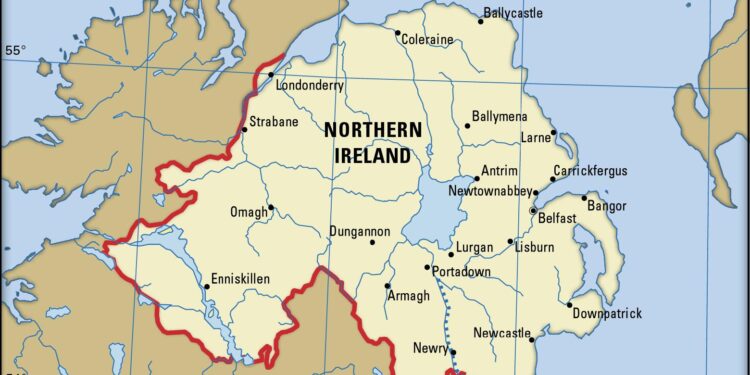
In the tumultuous aftermath of Brexit, Northern Ireland finds itself navigating a complex web of political and economic challenges, uniquely positioned between the European Union and the United Kingdom. The intricate arrangement known as the Northern Ireland Protocol, designed to prevent a hard border with the Republic of Ireland, has inadvertently introduced a new layer of uncertainty concerning tariffs and trade regulations that impact businesses and consumers alike. As Northern Ireland grapples with the fallout from these changes,questions loom over its economic stability and future relationship with both the EU and the UK. This article delves into the implications of the ongoing tariff uncertainties facing Northern Irish businesses, the concerns of local policymakers, and the broader consequences for a region already marked by ancient complexities.
Impact of Brexit on Northern Ireland’s Trade Dynamics
The trade landscape in Northern Ireland has become increasingly complex in the wake of Brexit, presenting unique challenges and opportunities for businesses on both sides of the border. With the establishment of the Northern Ireland Protocol, the region finds itself in a peculiar position where it is subject to EU customs regulations while still being part of the UK trading framework. This duality has resulted in a myriad of tariff implications and regulatory hurdles for companies seeking to navigate cross-border trade. As a outcome, many Northern Irish businesses have had to adapt their supply chains, often facing increased transportation costs, documentation requirements, and potential delays in goods movement.
To illustrate the shifting trade dynamics, here are some key factors affecting Northern ireland’s trade:
- Increased Tariffs: Goods moving from great Britain to Northern Ireland may incur additional tariffs, complicating pricing strategies and competitiveness.
- Regulatory Divergence: Businesses face a complex patchwork of regulations, as EU standards must be adhered to while also complying with UK laws.
- Market Access: The unique position of northern Ireland as both part of the UK and the EU enables access to two different markets,albeit with complications.
| trade Effects | Implications |
|---|---|
| New Tariff Structures | Potentially higher costs for imported goods from Great Britain. |
| Border Checks | Increased delays and operational challenges for businesses. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Need for businesses to adapt to dual regulatory requirements. |
Understanding the Role of the Northern Ireland Protocol
The Northern Ireland Protocol was established to address the complexities arising from Brexit, particularly concerning the border between Northern Ireland and the Republic of ireland. This agreement effectively creates a dual regulatory framework where Northern Ireland continues to follow EU customs rules while remaining part of the UK’s customs territory. As a result, goods moving from Great Britain to Northern Ireland are subject to inspections and potentially tariffs, depending on their final destination, creating a unique logistical challenge for businesses operating in the region. The protocol aims to prevent a hard border on the island of Ireland, which has been a significant concern since the good Friday Agreement.
Business leaders and stakeholders in Northern Ireland now face an atmosphere of uncertainty as they navigate the implications of the protocol. With regulations evolving and the potential for adjustments in tariffs and trade rules, companies must adapt quickly to ensure compliance and maintain their competitive edge. Factors contributing to this uncertainty include:
- Variable Tariff Rates: Goods imported from Great Britain could incur tariffs depending on their end use in Northern Ireland.
- Compliance Costs: Businesses may incur additional costs associated with custom checks and regulatory compliance.
- Market Fluctuations: Changes in trade relationships and tariffs can impact supply chain costs and consumer prices.
This dual system has created an environment where companies must remain vigilant,stay informed about changes,and adjust their strategies constantly to mitigate risks associated with the protocol.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Customs Regulations | Goods from GB may face tariffs when entering NI. |
| Business Adaptability | Companies must adjust to changing compliance requirements. |
| Trade Relations | Potential for fluctuating relationships with EU and UK markets. |
Tariff Implications for Businesses in the Region
The ongoing tariff implications for businesses operating in Northern Ireland create a challenging landscape, as they navigate the delicate balance between the EU and U.K. regulatory environments. The post-Brexit reality introduces complexities such as customs checks and potential tariff liabilities that can lead to increased operational costs. This dual regulatory framework not only complicates trade routes but also puts small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) at a disadvantage compared to larger corporations that can absorb fluctuations in import and export costs.
To further illustrate the impact on various sectors,consider the following key points affecting businesses:
- increased Compliance Costs: Companies must invest in compliance measures to meet both EU and U.K. standards.
- supply Chain Disruptions: Potential tariffs can disrupt established supply chains, leading to delays and increased prices.
- Market Access Challenges: Businesses may find it difficult to access EU markets due to new tariffs, affecting competitiveness.
| Sector | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Higher tariffs on exports to the EU could reduce profit margins. |
| Manufacturing | Increased costs for raw materials due to tariffs on imports. |
| Retail | Consumer prices may rise as additional costs are passed on. |
Challenges for Cross-Border trade with the Republic of Ireland
The complexities of cross-border trade between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland have intensified, particularly in the wake of Brexit. Businesses operating in this region are grappling with a myriad of regulatory and logistical challenges that complicate trade movements. Among the primary concerns are:
- Customs checks: Increased inspections and documentation can lead to delays.
- Tariff classifications: Goods moving across the border may incur tariffs that differ based on their treatment under EU and UK regulations.
- Market fluctuations: Uncertainty around tariffs can deter investments and planning for long-term business strategies.
Moreover, the reliance on digital solutions to streamline cross-border transactions is weighed down by inconsistent technology implementations across customs agencies. This results in additional administrative burdens for traders. Key issues include:
- Regulatory divergence: Businesses need to stay abreast of differing rules in the EU and UK that can be subject to frequent change.
- Supply chain disruptions: The potential for delays at customs could lead to higher inventory costs and risk of spoilage for perishable goods.
- Legal ambiguities: Confusion regarding compliance and enforcement can lead to disputes and penalties.
Economic Consequences of Tariff Uncertainty in Northern Ireland
The economic landscape of Northern Ireland has become increasingly complex due to tariff uncertainty resulting from its unique position between the European Union and the United Kingdom. Businesses in the region face significant challenges as they navigate fluctuating tariffs, which can directly influence their pricing strategies, profit margins, and competitiveness in both domestic and international markets. As companies grapple with this unpredictability, several key issues emerge:
- Investment Deterrence: The ongoing uncertainty may repel foreign investment, as potential investors typically seek stable environments.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Businesses relying on cross-border supply chains must adjust to the possibility of increased costs, complicating logistics and operational planning.
- Consumer Prices: Tariff levies could lead to increased prices for consumers, affecting purchasing power and overall economic well-being.
The impacts are not only confined to individual businesses but extend to the broader economic fabric of Northern ireland. A significant concern is the potential for market fragmentation, which can arise when businesses are unable to access EU or UK markets without incurring additional costs. This situation might foster an environment characterized by:
- Decreased Trade Volume: A rise in transactional costs may diminish the volume of goods exchanged with both the EU and UK.
- Employment Instability: As businesses adapt by reducing costs, job security for workers could become increasingly precarious.
- Economic Growth Stagnation: Inconsistent tariff policies can stall growth, limiting opportunities for developing sectors.
| Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Tariff Uncertainty | Deters investment and complicates pricing |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | increases costs and operational challenges |
| Consumer Prices | Affects purchasing power |
The Need for Clarity in Trade Regulations Post-Brexit
The prolonged uncertainty surrounding trade regulations post-brexit has created significant challenges for Northern Ireland, prompting widespread calls for enhanced transparency and uniformity. The region finds itself negotiating the complexities of two distinct regulatory environments: that of the European Union and the British Isles. This duality not only complicates compliance for businesses but also amplifies the risks of unintentional violations, which can lead to costly tariffs and fines.As a result, many companies must now invest additional resources in legal counsel and compliance frameworks, diverting attention from their core operations.
The need for clarity is further underscored by the implications on supply chains that traverse both territories. businesses must grapple with varying import tariffs, customs checks, and product standards, leading to potential delays and increased costs. A more coherent framework could alleviate these burdens significantly. Key elements that demand urgent attention include:
- Streamlined Customs Procedures: Simplifying processes to reduce transaction times and costs.
- Clear Tariff Schedules: Establishing predictable and consistent rates to eliminate surprises during trade.
- Regular Communication: Enhancing dialog between the UK and EU to clarify regulatory expectations.
Such strategic reforms could foster a more conducive environment for trade, ultimately safeguarding Northern Ireland’s economic stability. Without addressing these critical issues, the potential for increased fragmentation and confusion within the market remains ever-present.
Opportunities for Businesses Amidst Tariff Complexity
Amidst the challenges posed by tariff complexities, businesses in Northern Ireland can find unique opportunities to innovate and adapt. The intricate trade landscape presents a chance to reassess supply chains and explore new market avenues.By diversifying sourcing strategies, companies can mitigate risks associated with sudden tariff changes. Engaging closely with local suppliers and enhancing collaboration can lead to more resilient operations that not only weather disruptions but also thrive through them.
Furthermore, businesses can leverage the situation to strengthen their competitive edge. The current climate encourages investment in technology and digital solutions that streamline compliance with evolving regulations. Moreover, companies that embrace sustainability and ethical sourcing practices may capture a growing consumer demand for responsible goods. This presents an chance for brands to distinguish themselves, enhance customer loyalty, and ultimately drive growth during these turbulent times.
The Political Landscape: Navigating EU and U.K. Relations
The political landscape surrounding Northern Ireland is characterized by a complex interplay of interests between the European Union and the United Kingdom. As Brexit, Northern Ireland has found itself in a unique position, becoming the only part of the UK that shares a direct land border with the EU. This geographical reality has lead to specific arrangements intended to avoid a hard border with the Republic of Ireland, yet it has also given rise to heightened uncertainty regarding tariffs. Local businesses are particularly affected, as they must navigate a system that can apply both UK and EU tariff rates, depending on the origin of goods moving across the border.
As negotiations continue, the implications for trade and economic stability remain profound. Key challenges include:
- Tariff Variability: Goods entering Northern Ireland from Great Britain may face different tariff rates than those entering from the Republic of Ireland.
- Regulatory Divergence: The divergence in regulatory standards between the UK and EU can lead to additional barriers for businesses that wish to operate across both markets.
- Political Tensions: The ongoing discussions among UK, EU, and Northern Irish political leaders can create further uncertainty for local economies.
To illustrate the impact of these complexities, consider the following table:
| Goods Movement | Tariff Status | Impact on Businesses |
|---|---|---|
| From great Britain to Northern Ireland | Potential Tariffs | Increased costs, potential price rises |
| From Republic of Ireland to Northern Ireland | No Tariffs | Competitive advantage for Irish suppliers |
| Exports to EU from Northern Ireland | EU Tariffs Applied | Complex export processes, potential delays |
Recommendations for Policymakers to Alleviate Trade Pressures
To mitigate the ongoing trade pressures faced by Northern ireland, it is imperative for policymakers to adopt a multifaceted approach that not only addresses the immediate uncertainties but also lays down a framework for long-term stability. Key strategies should include:
- Enhanced Communication: Establish regular dialogue between the EU and UK authorities to ensure that any changes in trade regulations are transparently communicated and understood by businesses operating in Northern ireland.
- Support for Local Businesses: Implement financial assistance programs aimed at helping local firms adapt to new trade realities, particularly those most affected by tariffs and regulatory discrepancies.
- streamlined Customs Processes: Advocate for the simplification of customs procedures to reduce delays and costs, enabling easier movement of goods across borders.
- Trade Facilitation Initiatives: Foster partnerships with organizations focused on trade facilitation to share best practices and innovative solutions that can help ease the burden on exporters and importers.
Furthermore, the establishment of a cross-border trade advisory panel could provide essential insights and recommendations to policymakers.This panel would include representatives from the local business community, trade unions, and government officials, which would help ensure that stakeholder concerns are carefully considered in decision-making. A table outlining potential areas of focus for such a panel could look like this:
| Focus area | description |
|---|---|
| Tariff Implications | Analyse the impact of both UK and EU tariffs on local businesses. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Identify common compliance issues arising from conflicting regulations. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Assess risks to local supply chains due to crossing border challenges. |
| Market Access Strategies | Develop strategies to maintain and grow market access in key sectors. |
Engaging Stakeholders in the Discussion on Future Trade Agreements
Engaging stakeholders is crucial in navigating the complexities of future trade agreements, particularly in the unique situation faced by Northern Ireland. With the ongoing geopolitical shifts, the involvement of various stakeholders, including local businesses, government bodies, and community organizations, can foster a more inclusive dialogue. To facilitate these discussions, it’s critically important to identify and engage key participants who can offer insights on the implications of potential tariff changes. in this context, stakeholders should consider:
- Local Business Leaders: Their firsthand experience can highlight how tariff uncertainties affect trade practices.
- Economic Analysts: They can provide data-driven forecasts on the effects of trade agreements.
- Community Representatives: Engaging with them ensures that the broader public interests are included in negotiations.
A collaborative approach can lead to a more responsive framework that addresses both immediate concerns and long-term economic strategies. A transparent and structured dialogue can also be enhanced by creating platforms for real-time feedback on proposed agreements. One effective method could be to utilize interactive forums where stakeholders can share their perspectives and concerns. The following table illustrates the potential impacts of varying tariff scenarios from the EU and the UK:
| Tariff Scenario | Potential Impact on Northern Ireland |
|---|---|
| Zero Tariff | Increased trade flows and lower consumer prices. |
| 5% Tariff | Moderate price increases; potential strain on local businesses. |
| 10% Tariff | Significant rise in costs; risk of supply chain disruptions. |
Conclusion: Finding a Path Forward for Northern Ireland’s Economy
As Northern Ireland navigates its unique position post-Brexit, the need for innovative economic strategies has never been more pressing.Stakeholders must collaborate to create a cohesive approach that addresses tariff uncertainties while fostering growth. Potential pathways forward include:
- Enhanced Cross-border Trade: Strengthening existing ties with the Republic of Ireland and leveraging the EU Single Market can stimulate local economies.
- Investment in Technology and Innovation: Emphasizing sectors such as tech and renewable energy may attract both domestic and foreign investment.
- Support for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Providing targeted assistance can empower SMEs to adapt to changing trade regulations and compete more effectively.
Additionally, a strategic focus on workforce progress is crucial. By investing in education and training programs, Northern Ireland can equip its workforce with the skills necessary for emerging industries. A table summarizing key sectors for development may illustrate potential growth areas:
| Sector | Growth Potential | Key Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | High | Incentives for startups, partnerships with universities |
| Renewable Energy | Medium | Investment in infrastructure, grants for green projects |
| Tourism | Medium | Marketing campaigns highlighting local attractions |
By embracing collaboration and focusing on strategic development, Northern Ireland can emerge from the shadow of uncertainty, paving the way for a resilient and thriving economy that benefits all its communities.
Wrapping Up
Northern Ireland stands at a complex crossroads, grappling with the implications of its unique position between the european Union and the United Kingdom. The evolving landscape of trade tariffs and regulation not only challenges local businesses but also impacts the broader socio-economic fabric of the region.As stakeholders navigate this uncertain terrain, the need for clear policies and robust support mechanisms becomes paramount to safeguard Northern Ireland’s economic interests.The interplay of political will, community resilience, and strategic partnerships will ultimately determine how effectively the region can mitigate these challenges. with the stakes higher than ever, the path forward remains fraught with difficulty yet ripe with opportunity for innovation and collaboration. As Northern Ireland moves into this new era, its ability to adapt and thrive amidst uncertainty will be a critical narrative to watch in the months and years to come.