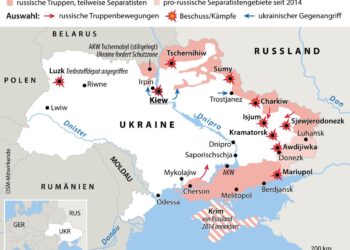
In a notable growth amid ongoing tensions in Eastern Europe, Russian President Vladimir Putin has proposed a controversial shift in the governance of Ukraine, suggesting that the nation should be placed under a UN-sponsored external administration. This assertion, made during a recent address, raises crucial questions about the future of Ukrainian sovereignty and the international community’s role in addressing the protracted conflict between Russia and Ukraine.The proposal underscores a critical intersection of geopolitics, international law, and the complex dynamics of post-Soviet relations, inviting scrutiny from world leaders and analysts alike. As the situation evolves, the implications of such governance for Ukraine’s political landscape, economy, and its citizens’ rights remain to be seen, intensifying the urgency for dialog among global powers.
Putin’s Proposal: A Shift in Ukraine’s Governance Landscape
In a surprising turn of events, President Vladimir Putin has put forth a proposal suggesting that Ukraine be placed under a framework of UN-sponsored external governance. This unprecedented idea raises significant questions regarding the sovereignty of Ukraine and the customary paradigm of international intervention. Supporters argue that such governance could stabilize the region, restore order, and pave the way for humanitarian aid and economic recovery.Critically, however, the concept is fraught with implications for Ukrainian autonomy and national identity, evoking historical memories of past interventions.
as discussions unfold, key stakeholders are delineating their positions on this shift. Major points of contention include:
- Legitimacy: Concerns over Ukraine’s right to self-governance.
- Implementation: Questions about the effectiveness of a UN-backed administration.
- International Reactions: The response of Western nations and organizations.
Additionally, a
| Aspect | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Economic Policy | Centralized control may hinder local entrepreneurship. |
| Security Measures | Increased foreign military presence could escalate tensions. |
| Humanitarian Aid | Potential for improved coordination but risks of politicization. |
Understanding UN-Sponsored External governance in Conflict Zones
The concept of UN-sponsored external governance has emerged as a potential solution for managing conflict zones, especially where traditional state structures have collapsed or failed. This governance model aims to restore stability and peace through the intervention of international bodies that provide oversight and administration. Key features of such governance include:
- Neutral Oversight: The UN acts as an impartial party to ensure fair governance and address local grievances.
- Humanitarian Aid Coordination: Effective management of humanitarian efforts to address the immediate needs of affected populations.
- Capacity Building: Initiatives to strengthen local governance and institutions that might potentially be weakened by conflict.
Implementing external governance can be contentious and complex, often raising questions about sovereignty and self-determination. While it may provide immediate relief and stability, the long-term success of this approach relies on various factors, including:
- Local Involvement: Engaging local leaders and communities to ensure that governance reflects their needs and perspectives.
- International Will: The commitment from major powers and international organizations to support the governance framework.
- Exit Strategy: Clear plans for transitioning from external governance to self-rule,preventing prolonged dependency.
| Pros of External Governance | Cons of External Governance |
|---|---|
| provides stability in a crisis | May infringe on national sovereignty |
| Facilitates international aid | Could create dependency on foreign intervention |
| Helps build local capacities | Potential for cultural insensitivity or alienation |
the legal Implications of External Governance for Ukraine
The proposal for Ukraine to be placed under UN-sponsored external governance introduces a complex web of legal implications,both domestically and internationally. Such a move could challenge Ukraine’s sovereignty and self-determination, key principles enshrined in international law. While the UN may aim to restore order and provide humanitarian support, the legitimacy of external governance hinges on several critical factors:
- Consent of the Ukrainian Government: For any external governance to be considered lawful, it must ideally be based on a formal agreement with Ukraine’s current government.
- International Law Compliance: The move must comply with international treaties and conventions, particularly those governing human rights and state sovereignty.
- Recognition by Global Powers: The support or opposition of major powers would play a significant role in determining the feasibility and acceptance of such governance.
In practical terms, the restructuring of governance could lead to significant legal challenges, particularly in defining the roles and responsibilities of the international bodies involved. Should external governance be instituted, potential issues may arise, including:
| Potential Legal Challenges | Implications |
|---|---|
| Legitimacy of Authority | Questions regarding which laws are applicable and who has the final word in legal disputes. |
| Protection of Human Rights | The need to maintain or enhance human rights standards amidst external control. |
| Economic Governance | Issues related to the management and allocation of resources under international oversight. |
International Reactions to Putin’s Suggestion on Ukraine
Reactions to Vladimir Putin’s suggestion of placing Ukraine under UN-sponsored external governance have been sharply divided across the international community. Many Western leaders have condemned the proposal, viewing it as yet another attempt by Russia to undermine Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity. Officials from countries such as the United States and members of the european Union have characterized the move as a blatant disregard for international law,asserting that any such governance must be based on Ukraine’s consent and the principles of self-determination. The European Commission President stated that “this proposal runs counter to the vital tenets of democracy” and encouraged a diplomatic solution that respects Ukraine’s autonomy.
Conversely, some nations have expressed a more nuanced outlook. Countries with closer ties to Russia, such as those in Central Asia and certain African nations, have shown a willingness to support discussions surrounding external governance on humanitarian grounds. They argue that a temporary international oversight might stabilize the region and facilitate humanitarian aid efforts amid ongoing conflicts. This divergence highlights a growing geopolitical rift, as illustrated in the table below:
| Region | Support for Proposal | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Western Nations | No | Violation of sovereignty |
| Central Asia | Conditional Support | Stability and humanitarian aid |
| African Nations | Mixed | Focus on development |
Exploring the Potential Benefits and Risks of External Governance
The concept of external governance, particularly in conflict zones like Ukraine, sparks a complex debate about its potential to stabilize politically and socially unstable regions. Proponents argue that introducing international oversight could ensure adherence to human rights standards and facilitate reconstruction efforts. with an unbiased entity overseeing governance, it might cultivate trust among the local populace, providing a mechanism for conflict resolution and peacebuilding. Some possible benefits include:
- Enhanced Security: A neutral party could create a safer habitat for civilians.
- Political Stability: External governance may help establish a transparent political framework.
- Economic Aid: An internationally sanctioned government could attract foreign investment and aid, essential for recovery.
Conversely, there are considerable risks associated with external governance. The intrusion of foreign entities might be perceived as a violation of sovereignty, leading to resentment or resistance among local populations. Furthermore, the effectiveness of such governance greatly depends on the commitment and integrity of the international overseeing body.Challenges may include:
- Cultural misunderstandings: outside governance might misinterpret local customs and needs.
- Dependency Issues: Prolonged external control could stifle local governance initiatives.
- Potential for Corruption: Mismanagement or corruption by external actors can exacerbate existing issues.
Historical Precedents: UN Administration in Post-Conflict Regions
The concept of UN administration in post-conflict regions has its roots in several notable historical precedents,which have shaped international approaches to governance in the aftermath of warfare.Notable examples include:
- East Timor (1999-2002): Following a violent struggle for independence from Indonesia, the UN established the United Nations Transitional Administration in East Timor (UNTAET) to oversee the territory until the establishment of an autonomous government.
- bosnia and Herzegovina (1995-2002): Following the Bosnian War, the UN and NATO played pivotal roles in stabilizing the region and facilitating democratic governance through the Office of the High Representative.
- Kosovo (1999-present): After the NATO bombing campaign,the UN implemented the United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK),which aimed to provide a temporary governance framework and promote a democratic society.
These examples illustrate the complexities and challenges of transitioning to stable governance in regions emerging from conflict. Partial approaches often emphasized the need for international support in various aspects,including:
| Focus Area | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Security | Deployment of peacekeeping forces to maintain order |
| Politics | Facilitation of elections and formation of local governments |
| Economy | International aid and investment to rebuild infrastructure |
Understanding these historical frameworks is crucial in the context of recent proposals,such as external governance for Ukraine,as they highlight both the potential for resolution and the pitfalls of international intervention.
Assessing the Feasibility of Implementing External Governance in Ukraine
The suggestion of placing Ukraine under UN-sponsored external governance, as voiced by President Putin, raises complex questions regarding political stability, national sovereignty, and international law. it prompts a critical evaluation of whether such a governance structure could be feasible and beneficial for the war-torn nation. To consider this possibility, several factors must be evaluated:
- International Support: Any external governance plan would require significant backing from major global powers and organizations to gain legitimacy.
- Local Reception: The acceptance of such governance by the Ukrainian populace, many of whom prioritize sovereignty, would be vital for its success.
- Governance Framework: A clear framework outlining the powers, responsibilities, and duration of external governance would be necessary to avoid chaos.
- Implementation Challenges: The practicalities of integrating an external administration into Ukraine’s existing structures would pose significant challenges.
Even though the idea of external governance might provide a pathway to stabilize the region, the nuances of implementation cannot be overlooked. The following table summarizes potential benefits and drawbacks of this approach:
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Increased international oversight | Possible loss of sovereignty |
| Opportunities for peace negotiations | Resistance from local factions |
| Reconstruction aid and support | Administrative complexities |
| Enhanced security presence | Dependency on foreign powers |
The Role of the International Community in Supporting or Opposing the Proposal
The suggestion to place Ukraine under a UN-sponsored external governance framework has stirred mixed reactions within the international community.Supporters of the proposal argue that it could provide a neutral mechanism to stabilize the region, facilitating peace talks and rebuilding efforts. Concrete arguments in favor include:
- Humanitarian Assistance: A governance model could streamline international aid to address urgent humanitarian needs.
- Security Assurance: UN oversight may alleviate fears regarding military escalation in the region.
- Political Neutrality: International governance could minimize the influence of national politics and promote a neutral ground for negotiations.
Conversely, a significant segment of the international community firmly opposes this initiative, viewing it as an encroachment on Ukrainian sovereignty. Critics fear that such a proposal may set a hazardous precedent for international intervention in domestic affairs. Key points of contention include:
- Sovereignty Concerns: many believe Ukraine should dictate its own governance without external imposition.
- Potential for Conflict: Critics warn that external governance could provoke resistance among the Ukrainian populace, leading to further unrest.
- political Implications: Opponents argue that this move could undermine established diplomatic efforts and prolong instability.
Strategic Recommendations for Ukraine’s Future Governance
Amid the ongoing discussions regarding Ukraine’s future governance, it is indeed crucial to consider strategic recommendations that align with the aspirations and needs of the Ukrainian population. Building a resilient governance structure requires emphasizing local autonomy while ensuring national cohesion. This can be achieved by empowering local governments through legislation that enhances their decision-making capacities and resource allocations. Additionally, the integration of civic engagement initiatives will facilitate greater transparency and accountability, allowing citizens to actively participate in governance processes. Fostering a collaborative environment between government and civil society organizations will further strengthen trust and legitimacy in the political system.
In terms of external oversight or support, Ukraine might benefit from establishing strategic partnerships with international bodies and regional allies. These partnerships can focus on areas such as economic development, security cooperation, and democratic governance practices. Collaborating with entities like the European Union and NATO could offer frameworks for modernization and reform,ultimately leading to the establishment of a more resilient state.Below is a summary of essential areas for cooperation:
| Focus Area | Potential Collaborators | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Development | EU, World Bank | Investment and job creation |
| Security Enhancements | NATO | Increased defense capabilities |
| Judicial Reforms | OSCE, EU | Strengthened rule of law |
The Impact of External Governance on Ukraine’s Sovereignty and Territorial Integrity
The proposal to establish a UN-sponsored external governance for Ukraine raises significant concerns regarding the nation’s sovereignty and territorial integrity. historically, external governance has been used in various parts of the world, frequently enough with mixed results. In Ukraine’s case,some potential implications include:
- Loss of Autonomy: External governance may limit Ukraine’s ability to make independent political and economic decisions,thus undermining its sovereignty.
- Influence of Foreign Powers: The presence of external governance may open channels for undue influence by other nations or organizations, complicating Ukraine’s geopolitical landscape.
- Societal Divisions: Implementing external control could exacerbate existing societal and regional tensions, perhaps leading to further instability.
moreover, the legitimacy of this governance mechanism may come under scrutiny. Should such governance be enforced,it would necessitate careful monitoring to ensure that it aligns with Ukraine’s aspirations for self-determination. A pertinent consideration is how this framework could affect international perceptions and relations. The following table outlines key aspects of external governance models that have been attempted elsewhere:
| Model | Pros | cons |
|---|---|---|
| Trusteeship | Restores stability | Limited self-governance |
| Interim Administration | Facilitates peacekeeping | Dependency on foreign intervention |
| International Oversight | Ensures human rights protection | Potential disputes over authority |
Public Opinion in ukraine: Support and Opposition to External Governance
recent revelations surrounding proposals for external governance in Ukraine have spurred intense debate among the populace. A sizable portion of the Ukrainian population perceives the idea, suggested by russian President Vladimir Putin, as a significant threat to the nation’s sovereignty and self-determination. Many citizens express a strong desire for Ukraine to forge its own path without foreign interference, highlighting key points of resistance such as:
- Historical Context: Years of conflict have fostered a deep sense of nationalism.
- Political Agency: A push for domestic leadership that reflects the will of the people.
- Geopolitical Consequences: Concerns over the implications for Ukraine’s standing in the international community.
On the other hand, there exists a segment of the population that views external governance as a necessary mechanism to restore stability amidst ongoing turmoil.Advocates for this perspective argue that an international presence could provide:
- Security Guarantees: Potential protection against further aggression.
- Reform Implementation: Assistance in implementing vital political and economic reforms.
- Humanitarian Aid: Enhanced support and relief for civilians affected by the conflict.
| Support Perspectives | Opposition Perspectives |
|---|---|
| Stability and Security | risk of Loss of Sovereignty |
| International Support | Unwanted Foreign Influence |
| Reform Assistance | Internal Leadership Preference |
Long-Term Consequences: Stability, Security, and Reconstruction in Ukraine
The suggestion of placing Ukraine under UN-sponsored external governance has reignited discussions about the long-term stability and security of the nation. While some argue that international oversight could provide a temporary buffer against further aggression, others caution that such a move might undermine ukraine’s sovereignty and self-determination. The potential for external management raises critical concerns about the effectiveness and legitimacy of governance structures imposed from outside, especially in a region marked by complex historical grievances and ethnic divisions. The balance between maintaining stability and respecting national autonomy is delicate, and any governance framework must ensure broad societal buy-in to avoid further alienation of the Ukrainian populace.
Reconstruction efforts following the conflict are essential for Ukraine’s path towards stability, but they must be strategically aligned with any proposed governance model. Key factors to consider include:
- Infrastructure Restoration: Rebuilding critical infrastructure with a focus on resilience and modernity.
- economic Revitalization: Implementing policies that foster investment,support local businesses,and stimulate job creation.
- Social Cohesion: Promoting programs that bridge ethnic and political divides to foster unity.
- International Support: Securing ongoing support from global partners to finance and oversee reconstruction efforts.
| Area of Focus | Priority Actions |
|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Assess and rebuild key facilities |
| Economy | Introduce incentives for investment |
| Social Services | Enhance healthcare and education access |
In navigating this complex landscape, Ukraine’s long-term success may hinge on the careful integration of external support with internal governance frameworks that resonate with the aspirations of its citizens. The international community must tread cautiously, ensuring that any governance model promotes not only stability but also the long-lasting security that Ukrainian citizens desire and deserve.
Engaging with civil Society: Including Ukrainian Voices in Governance Decisions
In light of recent statements from Russian President Vladimir Putin regarding the potential for Ukrainian governance to be placed under United Nations authority, a critical dialogue surrounding the inclusion of Ukrainian voices in future governance decisions emerges. Civil society organizations within ukraine, alongside grassroots movements, have long articulated the necessity of integrating local perspectives and ensuring that any externally imposed frameworks respect the sovereignty and aspirations of the Ukrainian people. There is a palpable concern that international interventions may inadvertently sideline those who are directly affected by these governance changes.
Engagement with civil society can take various forms, encompassing diverse stakeholders such as NGOs, community leaders, and activist groups. To foster effective dialogue and decision-making, the following strategies could be employed:
- Facilitated forums for inclusive discussions where Ukrainian voices can articulate their needs and priorities.
- Partnerships with international organizations to ensure a holistic approach to governance that acknowledges local insights.
- Regular consultations with local communities to keep governance frameworks dynamic and reflective of real-time challenges.
| Stakeholder Group | Role in Governance |
|---|---|
| Local NGOs | Advocacy and community engagement |
| Grassroots Movements | Empowering citizen participation |
| Academics and Think Tanks | Research and policy analysis |
| International Observers | Monitoring and support |
Potential Scenarios: What If Ukraine Embraces UN-Sponsored governance?
The suggestion of placing Ukraine under UN-sponsored governance raises a multitude of potential outcomes that could reshape the nation’s political landscape. Firstly, such a governance model could provide a structured environment for peace negotiations, potentially leading to stabilization in the region. With international oversight,Ukraine might benefit from a neutral platform for dialogue,allowing conflicting interests to find common ground. Moreover, resources from UN agencies could be channeled into rebuilding infrastructure, bolstering economic recovery, and addressing pressing humanitarian issues, creating a more resilient state in the long run.
Though, the implications of UN governance could also introduce significant challenges. Potential scenarios include:
- Criticism over sovereignty issues: Many Ukrainians may view UN oversight as an infringement on national independence.
- Power struggles between Ukrainian officials and UN representatives could foster political instability.
- __Delays in governance and decision-making may arise due to bureaucratic processes, hindering urgent action on critical matters.
In navigating these complexities, the international community would need to find a delicate balance between support and autonomy, ensuring that policies foster genuine progress while respecting Ukraine’s right to self-determination.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Ukraine Through External Governance
The proposal for UN-sponsored external governance over Ukraine raises significant questions about the future of the nation and its sovereignty. Such a move, suggested by Putin, could be seen as a double-edged sword: on one side, potential international oversight might stabilize a country ravaged by conflict, while on the other, it risks undermining Ukraine’s self-determination and identity.As we navigate this complex landscape,it is crucial to consider the implications of external governance on the political,economic,and social fabric of Ukraine.
Key factors that will play a role in determining the viability and effectiveness of this governance model include:
- International Support: The levels of backing from global powers and institutions will heavily influence the legitimacy and success of any governance efforts.
- Local Engagement: For any external governance model to thrive,the involvement and acceptance of the Ukrainian populace are paramount.
- Security Concerns: The ongoing threat of military conflict necessitates robust security measures that an external body must address.
To better understand these dynamics, consider the table below, which summarizes potential outcomes of external governance:
| Outcome | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Stabilization | Reduction in violence | Perceived loss of sovereignty |
| Economic recovery | Access to international aid | Dependency on foreign support |
| International Perception | increased legitimacy | Criticism of autonomy |
ultimately, the path forward for Ukraine under any form of external governance necessitates careful deliberation, balancing the need for support and oversight with the invaluable aspects of independence and self-governance.
To Conclude
President Vladimir Putin’s recent suggestion to place ukraine under UN-sponsored external governance marks a significant pivot in the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine, raising critical questions about sovereignty, international law, and the future of Ukrainian national identity. As global stakeholders respond to this proposal, the implications for diplomatic relations, peace negotiations, and the broader geopolitical landscape remain unclear. This development underscores the pressing need for a coordinated international approach to address the multifaceted challenges posed by the war, while emphasizing the necessity of prioritizing the Ukrainian people’s voice in any governance discussions. As this situation continues to evolve, it will be essential to monitor how both Western and Eastern powers react to Putin’s proposition and what it might mean for the region’s stability moving forward.