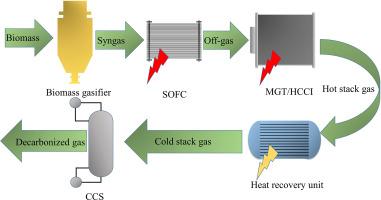
As the global push for sustainable energy solutions intensifies, the role of biomass-fueled combined heat and power (CHP) systems is once again under the spotlight. A recent study featured on ScienceDirect.com revisits the potential of biomass CHP within future energy frameworks, focusing on the Ă…land Islands as a compelling case study. This investigation sheds new light on the viability of integrating biomass technologies to meet energy demands while supporting carbon reduction goals in isolated energy systems. With renewable energy priorities evolving rapidly, the findings could have significant implications for similar communities striving for energy resilience and sustainability.
Feasibility of Biomass CHP in Ă…land Islands Unveiled through Comprehensive Case Study
The latest investigation into the energy systems of the Ă…land Islands reveals promising potential for biomass combined heat and power (CHP) plants to play a pivotal role in the archipelago’s transition towards sustainable energy. The study meticulously evaluates both technical and economic factors, highlighting how biomass CHP can effectively meet local heat demands while reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. Key findings emphasize the system’s ability to integrate with existing renewable technologies, ultimately enhancing energy security and lowering carbon emissions in a region heavily focused on environmental sustainability.
Critical variables influencing feasibility include:
- Availability of local biomass resources such as forestry residues and agricultural by-products
- Grid integration challenges given the islands’ isolated electrical network
- Cost comparisons between biomass CHP and alternative renewable options
- Scalability potential to adjust capacity based on seasonal energy demands
| Factor | Impact on Feasibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Biomass Supply | High | Locally abundant forestry residues |
| Grid Stability | Moderate | Requires advanced control systems |
| Investment Costs | Medium | Comparable to alternative renewables |
| Environmental Benefits | High | Significant COâ‚‚ reductions achievable |
Detailed Insights on Integrating Biomass-Fueled CHP into Future Energy Systems
Integrating biomass-fueled combined heat and power (CHP) systems into future energy frameworks demands a multidimensional evaluation of both technical and economic factors. The case of the Ă…land Islands exemplifies this complexity, showcasing how localized biomass resources can substantially reduce fossil fuel dependence while enhancing energy security. Crucially, the adaptability of CHP technologies to fluctuating biomass supply chains and their compatibility with existing grid infrastructures underpin their long-term viability. The study highlights that biomass CHP plants offer significant flexibility in balancing decentralized energy demands, especially in archipelagic regions where energy logistics pose unique challenges.
Key drivers influencing successful integration include:
- Resource availability: Sustainable biomass supply chains that align with environmental regulations.
- System efficiency: Optimization of heat-to-power ratios to maximize output and minimize waste.
- Policy incentives: Supportive frameworks encouraging low-carbon technologies adoption.
- Community engagement: Local acceptance and participation in energy planning.
| Parameter | Ă…land Biomass CHP | Conventional Fossil CHP |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Emissions (kg/MWh) | 45 | 320 |
| Fuel Cost (€/MWh) | 40 | 60 |
| Operational Flexibility | High | Medium |
| Community Impact | Positive | Neutral |
Policy and Investment Recommendations to Boost Biomass CHP Adoption in Remote Regions
Enhancing policy frameworks is critical to accelerating the adoption of biomass combined heat and power (CHP) technologies in remote regions like the Ă…land Islands. Governments should prioritize the design of flexible subsidy schemes that reflect regional biomass availability and logistical challenges unique to isolated communities. Introducing feed-in tariffs specifically tailored for biomass CHP can incentivize local stakeholders, while streamlined permitting processes will reduce administrative delays that often stall projects. Collaborative policy efforts that integrate energy, forestry, and environmental sectors will ensure sustainable biomass harvesting, aligning economic development with ecological preservation.
Strategic investment must focus on overcoming infrastructure constraints and scaling operational efficiency. Targeted funding for upgrading existing heat networks and enabling smart grid integration can maximize the benefits of biomass CHP systems by balancing fluctuations in energy supply and demand. Additionally, fostering public-private partnerships that bring together technology providers, local governments, and community groups can lower upfront capital risks and encourage knowledge sharing. The table below illustrates a simplified investment framework tailored to remote regions, highlighting priority actions and expected outcomes:
| Investment Focus | Key Actions | Expected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Upgrades | Modernize heat distribution networks | Improved energy efficiency and reduced losses |
| Incentive Schemes | Implement region-specific feed-in tariffs | Increased local investor engagement |
| Collaborative Partnerships | Form alliances between stakeholders | Shared risks and innovation acceleration |
| Capacity Building | Provide training and knowledge transfer | Enhanced technical expertise at community level |
The Way Forward
As the Ă…land Islands explore pathways to a sustainable energy future, this case study highlights both the potential and challenges of integrating biomass-fueled combined heat and power (CHP) systems into evolving energy landscapes. While biomass CHP presents a promising option for local renewable energy generation and enhanced system resilience, factors such as resource availability, technological advancements, and economic viability remain critical considerations. Ultimately, the Ă…land experience underscores the need for tailored, context-specific approaches in transitioning towards greener and more efficient energy systems worldwide.