas supplies has plunged the breakaway moldovan region into a crisis, significantly impacting the heating and hot water systems that many families rely on during the harsh winter months. The termination of these gas flows highlights the critical vulnerabilities in energy dependency that moldova faces. As local authorities scramble to find alternative energy sources, the situation underscores the urgent need for Moldova to reevaluate its energy strategy and diplomatic relations with Moscow. Given the geopolitical tensions, both the Moldovan government and its breakaway regions are compelled to explore energy diversification strategies to mitigate future risks.
In light of these developments, it is essential to assess potential scenarios for future energy relations between Moldova and russia. Key factors that will play a role in shaping the energy landscape include:
- Geopolitical Alignments: The influence of the European Union and neighboring states may shift Moldova’s reliance on Russian energy.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Moldova could seek partnerships with alternative suppliers, including investments in renewable energy.
- Energy Infrastructure Investments: Upgrading local infrastructure may provide resilience against future supply disruptions.
To better understand the evolving dynamics, consider the following table illustrating the energy supply scenarios for Moldova in the coming years:
| Scenario | Potential Outcome | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Increased EU Cooperation | Reduced dependency on Russian energy | Strengthened geopolitical ties with Europe |
| Investment in Renewables | Sustainable energy independence | Long-term economic growth and stability |
| Negotiations with Russia | Possible resumption of gas supplies | Continued vulnerability to external pressures |
Exploring Renewable Energy Alternatives for moldovan Region
The cessation of Russian gas supplies has propelled the Moldovan region into a critical juncture, forcing immediate consideration of renewable energy alternatives. With heating and hot water services now disrupted, local authorities and energy experts are exploring sustainable solutions to provide reliable energy sources.The transition to renewables not only addresses the immediate energy crisis but also aligns with broader global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and dependency on fossil fuels. Initiatives are underway to harness various forms of clean energy, including:
- Solar Energy: The vast potential for solar panel installations, especially in urban areas, can provide significant electricity generation.
- Wind Energy: The region’s geography offers suitable conditions for wind farms, capable of generating substantial electrical power.
- Biomass Utilization: Libraries of agricultural waste and organic material present a unique opportunity for biomass conversion into heating fuel.
In parallel, discussions are ongoing about establishing community-based energy projects and incentivizing private investments in renewable technologies.To support these initiatives,a collaborative approach involving local government,international partners,and private entities is essential. A table highlighting potential renewable energy projects could illustrate their capacity, estimated costs, and expected completion timelines:
| project Type | Capacity (MW) | Estimated Cost ($ million) | Expected Completion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Farm | 10 | 8 | 2024 |
| Wind Turbines | 15 | 12 | 2025 |
| Biomass Plant | 5 | 6 | 2023 |
Lessons from the Crisis: Enhancing Energy Resilience in Similar Regions
The recent energy crisis in the breakaway Moldovan region underscores the urgent need for communities reliant on external gas supplies to diversify their energy sources. To enhance resilience, regions facing similar vulnerabilities should prioritize renewable energy investments. By incorporating solar, wind, and bioenergy solutions, they can create a more sustainable energy mix. Additionally,improving energy efficiency in residential and commercial buildings can reduce overall demand,lessening reliance on imports during critical periods.
Furthermore, establishing regional energy cooperation can bolster collective security against supply disruptions. Collaborations between neighboring nations or regions can facilitate the sharing of resources and energy infrastructure, such as interconnectors and storage capacities. A strategic approach may involve:
- Investment in grid modernization to accommodate diverse energy sources.
- Implementation of demand-response programs to manage energy consumption during peak times.
- Enhancing public awareness about energy conservation practices.
Through these measures, vulnerable regions can enhance their energy resilience and safeguard against future crises, ensuring that critical services remain operational in the face of external shocks.
Closing Remarks
the cessation of Russian gas supplies marks a critical turning point for the breakaway region of Transnistria, where the decision to cut off heating and hot water services has left residents in a precarious situation. As temperatures plummet and the impact of this energy crisis becomes more palpable, local authorities face mounting pressure to find alternative solutions amidst geopolitical tensions and economic instability. The unfolding scenario serves as a stark reminder of the region’s vulnerability and the broader implications for energy security in areas reliant on external sources for essential services. As the situation develops, the focus will undoubtedly shift to both humanitarian responses and the potential for diplomatic engagements aimed at mitigating the fallout from this disruption.