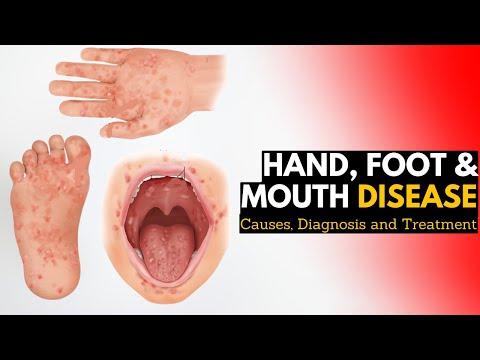
Foot-and-Mouth Disease outbreak in Central Europe Triggers Animal Culls and Nationwide Border Closures
In a alarming resurgence of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), Central Europe is grappling with an outbreak that has prompted severe measures across affected nations. The highly contagious viral disease, which primarily affects livestock, has led to extensive animal culls in an effort to contain the infection. In response to the escalating crisis, several governments have enforced border closures and tightened restrictions on the movement of cattle and other susceptible species. As farmers face devastating losses and authorities scramble to halt the spread of the virus, the implications of this outbreak extend beyond agriculture, raising concerns about food security and economic stability in the region. This article delves into the current situation, the actions being taken by governments, and the potential long-term effects of the outbreak on Central Europe’s agricultural landscape.
Impact of Foot-and-Mouth Disease Outbreak on Livestock Farmers and Regional Economies
The recent outbreak of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) in Central Europe has sent shockwaves through the agricultural sector, forcing livestock farmers to face unprecedented challenges. As authorities implement culling measures to contain the spread, many farmers are experiencing significant losses. The mandatory culling not only affects infected animals but also extends to healthy livestock within proximity to quarantine zones. This preemptive action, while necessary for public health mitigation, disrupts the entire supply chain, leading to shortages and inflated prices for dairy and meat products. The financial impact is compounded by the loss of livestock, as farmers are left with diminished herds and significant economic repercussions.
Furthermore, the outbreak has led to border closures that exacerbate existing supply chain issues and restrict trade across regions. Farmers who rely on exporting their livestock or meat products face additional obstacles, as international markets tighten regulations and halt transactions. The ripple effects are manifold, impacting not only individual farmers but also regional economies heavily dependent on agriculture. As an inevitable result,local economies are witnessing a spike in unemployment rates within rural communities,as businesses that support the livestock sector,such as feed suppliers and veterinary services,also suffer the consequences. To illustrate the far-reaching ramifications of this crisis, consider the table below, which highlights key impacts on various sectors:
| Sector | Impact |
|---|---|
| Livestock Farmers | Significant loss of income and livestock |
| Meat Processors | Supply chain disruptions and price surges |
| Feed Suppliers | Decrease in demand leading to potential layoffs |
| Veterinary Services | Increased demand for disease management and vaccination |
Emergency Response Strategies: Assessing Culls and Their Long-term Implications
The recent outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) in Central Europe has prompted a series of drastic emergency response measures, most notably extensive animal culls. These culls, while aimed at controlling the spread of the virus and safeguarding regional livestock, have raised profound concerns regarding their long-term implications. Experts warn that such actions may lead to a disruption in the agricultural ecosystem, potentially affecting not only animal populations but also farming communities reliant on these animals for their livelihoods.The immediate benefits of disease control must be weighed against the potential for diminished genetic diversity and the economic fallout for farmers facing losses in livestock and production.
Moreover, the impact of border closures, another critical strategy implemented during the outbreak, further complicates the situation.Restrictions on the movement of livestock and animal products can lead to supply chain disruptions and heightened tensions between neighboring countries. This may encourage illegal crossings and black-market activities, undermining efforts to manage the outbreak effectively.As the region navigates these challenges, it is crucial for policymakers to develop strategies that incorporate not only immediate containment measures but also long-term planning that considers the resilience of the agricultural sector, the welfare of farmers, and the health of livestock populations.
Recommendations for Enhanced Biosecurity Measures to Prevent Future Outbreaks
To bolster defenses against future outbreaks of diseases like foot-and-mouth disease, it is indeed imperative that both governmental and agricultural stakeholders adopt a multifaceted strategy focused on enhanced biosecurity measures. This includes the implementation of strict hygiene protocols on farms, such as:
- Regular sanitation of equipment and facilities to minimize the risk of pathogen transmission.
- Biosecure access controls to limit the movement of persons and vehicles into sensitive areas.
- Immediate reporting systems for any signs of illness in livestock to facilitate rapid response.
Moreover, cross-border collaboration is essential to detect and manage disease outbreaks effectively. Countries can establish joint task forces focused on:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Facts Sharing | Regular exchange of data on animal health and outbreak notifications. |
| Joint Vaccination Programs | Coordinated vaccination campaigns to create buffer zones against outbreaks. |
| Training and Workshops | Educational initiatives focused on biosecurity practices for farmers and veterinary staff. |
In Summary
the recent outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease in Central Europe has prompted urgent measures, including widespread animal culls and the implementation of border closures, in a bid to contain this highly contagious virus. As authorities grapple with the challenges posed by this outbreak, the implications for livestock markets, farmers, and regional economies are becoming increasingly evident. Stakeholders must remain vigilant as they navigate the complex landscape of biosecurity and public health. Continued monitoring, timely reporting, and proactive strategies will be essential in addressing this crisis and mitigating future risks to the agricultural sector. The situation remains fluid, and updates will be vital as developments unfold.