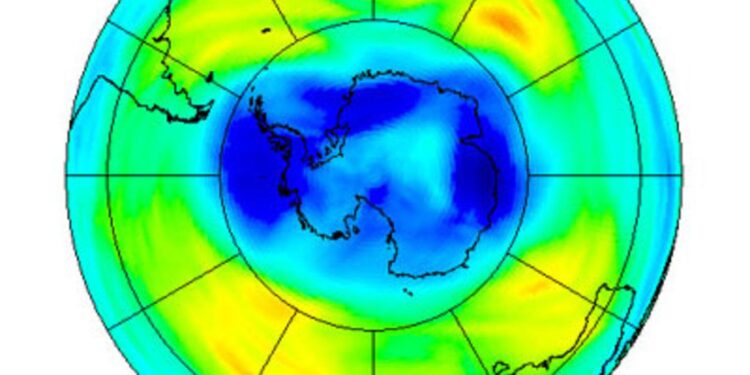
Norway has recorded an unprecedented increase in the thickness of its ozone layer in 2024, according to a recent report by Anadolu AjansńĪ. Scientists attribute this remarkable development to ongoing global efforts to reduce ozone-depleting substances, marking a significant milestone in environmental recovery. The findings not only highlight Norway’s unique atmospheric conditions but also offer a promising glimpse into the future of the planet’s protective shield against harmful ultraviolet radiation.
Norway Achieves Unprecedented Ozone Layer Thickness in 2024 Satellite Data Reveals
Satellite observations throughout 2024 have indicated a remarkable increase in the ozone layer’s thickness over Norway, marking a milestone in atmospheric recovery efforts. Experts attribute this progress to stringent environmental policies, reduced emissions of ozone-depleting substances, and global adherence to protocols such as the Montreal Agreement. The enhanced ozone concentration not only signals improved protection against harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation but also strengthens Norway’s position as a leader in environmental stewardship.
Key factors contributing to this phenomenon include:
- Decreased usage of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) since international regulations tightened emissions.
- Improved atmospheric circulation patterns favoring ozone replenishment in the Arctic region.
- Collaborative scientific monitoring enabling real-time tracking and responsive policy adjustments.
| Month | Average Ozone Thickness (Dobson Units) | Change from 2023 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| January | 345 | +5.7% |
| April | 360 | +6.1% |
| July | 373 | +6.9% |
| October | 368 | +6.3% |
Environmental Impact and Scientific Implications of Enhanced Ozone Recovery Explored
Recent observations revealing unprecedented ozone layer thickness over Norway signify not only a triumph for atmospheric recovery efforts but also present substantial environmental benefits. The rejuvenation of the ozone layer reduces the harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation reaching the Earth’s surface, mitigating risks such as increased skin cancer rates and damage to marine ecosystems. This natural shield’s restoration plays a vital role in preserving biodiversity and supporting agricultural productivity by protecting sensitive plant species from UV-induced stress.
Scientific implications of enhanced ozone recovery extend beyond direct environmental advantages, influencing climate dynamics and atmospheric chemistry. For instance, the stabilization of ozone concentrations alters the balance of key greenhouse gases, indirectly affecting temperature regulation. Researchers emphasize how these changes could inform climate modeling and policy decisions. The table below highlights some critical parameters impacted by ozone health:
| Parameter | Pre-Recovery Status | 2024 Status | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| UV Radiation Levels | High | Moderate | Reduced skin & ecosystem damage |
| Ozone Concentration | Below norm | Record thickness | Enhanced atmospheric protection |
| Climate Feedback | Unstable | More balanced | Improved climate modeling |
- Strengthened UV defense: Protects human health and ecosystems.
- Improved climate predictions: Enhances understanding of atmospheric interactions.
- Policy reinforcement: Underscores success of international treaties like the Montreal Protocol.
Experts Urge Continued Global Commitment to Emission Controls to Sustain Ozone Health
Scientists emphasize that the recent milestone in the ozone layer’s recovery is a result of decades of sustained global cooperation under agreements such as the Montreal Protocol. Despite this success, experts warn that relaxation in emission controls could reverse the positive trend, endangering both environmental stability and public health. They highlight that continuous monitoring and stringent regulations on ozone-depleting substances remain critical, particularly as emerging industrial activities and climate change introduce new variables to atmospheric chemistry.
Key areas of focus recommended by specialists include:
- Maintaining phased reductions of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and other harmful chemicals.
- Enhancing global data sharing to track ozone evolution and potential threats effectively.
- Investing in innovative technologies that can minimize inadvertent emissions from new products and sectors.
- Raising public awareness on the continued importance of ozone protection in relation to UV radiation exposure and ecosystem health.
| Year | Average Ozone Thickness (Dobson Units) | Global Emission Level (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 290 | 100 |
| 2015 | 305 | 75 |
| 2020 | 320 | 45 |
| 2024 | 335 | 30 |
In Conclusion
As Norway records unprecedented growth in ozone layer thickness in 2024, experts emphasize the significance of continued environmental vigilance and global cooperation. While the positive trend offers hope for the planet’s atmospheric health, scientists caution that sustained efforts are essential to protect this vital shield against harmful ultraviolet radiation. The latest findings serve as a reminder of both the progress achieved through international climate policies and the ongoing challenges in safeguarding the Earth’s fragile ozone layer.