The Faroese government’s recent revision to the salmon tax regime is generating a spectrum of reactions from the local aquaculture industry. Announced last week, the updated tax structure aims to balance fiscal revenue with sustainable growth, but producers are voicing concerns over potential impacts on profitability and competitiveness. As the amendments take effect, stakeholders weigh the benefits of increased investment in environmental initiatives against the burden of higher levies, highlighting a complex outlook for the Faroese salmon sector.
Faroese Salmon Tax Revision Sparks Diverse Reactions Among Producers
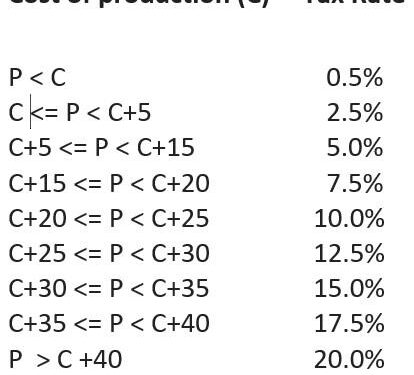
The recent changes to the salmon tax framework in the Faroe Islands have ignited a spectrum of responses from the local aquaculture industry. While some producers applaud the adjustments for providing tax relief on smaller operations and encouraging sustainable growth, others express concern over increased rates impacting larger producers’ profitability. The government’s objective to balance economic growth with environmental responsibility has introduced new tax brackets that prioritize reduced environmental footprints, a move seen as both progressive and challenging depending on the scale of the producer.
Key elements of the tax revision include:
- Lowered rates for producers with annual yields under 1,000 metric tons
- Introduction of an environmental impact surcharge for farms exceeding set pollution thresholds
- Incentives for operations adopting innovative waste management technologies
| Producer Category | Previous Tax Rate | Revised Tax Rate | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Scale (<1,000 MT) | 5% | 3% | Reduced tax burden |
| Medium Scale (1,000-5,000 MT) | 7% | 7% | No change |
| Large Scale (>5,000 MT) | 10% | 12% | Increased tax with environmental surcharge |
Economic Impact and Operational Challenges Arising from Policy Changes
The recent revision of the Faroese salmon tax has introduced a complex landscape for producers, blending opportunities with notable operational hurdles. While the adjusted tax rates aim to increase governmental revenues, producers face tightened profit margins, especially smaller-scale operators. This fiscal shift compels companies to revisit their financial strategies, weighing production costs against potential returns. Additionally, fluctuations in market demand and export pricing exert further pressure, challenging producers to maintain competitiveness in an increasingly volatile industry.
Operationally, several challenges have surfaced, including:
- Compliance complexity: Navigating new tax brackets and reporting standards demands enhanced accounting oversight.
- Resource allocation: Redirecting funds toward tax obligations reduces capital available for infrastructure upgrades and sustainability initiatives.
- Supply chain adjustments: The revised tax framework influences harvesting schedules and inventory management to optimize tax benefits.
| Impact Area | Positive Effects | Challenges | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Revenue | Increased government income | Higher producer tax burden | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operational Costs | Potential for streamlined tax incentives | Increased compliance expenditures | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Market Position | Encourages efficient production | Risk of reduced export competitiveness |
| Impact Area | Positive Effects | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Revenue | Increased government income | Higher producer tax burden |
| Operational Costs | Potential for streamlined tax incentives | Increased compliance expenditures |
| Market Position | Encourages efficient production | Risk of reduced export competitiveness |
If you would like, I can also assist in summarizing or expanding on any of these points!
Strategies for Producers to Navigate New Tax Landscape Effectively
Producers must embrace a proactive approach to mitigate potential financial strain from the revised tax structure. Key tactics include diversifying revenue streams beyond salmon farming to buffer against fluctuating tax liabilities and exploring efficiencies in production to offset increased operational costs. Emphasizing innovation in sustainable practices can also unlock tax incentives and improve cost-effectiveness in the long run. Additionally, staying informed and maintaining close communication with tax consultants will help in anticipating regulatory changes and optimizing fiscal planning.
Implementing robust financial modeling tools can empower producers to simulate various tax scenarios and evaluate their impacts on profit margins. The following quick-reference table outlines strategic pivots producers should consider:
| Strategy | Benefit | Implementation Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Diversification | Risk reduction | Explore alternative aquaculture species |
| Operational Efficiency | Cost control | Adopt automation and digital monitoring |
| Tax Consultancy | Compliance & savings | Regular audits and scenario planning |
| Sustainability Innovation | Access to incentives | Invest in eco-friendly technologies |
Key Takeaways
As the Faroese government moves forward with its revised salmon tax policy, the response from producers remains cautiously divided. While some welcome the potential for a more balanced regulatory framework, others express concern over the financial implications and operational uncertainties ahead. Market watchers will be closely monitoring how these changes impact the Faroese salmon industry’s competitiveness and sustainability in the months to come.