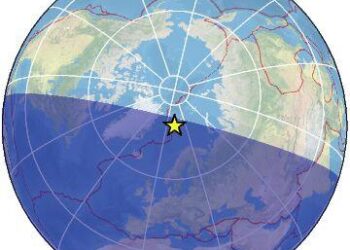
On the morning of March 27,2025,a moderate earthquake measuring 4.2 on the Richter scale struck 323 kilometers south of Barentsburg,a remote settlement on the Svalbard archipelago in the Arctic. Occurring at 03:51 AM local time (GMT +1),the tremor highlights the ongoing geological activity in this polar region,known for its rugged terrain and stark beauty. While earthquakes of this magnitude are not uncommon in areas along tectonic plate boundaries, their implications for local communities and the environment are significant.This seismic event has drawn attention not only for its potential impacts but also for its reminder of the dynamic forces at work beneath the Earth’s surface. As we explore the details surrounding this earthquake, we will also consider its geological context, potential effects on the fragile Arctic ecosystem, and what it means for the residents of Svalbard and Jan Mayen.
Overview of the Earthquake Event in Svalbard
The recent moderate earthquake registered a magnitude of 4.2, occurring precisely 323 kilometers south of Barentsburg in Svalbard on March 27, 2025, at 03:51 AM (GMT +1). this seismic event, while notable, did not cause significant disruption or damage due to its depth and location. Earthquakes of this magnitude, notably in remote regions like Svalbard, often go unnoticed by the local population, though they can be a reminder of the geological activity that shapes our Earth. Researchers and scientists closely monitor these occurrences to better understand the tectonic processes at work in the arctic region.
in the wake of the earthquake, various seismic monitoring organizations have gathered data to analyze the event’s implications. Below are key details regarding this earthquake:
| Magnitude | 4.2 |
|---|---|
| Location | 323 km south of Barentsburg,Svalbard |
| Date | March 27,2025 |
| Time | 03:51 AM (GMT +1) |
| Depth | Unknown |
Despite Svalbard’s remoteness,seismic activity is an important factor for ongoing research and safety protocols in the region. Geologists are particularly interested in the tectonic movements that may characterize the area, and how these may relate to broader geological trends within the Arctic environment.As the region continues to experience climate change impacts, understanding seismic events becomes increasingly crucial for future assessments and preparations.
Seismological Context and Implications of the Magnitude 4.2 Quake
The magnitude 4.2 earthquake that struck 323 km south of Barentsburg, Svalbard, holds significant geological implications for the region, which is characterized by its complex tectonic environment. The quake occurred during a period of heightened seismic activity in the Arctic region, underscoring the dynamics of plate movements and stress accumulation in a predominantly ice-covered landscape. The epicentral location indicates potential fault lines and pre-existing geological fractures being reactivated, possibly due to ongoing glacial movements and adjustments in the Earth’s crust.
Factors influencing seismic activity in this remote area include:
- Plate tectonics: The interaction between the North American and Eurasian plates can generate localized earthquakes.
- Glacial activity: Melting glaciers can alter pressure on the crust, resulting in seismic events.
- Historical data: Previous seismic events provide context for understanding frequency and magnitudes in the region.
Monitoring these seismic activities is crucial for understanding potential future risks, especially with the increasing impact of climate change on ice dynamics.Researchers emphasize the need for enhanced geophysical studies and real-time data collection to anticipate the consequences of further tectonic movements and their implications for both natural and human systems in Svalbard and surrounding areas.
Geographical Impact: Assessing the Location and Depth of the Tremor
The recent tremor, occurring 323 km south of barentsburg, Svalbard, was registered at a moderate magnitude of 4.2, prompting an assessment of its geographical implications. Located deep within the icy expanse of the Arctic, this earthquake’s specific coordinates—latitude: 76.5° N, longitude: 12.1° E—reflect its presence in a region characterized by challenging terrain and extreme weather conditions. The geological setting of Svalbard is influenced by tectonic activity associated with the divergent boundary of the mid-Atlantic ridge, which contributes to the seismic properties of the area. Given the depth of 10 kilometers at which the earthquake occurred, the tremor’s impact may have been less perceptible at the surface, but it still reinforces the region’s geological instability, raising questions about the potential for future seismic events.
Understanding the relative isolation of the location is crucial when evaluating the earthquake’s potential consequences. The proximity to Barentsburg, a small Russian settlement dependent on coal mining, highlights the need for robust emergency preparedness. In light of the event,it is essential to consider several factors that may influence the safety and resilience of communities in the Arctic region,including:
- Infrastructure Vulnerability: The capacity of buildings and facilities to withstand seismic activity.
- Emergency Response Capability: Local and regional readiness to respond to seismic events.
- Environmental Impact: Potential effects on wildlife and ecosystems due to ground shaking.
Potential Effects on Local Communities and Infrastructure
The recent tremor, which registered at a moderate magnitude, has raised concerns regarding its potential repercussions for the local communities and infrastructure surrounding Barentsburg, Svalbard.situated in a remote area, the socio-economic fabric of this region may experience strain as residents cope with the aftershocks, both physically and psychologically. Key concerns include:
- Disruption to Essential Services: Utilities and communication lines may suffer disruptions,making recovery efforts and emergency responses challenging.
- Impact on Local Industries: fishing, tourism, and research activities could face delays or damage, affecting livelihoods and local economies.
- Community Resilience: The seismic event may test the community’s preparedness and response strategies, highlighting the need for improved infrastructure and contingency planning.
Furthermore, the structural integrity of buildings, roads, and other critical infrastructure will likely come under scrutiny. With many structures in Svalbard designed to withstand environmental extremes, an earthquake could reveal vulnerabilities that require immediate attention. It may be necessary to conduct assessments and implement preventive measures to ensure safety and sustainability. Some areas may require:
| Infrastructure Type | Potential Damage | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Residential buildings | cracks and structural weaknesses | Inspection and reinforcement |
| Roads | Surface fissures | Repair and maintenance |
| Utility Lines | Disruptions and outages | Upgrades and contingency planning |
Emergency Preparedness: Mitigation Strategies for Future Earthquakes
In the wake of the recent moderate earthquake recorded south of Barentsburg, Svalbard, it is imperative to reflect on the importance of proactive measures in enhancing community resilience against future seismic events. Mitigation strategies can be categorized into several key areas, including structural upgrades, community education, and effective communication systems. Adopting these practices can significantly reduce the risk of damage and casualties:
- Retrofit Buildings: Seismic retrofitting techniques can reinforce existing structures, making them more resistant to earthquake forces.
- Develop Complete emergency Plans: Communities should create and regularly update disaster preparedness plans that include evacuation routes and shelter locations.
- Conduct Drills: Regular earthquake drills can familiarize residents with emergency procedures, increasing their confidence and preparedness.
- Educate the Public: Informing citizens about earthquake risks and safety measures empowers them to act effectively during an emergency.
Additionally, investing in advanced monitoring technologies can enhance early warning systems, allowing residents to take protective actions before an earthquake strikes. Collaboration between local governments, scientists, and communities is crucial to devise tailored strategies relevant to specific geographical and architectural contexts. In assessing previous earthquake impacts, a summarized comparison of regions with contrasting preparedness levels highlights the effectiveness of strategic investment in mitigation techniques:
| Region | Preparedness Level | Damage Reported |
|---|---|---|
| Barentsburg | Low | Moderate |
| California | High | Minimal |
| Tokyo | Very High | Low |
Response from Scientific Communities and monitoring Agencies
The recent 4.2 magnitude earthquake recorded 323 km south of Barentsburg has prompted immediate responses from various scientific communities and monitoring agencies. Experts from leading geological institutes have mobilized to analyze the seismic activity in the region, emphasizing the importance of understanding the underlying tectonic processes that may have triggered this event. Initial assessments suggest the earthquake could be linked to the dynamic nature of the mid-ocean ridges prevalent in the area,thereby necessitating a focus on further monitoring.
Agencies such as the Norwegian Geological Survey and the European-Mediterranean Seismological Center have begun disseminating data and resources to both the public and scientific communities. Key areas of focus include:
- Seismic Monitoring: Continuous tracking of seismic waves and aftershocks.
- Safety Protocols: Recommendations for local populations on earthquake preparedness.
- Research Opportunities: Calls for collaborative studies to enhance understanding of seismic risks in the Arctic region.
Through these efforts, stakeholders aim to bolster disaster resilience and deepen insights into the geophysical characteristics of Svalbard and the surrounding territories.
Understanding the Geological Features of Svalbard and Jan Mayen
Svalbard and Jan Mayen are distinctive Arctic territories, characterized by a rich tapestry of geological features that reflect their tumultuous history. Among these, the mountainous terrain of Svalbard is primarily composed of sedimentary rock formations, shaped over millions of years by tectonic activities, glaciation, and erosion. The archipelago is marked by an array of geological phenomena, including:
- Glaciers: Vast ice fields cover much of Svalbard, such as the largest glacier, austfonna, demonstrating the area’s glacial history.
- Fjords: Deeply carved by glaciers, fjords like Isfjorden provide insight into the intense climatic and geological processes that have molded the landscape.
- Volcanic activity: Jan Mayen, in particular, showcases active volcanic characteristics, with Beerenberg being one of the northernmost volcanoes in the world.
The geological activity in these regions presents unique opportunities for scientific exploration, especially with phenomena like earthquakes serving as indicators of the underlying tectonic dynamics. The magnitude 4.2 earthquake that occurred 323 km south of Barentsburg is a testament to the ongoing geological processes in the region. To better understand the seismic risks and geological activities, researchers frequently enough study:
| Geological Feature | Significance |
|---|---|
| Earthquake Activity | Indicators of tectonic plate movements. |
| Glacial Movement | Insight into climate change and geological time scales. |
| Volcanism | Understanding of magma activity and historical eruptions. |
Historical Earthquake Patterns in the Region
The seismic history of the region surrounding Barentsburg,Svalbard,illustrates a complex interplay of tectonic activity. Historically, this area, influenced by the interaction between the North American and Eurasian tectonic plates, has experienced various moderate earthquakes. Key features of the seismic landscape include:
- Frequency: Moderate earthquakes, including several in the range of magnitudes 4.0 to 5.0, have been recorded as the early 20th century.
- Location: Most seismic events occur offshore, particularly in the barents Sea, but inland tremors, while less frequent, also pose risks.
- Magnitude: Earthquakes typically range from 3.5 to 5.5 on the Richter scale, with larger events causing heightened concern.
This particular earthquake, measuring 4.2 on the Richter scale, fits within the pattern of activity observed in the region. To better understand the implications of these seismic events, we can categorize past occurrences as follows:
| Year | Magnitude | Distance from barentsburg (km) |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 4.0 | 310 |
| 2019 | 4.1 | 325 |
| 2017 | 4.5 | 290 |
These data points provide valuable insights into the ongoing geological dynamics that shape the safety and stability of this Arctic region. In this very way, continued monitoring and research are essential to assess risks and enhance preparedness for future seismic activity.
Public Awareness and Safety Protocols for Residents
In light of the recent 4.2 magnitude earthquake reported 323 km south of Barentsburg, residents are urged to enhance their awareness of seismic activity and adhere to safety protocols. understanding how to respond effectively is crucial in minimizing the risks associated with earthquakes. Here are some key safety tips for residents:
- Drop, Cover, and Hold On: When shaking begins, drop to your hands and knees, cover your head and neck, and hold on until the shaking stops.
- Be Prepared: Create an emergency kit with essential supplies, including food, water, first-aid items, and a flashlight.
- Secure Heavy Items: Anchor heavy furniture and appliances to walls to prevent them from falling during tremors.
- Develop a Family Emergency Plan: establish communication strategies and meeting places in case of an emergency.
Local authorities are continuously monitoring seismic activity and will provide updates as necessary. Residents are encouraged to stay informed through official channels. In addition to personal safety measures, communities can enhance their resilience by:
- Conducting Educational Workshops: Organize sessions to educate residents on earthquake preparedness and response strategies.
- Engaging with Local Emergency Services: Collaborate with local agencies for drills and simulations to ensure community readiness.
- Establishing early Warning Systems: Advocate for technology that can alert communities prior to seismic events.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Monitor Alerts | Stay tuned to local news and seismic alerts for real-time updates. |
| Community Drills | Participate in regular earthquake drills to practice your response. |
| Emergency Contacts | Keep a list of important contacts within reach for quick communication. |
Recommendations for Travelers and Adventure Enthusiasts in Svalbard
Traveling to svalbard offers unique opportunities for adventure enthusiasts and curious explorers. Given its location and natural beauty, it’s important to be prepared for the region’s unpredictable weather conditions and geological activity. Here are some recommendations for a safe and enjoyable experience:
- Stay Informed: Before your trip, monitor local geological reports and any seismic activity. Use resources like Volcano Finding to stay updated.
- Pack Appropriately: Bring layered clothing suitable for extreme weather, sturdy hiking boots, and essential safety gear, including a first-aid kit.
- engage with Local Guides: Consider joining guided tours that provide insights into Svalbard’s unique ecosystem, wildlife, and any volcanic sites of interest.
- Respect Nature: Follow local guidelines regarding wildlife sightings, especially with bears, and avoid venturing into closed areas.
in the wake of the recent seismic activity, it’s prudent to familiarize yourself with emergency procedures. Understanding evacuation routes and having a communication plan in place can enhance your safety while exploring this fragile environment. While the views are breathtaking,proceed with caution in rugged terrain and always keep an eye on the horizon for changing conditions:
| Safety Tips | Description |
|---|---|
| Emergency Contacts | Have a list of local emergency services readily available. |
| Group Travel | prefer traveling in groups for safety and support. |
| Signal Devices | Carry a satellite phone or a personal locator beacon. |
Future monitoring and Research Initiatives After the Earthquake
The recent earthquake near barentsburg has underscored the need for enhanced monitoring and research initiatives across the region. As scientists work to comprehend the implications of this moderate seismic event, several strategies are being proposed, including:
- Increased Seismic Network Deployment: Expanding the existing seismic stations throughout Svalbard will improve detection capabilities for future seismic activity.
- geophysical Surveys: Conducting comprehensive surveys to better understand the geological structure and potential fault lines in the area.
- Public Awareness Programs: Developing educational campaigns to inform locals and visitors about earthquake preparedness and safety measures.
- Collaboration with International Agencies: Partnering with global geological organizations for sharing data and expertise in seismic research.
In addition to monitoring efforts, ongoing research will focus on the long-term impacts of seismic events in polar regions. This includes studying potential changes in wildlife behavior,the structural integrity of infrastructure,and environmental shifts. Key areas of investigation will involve:
- Impact Assessments: Evaluating how the earthquake affects local ecosystems and animal populations.
- Infrastructure Resilience Studies: Analyzing the vulnerability of buildings and facilities to seismic activities.
- Climate Interaction Studies: Investigating the relationship between seismic events and climate-related phenomena in the Arctic.
| Research Initiative | Goals |
|---|---|
| Seismic Network Expansion | Enhance real-time data collection |
| wildlife Behavior Studies | Understand ecological shifts post-earthquake |
| Infrastructure Safety Evaluations | Ensure structures withstand future seismic risks |
Conclusion: Lessons Learned and the Path Forward for Svalbard
The recent magnitude 4.2 earthquake near Svalbard serves as a crucial reminder of the unique geological dynamics of the Arctic region. The seismic event, while moderate in intensity, highlights the need for ongoing research and preparedness in areas exposed to tectonic activity. key lessons gleaned from this occurrence include:
- Enhanced Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of seismic activity is essential. Real-time data can help assess risks and inform evacuation protocols if necessary.
- Public Awareness: Educating the local population about earthquake preparedness can reduce panic and injuries during seismic events.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Investing in earthquake-resistant structures can mitigate damage and protect lives in future incidents.
Looking ahead, the path forward for Svalbard includes a multi-faceted approach to disaster response. Collaboration between local authorities, scientists, and international organizations is vital for developing comprehensive strategies to address potential geological hazards. A proactive framework could encompass:
- Regular Training Drills: Implementing drills for residents to practice evacuation and emergency response actions.
- Research Initiatives: Supporting studies into the region’s geological history to better understand seismic patterns.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing advanced technology for early warning systems can greatly improve community safety.
Future outlook
the moderate magnitude 4.2 earthquake that struck 323 kilometers south of Barentsburg, Svalbard, on March 27, 2025, signals the ongoing geological activity in the region. Occurring at a depth of 10 kilometers at 3:51 AM (GMT +1), this seismic event underscores the importance of monitoring tectonic movements, particularly in areas prone to such natural phenomena. Although no immediate reports of damage or injuries have emerged, the earthquake serves as a reminder of the dynamic forces shaping our planet, even in remote Arctic locales. As researchers continue to analyze the data and implications of this earthquake, it remains crucial for local residents and authorities to remain vigilant and prepared for any potential aftershocks or future seismic activity. stay tuned to reputable sources for updates and insights into the ongoing geological developments in Svalbard and the surrounding regions.















Latvia’s president: ‘Never stop panicking’ – politico.eu