The Netherlands, often characterized by its picturesque landscapes of windmills and tulip fields, is more than just a visual delight; it is a nation shaped by its unique geographical features, robust economy, and dynamic political landscape. Situated in the lowlands of Northwestern Europe, this small yet influential country has cultivated a distinctive identity marked by its rich maritime history and progressive social policies. In this article, we delve into the interplay between the Netherlands’ geography and its economic prowess, exploring how its low-lying terrain has not only influenced agricultural practices but also propelled the nation into a global trade hub. Furthermore, we will examine the political framework that has allowed the Netherlands to thrive in an increasingly complex world, highlighting its commitment to democracy, innovation, and sustainability. Join us as we explore the multifaceted character of the netherlands through the lenses of its lowlands,economy,and political system,as encapsulated in the latest insights from Britannica.
Overview of the Netherlands: A unique Geography and Cultural Landscape
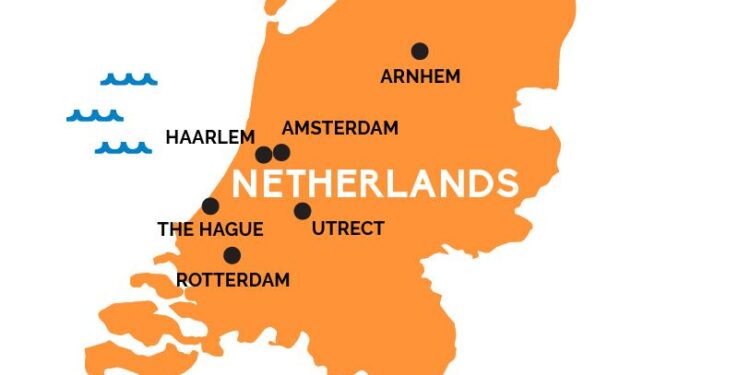
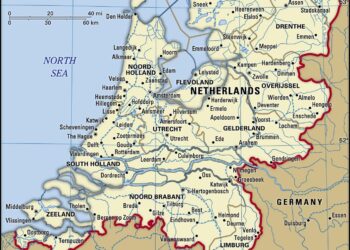
The netherlands is renowned for its distinctive geographical features that have profoundly shaped its identity and heritage. Covering an area of approximately 41,543 square kilometers, this country is famously flat, with about 26% of its land lying below sea level. A remarkable feat of engineering, an extensive network of dikes and drainage systems protects the land from flooding. The landscape is characterized by a patchwork of polders, lakes, and rivers while dotted with picturesque windmills and tulip fields, symbolizing the Dutch spirit of ingenuity and resilience. Key geographical highlights include:
- The Frisian Islands, a unique chain of islands in the Wadden Sea, known for their natural beauty and biodiversity.
- The Rhine and Meuse Rivers, crucial waterways that have historically facilitated trade and cultural exchange.
- The Delta Works, a breathtaking engineering project designed to manage the region’s water and safeguard against the North Sea.
Culture in the Netherlands is as diverse and vibrant as its landscape, steeped in rich history while embracing modern influences. The population is a blend of various ethnicities, with a significant portion of Dutch citizens originating from immigrant backgrounds, which adds to the multicultural tapestry of the nation. Artistic expressions manifest in numerous forms, from the Dutch Golden Age painting schools to contemporary art and architecture.The Netherlands is also known for its liberal policies that often spark global discussions, especially in areas such as environmental sustainability, social issues, and human rights. Prominent cultural highlights include:
- Rijksmuseum,showcasing masterpieces of Dutch art,including works by Rembrandt and Vermeer.
- Van gogh Museum, housing the largest collection of Van Gogh’s artworks.
- Annual King’s Day celebrations, fostering national pride and cultural unity.
The Lowlands of the Netherlands: Navigating Water and Land
The landscape of the Netherlands is a captivating blend of water and land, intricately woven together through a history of innovation and adaptation.The lowlands, which constitute a significant portion of the country’s geography, are characterized by their unique relationship with water. This relationship has shaped not only the physical landscape but also the socio-economic fabric of the nation. The Dutch have long been known for their advanced water management systems, including windmills, dikes, and canals, which not only protect them from flooding but also serve as vital infrastructure for transportation and trade. Key elements of this intricate system include:
- Dikes and Levees: Engineered barriers to prevent flooding.
- Canals: Serving as transport routes and aiding in irrigation.
- Polders: Reclaimed land that illustrates triumphant land management.
The economic prosperity of the Netherlands is intertwined with its low-lying geography. The fertile soil of the lowlands supports agriculture, which is a cornerstone of the national economy. This sector benefits from the abundant water supply,fostering a variety of crops that thrive in the region. Moreover,Amsterdam and Rotterdam stand as pivotal commercial hubs due to their strategic locations and robust maritime facilities. As a result, the country has developed into a major player in international trade.Below is a summary of some vital economic sectors influenced by the lowlands:
| Sector | Contribution to GDP (%) | Key Products |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | 2.5 | Dairy, Vegetables, Flowers |
| Transport & Logistics | 8.5 | Shipping, Freight Handling |
| Tourism | 10.8 | Attractions, cultural Experiences |
Economy of the Netherlands: A Stronghold of Innovation and Trade
The Netherlands boasts a robust economy characterized by its innovative spirit and strong trade networks.As one of the largest exporters in the world, the country thrives on its strategic geographical location as a gateway to Europe. Key sectors driving the Dutch economy include agriculture, technology, and energy. The nation’s agricultural sector is particularly remarkable, with advanced techniques and innovations allowing it to become a top food exporter, despite its relatively small size. This success is bolstered by strong collaboration between research institutions and businesses, fostering a continuous flow of new ideas and methodologies.
Furthermore, the Dutch economy is increasingly recognized for its commitment to sustainability and green energy. The government actively promotes startups and innovative enterprises through various initiatives,ensuring an environment conducive to technological advancement. The rise of high-tech industries, particularly in semiconductors and biotechnology, exemplifies this dedication to innovation.notably,the Netherlands’ logistics and transportation sector remains vital,with Rotterdam being one of the world’s busiest ports,facilitating extensive international trade.The interplay between these dynamic sectors underscores the Netherlands’ position as a formidable stronghold of economic prowess on the global stage.
Key Industries driving Dutch Economic Advancement
The Netherlands boasts a diverse array of industries that significantly contribute to its burgeoning economy. Central to this advancement are sectors such as agriculture, technology, and trade. With its unique geographical advantage and a highly developed infrastructure, the country excels in agricultural exports, being among the world leaders in the sector. Innovative practices and enduring farming techniques have further cemented its status, enabling it to export a remarkable variety of products, from tulips to dairy. Similarly, the tech industry is rapidly evolving, driven by a skilled workforce and robust startup ecosystem that attracts both domestic and international investment.
In addition to agriculture and technology, the logistics and creative industries play a pivotal role in enhancing the Dutch economy. With major ports like Rotterdam serving as critical gateways for international trade, the logistics sector is essential for economic growth. The creative industry, encompassing design, media, and art, not only empowers cultural expression but also significantly contributes to job creation and tourism. The interplay between these industries demonstrates the Netherlands’ strategic focus on innovation, sustainability, and global connectivity, ensuring that it remains a competitive player in the global economy.
The Role of Agriculture in the Dutch Economy: From Farming to Global Exports
In the Netherlands,agriculture plays a pivotal role in shaping the national economy,contributing significantly to both local livelihoods and international trade. The country is renowned for its innovative farming practices and advanced agricultural technologies, making it one of the world’s leading food exporters. Notably, Dutch farmers have embraced sustainability and efficiency, employing methods such as precision farming and greenhouse cultivation to maximize yields while minimizing environmental impact. This commitment to excellence has helped the Netherlands rank as the second-largest agricultural exporter globally, despite its relatively small geographical size.
the diversity of agricultural products from the Netherlands is remarkable,encompassing a wide range of produce that appeals to both local and international markets. Key exports include:
- Vegetables: Carrots,onions,and tomatoes
- Flowers and Plants: Tulips and other ornamental flora
- Dairy Products: Cheese and milk
- Meat: Pork and poultry
Table below summarizes the export figures of major agricultural products:
| product | Export Value (in billion €) |
|---|---|
| Vegetables | 2.5 |
| Flowers and Plants | 1.9 |
| Dairy Products | 6.3 |
| Meat | 4.1 |
Sustainable Economic Practices in the Netherlands: Leading by Example
The Netherlands has emerged as a global leader in sustainable economic practices, showcasing innovative approaches that prioritize both ecological integrity and economic resilience. The country’s diverse strategies include extensive investments in renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, complemented by robust policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Moreover, the Dutch government actively encourages circular economy models, where products are designed for reuse, repair, and recycling, significantly diminishing waste. This commitment is evident in urban developments that emphasize public transport, green spaces, and energy-efficient buildings.
In agriculture, the Netherlands has revolutionized its agricultural model to enhance sustainability, becoming one of the world’s first countries to integrate high-tech solutions with traditional farming methods. For example, precision farming techniques utilize data analytics and IoT systems to optimize resource use, significantly lowering the carbon footprint of food production. Key practices also include:
- Vertical Farming: Maximizing space and minimizing resource consumption.
- Organic Farming: Promoting biodiversity and healthier food systems.
- agroecology: Enhancing soil health through natural farming techniques.
The following table illustrates the transitions in sustainable practices across various sectors in the Netherlands:
| Sector | Initiative | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| energy | Wind and Solar Investments | Increased renewable share in energy mix by 50% |
| Agriculture | precision Farming | Resource use efficiency increased by 30% |
| Waste Management | Circular Economy Policies | Waste reduced by 40% within urban areas |
Political Landscape of the Netherlands: A Constitutional Monarchy in Action
The political landscape of the Netherlands is characterized by its unique system as a constitutional monarchy, where the monarchy coexists harmoniously with a parliamentary democracy. The King, currently king willem-Alexander, serves primarily ceremonial functions, while actual governance is in the hands of elected officials. The Prime Minister, originating from the majority party or coalition in the Tweede Kamer (House of Representatives), leads the executive branch and orchestrates the country’s domestic and foreign policies.The Netherlands employs a system of proportional representation, which ensures a multiparty framework, often leading to coalition governments that reflect a wide spectrum of voter preferences. Key political parties include:
- People’s Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD)
- Labor Party (PvdA)
- GreenLeft (GroenLinks)
- Party for Freedom (PVV)
this intricate relationship between the monarchy and the government manifests through various official functions and state ceremonies, emphasizing the unity of the Dutch state. Legislative processes operate through a bicameral system comprised of the Eerste Kamer (Senate) and the Tweede Kamer. This structure allows for thorough examination and debate of proposed laws, ensuring comprehensive representations of citizens’ interests. the political environment is also influenced by pressing issues such as climate change, immigration, and economic stability, shaping party platforms and governmental priorities. The following table highlights the current major political parties and their foundational principles:
| Political Party | Foundation Year | Core Principles |
|---|---|---|
| VVD | 1948 | Liberalism, Economic Growth |
| PvdA | 1946 | Social democracy, Equality |
| GroenLinks | 1990 | Green Politics, Sustainability |
| PVV | 2006 | Nationalism, Immigration Control |
The Role of Political Parties in Shaping Dutch Governance
Political parties in the Netherlands play a pivotal role in shaping governance and influencing policy decisions, reflecting the diverse interests of the Dutch populace. with a multi-party system, the country’s political landscape is marked by a variety of parties that span the ideological spectrum, including liberals, socialists, Christian democrats, and green parties. This diversity facilitates a dynamic political dialogue and promotes the principle of consensus-building, where parties frequently enough collaborate to form coalitions in a parliamentary system. As these coalitions govern, the interplay among parties can lead to comprehensive policies that accommodate a wide range of views and priorities, ultimately fostering stability within a coalition framework.
The proportional representation electoral system encourages smaller parties to enter the political arena, thereby enhancing citizen representation in governance.As a result, the composition of the dutch Parliament, or Tweede kamer, is ever-changing, often reflecting the immediate social and economic concerns of the electorate. Notably, parties like the party for Freedom (PVV) and the Green Left (GroenLinks) have gained traction by emphasizing themes such as immigration and environmental sustainability, respectively. This phenomenon is underscored by the following table, illustrating the recent distribution of parliamentary seats among major parties:
| Political Party | Seats in Tweede Kamer | % of Total Seats |
|---|---|---|
| People’s Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) | 35 | 21.4% |
| Labour Party (PvdA) | 27 | 16.5% |
| party for Freedom (PVV) | 17 | 10.5% |
| Green Left (GroenLinks) | 17 | 10.5% |
| Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) | 15 | 9.2% |
Social Policies and Welfare Systems in the Netherlands: A Model for Inclusivity
The Netherlands stands as a beacon of inclusivity through its comprehensive social policies and welfare systems, designed to promote equality and support vulnerable groups. Central to this approach is a robust framework that encompasses various areas, including education, health care, and unemployment support. The emphasis on social justice influences policies aimed at alleviating poverty and ensuring access to essential services,fostering a culture where both individuals and families can thrive. Key components include:
- Universal Health Care: Providing all citizens access to necessary medical services,significantly reducing health disparities.
- Generous Parental Leave: Allowing new parents to balance work and family responsibilities effectively.
- Unemployment Benefits: Offering financial support that helps workers transition during job loss.
Additionally, the Dutch welfare state focuses on active labor market policies, which aim to integrate job seekers into the workforce through training and education programs.this is complemented by inclusive housing policies that address the needs of low-income residents, ensuring secure living conditions. Notably, the government collaborates closely with local municipalities to tailor social services, making them more responsive to community-specific needs. This decentralized approach contributes to greater effectiveness and strengthens social cohesion across diverse populations, resulting in a model that can be emulated globally.
| Policy Area | Key Feature | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Health Care | Universal Access | reduces health inequalities |
| Parental Leave | Extended Duration | Encourages work-life balance |
| Employment | Training Programs | Facilitates job market integration |
Urban and Regional Development: Tackling Housing Shortages in Dutch Cities
As Dutch cities face escalating housing shortages, stakeholders from various sectors are increasingly recognizing the necessity of innovative policy interventions and collaborative efforts. The challenges stem from ambitious urbanization,where demand significantly outpaces supply,leading to soaring rents and inadequate living conditions for many residents. To address these pressing issues,cities like Amsterdam,Rotterdam,and Utrecht have begun implementing more inclusive zoning laws that facilitate higher-density housing developments,as well as prioritizing affordable housing units in new projects. Factors contributing to the crisis include:
- Population Growth: An influx of individuals seeking urban living has intensified competition for housing.
- Economic Disparities: Rising property prices have disproportionately affected lower-income families and young professionals.
- Regulatory Challenges: Complex planning protocols often delay construction efforts.
Local governments are exploring innovative solutions, such as the promotion of sustainable building practices and the conversion of vacant commercial spaces into residential units. Partnerships with private developers have also become increasingly vital, enabling municipalities to leverage financial resources and expertise for large-scale projects. Moreover, initiatives that encourage communal living and co-housing are gaining traction, appealing to those who seek option lifestyles without compromising affordability. The table below highlights some notable housing projects currently underway in major Dutch cities:
| City | project Name | Type of Housing | Completion Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amsterdam | Bouwen in de Bijlmer | Mixed-use development | 2024 |
| Rotterdam | Woonboulevard | Affordable apartments | 2023 |
| Utrecht | Zuylenstede | Sustainable co-housing | 2025 |
Public Transport and Infrastructure: The Netherlands as a Model of Efficiency
The Netherlands stands as a forerunner in effective public transport and infrastructure systems, demonstrating how a well-integrated approach can boost economic growth and civic satisfaction. The country’s extensive network of trains, trams, buses, and boats ensures seamless connectivity across urban and rural areas. Key features include:
- High-frequency train services: Intercity trains operate with remarkable punctuality, making long-distance travel efficient.
- Innovative ticketing systems: The OV-chipkaart system simplifies fare payments across diffrent transport modes.
- Bicycle-kind infrastructure: bike lanes and rental systems encourage eco-friendly transport, easing congestion in cities.
- Investment in sustainable transport: The government prioritizes green technologies and electric public transport options.
along with public transport, the Netherlands excels in creating robust infrastructure that supports economic activities. The strategic location between major European markets facilitates trade, while the following initiatives bolster its infrastructural framework:
| Infrastructure Element | Impact |
|---|---|
| Ports | Amsterdam and Rotterdam are among the largest and busiest ports in Europe, vital for maritime trade. |
| Canals | The extensive canal system supports tourism and freight transport while showcasing the nation’s unique history. |
| Road Networks | A comprehensive road system connects major cities and regions, enabling efficient logistics and travel. |
Environmental Policies and Climate change Initiatives in the Netherlands
The Netherlands is renowned for its proactive approach to environmental policies and climate change initiatives, standing as a global leader in sustainability. The nation’s commitment is deeply embedded in its political framework, where climate governance incorporates ambitious targets aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions significantly. By 2030, the goal is to cut emissions by 49% compared to 1990 levels, with an even more ambitious aim to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. Key strategies driving this agenda include the transition to renewable energy, investments in energy efficiency, and the promotion of sustainable agriculture practices.
To facilitate these efforts, the Dutch government has implemented a range of comprehensive measures, including:
- Wind and Solar Energy Initiatives: Promotion of both onshore and offshore wind farms along with solar panel incentives for residential and commercial buildings.
- Circular Economy Policies: Encouragement of recycling and reuse of resources to minimize waste generation.
- Urban Mobility Plans: Investment in public transport and cycling infrastructure to reduce dependency on fossil fuel vehicles.
- International Collaboration: Active participation in european Union climate initiatives and global environmental accords.
| Year | Target Emission Reduction | Progress Status |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 25% from 1990 | Achieved |
| 2030 | 49% from 1990 | On Track |
| 2050 | Carbon Neutrality | Ongoing Efforts |
The Impact of European Union Membership on the Netherlands’ Economy and Politics
The economic landscape of the netherlands has significantly evolved since its accession to the European Union in 1994. the country’s strategic location as a trading hub benefited from the EU’s single market,which facilitated the free movement of goods,services,and capital. Consequently, the Netherlands has experienced enhanced trade opportunities, evidenced by a remarkable increase in export volumes. Key economic impacts include:
- Boost in Trade: The Netherlands has established itself as one of the largest exporters in Europe, leveraging its advanced logistics and transportation networks.
- Investment Flows: Foreign direct investment has surged,with multinational corporations setting up their European headquarters in the Netherlands,drawn by favorable tax regimes.
- Employment Growth: The integration into the EU market contributed to job creation, particularly in sectors such as technology, agriculture, and finance.
politically, the Netherlands has navigated its EU membership with a dual focus on national interests and collective European goals. the country’s commitment to EU policies has reinforced its position as a proponent of economic stability and environmental sustainability. However, this has not come without challenges, as domestic political debates often center around issues such as:
- Sovereignty Concerns: Discussions about the extent of EU influence on national legislation have stirred public sentiment and political discourse.
- Immigration Policies: The flow of migrants has led to significant political discussions, shaping national policy and affecting party platforms.
- Financial Contributions: The financial commitments to the EU budget have sparked debates about the return on investment for the Dutch taxpayer.
Future Challenges for the Netherlands: Balancing Growth and Sustainability
The Netherlands is at a critical juncture where economic ambitions must be harmonized with sustainable practices. As one of the leading economies in Europe, the country faces a series of pressing challenges that demand innovative solutions. Key concerns include:
- Climate change Impact: Rising sea levels and increased flooding threaten the low-lying infrastructure.
- Resource Management: Striking a balance between agricultural output and biodiversity conservation is crucial.
- Energy Transition: Moving towards renewable energy sources while reducing dependency on fossil fuels is imperative.
To tackle these issues effectively, collaboration among stakeholders—government, businesses, and civil society—is essential. The future landscape will likely see:
- investment in Green Technologies: The shift towards circular economies will necessitate significant funding in technology that minimizes waste.
- Urban Planning innovations: cities will need adaptive measures to integrate green spaces, enhancing livability while promoting sustainability.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Leverages the Netherlands’ strong agricultural sector to lead in sustainable practices that enhance food security without compromising ecosystems.
Recommendations for Strengthening the dutch Economy and Political Stability
To bolster the Dutch economy, it is crucial to foster innovation and sustain the country’s historical strengths in trade and technology. emphasizing the development of startups and supporting small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can drive job creation and economic resilience. Key recommendations include:
- Enhancing Technology Investments: Encourage public-private partnerships in sectors like renewable energy, AI, and biotechnology.
- Strengthening Education and Skills training: Invest in STEM education to prepare the workforce for a rapidly evolving economy.
- Promoting Sustainable Practices: Implement policies that reward companies for reducing their carbon footprints.
Along with economic measures, political stability remains paramount for the Netherlands’ future. Building trust in public institutions and promoting civic engagement can create a more resilient political landscape. Recommended actions include:
- Increasing Transparency: Ensure government accountability through open data initiatives and regular civic forums.
- Encouraging Political Participation: Support grassroots movements and initiatives that enable citizen dialogue with policymakers.
- Bolstering Diplomatic Relations: Strengthen alliances with EU partners to enhance regional cooperation and security.
Future Outlook
the Netherlands remains a remarkable case study in balancing its unique geographical challenges with robust economic strategies and progressive political frameworks. as a nation defined by its lowland terrain, the dutch have not only mastered the art of water management but have also leveraged their geographical position to cultivate a dynamic trade-based economy. Furthermore, the Netherlands’ political landscape showcases a commitment to inclusive governance and social progress, epitomizing democratic values in a modern context. Looking ahead, the interplay between sustainable development, economic resilience, and political stability will be crucial as the country navigates the complexities of a rapidly changing global environment. With its rich history and innovative spirit, the Netherlands continues to play a pivotal role on the world stage, embodying the strength of adaptation and forward-thinking in addressing both local and global challenges.