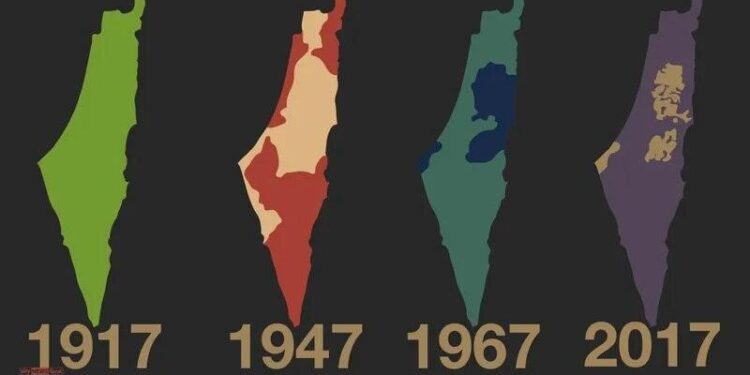
In a significant diplomatic development, Britain, Canada, Australia, and Portugal have collectively recognized a Palestinian state, marking a notable shift in international relations surrounding the long-standing Israeli-Palestinian conflict. This unprecedented move, reported by IMEMC News, underscores growing global support for Palestinian statehood and could have far-reaching implications for peace negotiations and regional stability. The recognition by these Western nations signals a potential recalibration of foreign policy approaches toward the Middle East, sparking reactions from governments and stakeholders worldwide.
Britain Canada Australia and Portugal Officially Recognize Palestinian Statehood
In a significant diplomatic development, four prominent nations-Britain, Canada, Australia, and Portugal-have formally extended their recognition to Palestinian statehood. This move marks a pivotal shift in international relations, signaling growing support for Palestinian sovereignty amid ongoing tensions in the Middle East. The announcements were met with mixed reactions globally, with advocates praising the decision as a step toward peace and self-determination, while critics warned of potential diplomatic strains in the region.
Key highlights of the recognition include:
- Britain: Acknowledged the importance of a two-state solution while recognizing Palestinian governance structures.
- Canada: Emphasized adherence to international law and the rights of the Palestinian people.
- Australia: Highlighted its commitment to fostering dialogue and conflict resolution.
- Portugal: Joined as a new voice supporting Palestinian statehood within the European context.
| Country | Date of Recognition | Official Statement Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Britain | June 2024 | Two-State Solution & Sovereignty |
| Canada | June 2024 | International Law & Rights |
| Australia | June 2024 | Dialogue & Peacebuilding |
| Portugal | June 2024 | European Support & Solidarity |
Implications for International Diplomacy and Middle East Peace Efforts
The recognition of a Palestinian state by Britain, Canada, Australia, and Portugal marks a significant shift in international diplomatic dynamics. These countries, traditionally seen as key Western allies to Israel, have now signaled a recalibration of their foreign policies, reflecting growing global acknowledgment of Palestinian statehood aspirations. This development is likely to intensify diplomatic dialogues, pressuring other nations to reconsider their positions while potentially creating new avenues for multilateral negotiations involving both Palestinian representatives and Israeli officials.
Key consequences of this recognition include:
- Reinvigoration of peace talks through increased international mediation efforts
- Enhanced legitimacy and bargaining power for Palestinian leadership
- Heightened tensions in diplomatic relations among countries with divergent stances
- Potential restructuring of aid and economic cooperation frameworks in the region
| Country | Previous Position | New Diplomatic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Britain | Supportive of two-state solution | Shift towards formal recognition and encouragement of direct talks |
| Canada | Aligned with Israel’s policies | Broadened diplomatic engagement with Palestinian authorities |
| Australia | Cautious neutrality | Adoption of clearer stance on statehood recognition |
| Portugal | Support for EU consensus | Active promoter of renewed peace efforts |
Recommendations for Strengthening Multilateral Support and Negotiating Frameworks
To enhance the effectiveness of multilateral support for Palestinian statehood, it is vital to prioritize the establishment of inclusive platforms where all stakeholders – including regional actors, international organizations, and civil society groups – can engage in open dialogue. Strengthening these platforms demands sustained political will and the allocation of adequate resources to ensure meaningful participation and transparency. Additionally, fostering collaboration among key international bodies such as the United Nations, European Union, and Arab League can create a more unified approach that reduces fragmentation and leverages collective influence.
Negotiating frameworks must also adapt to the complexities on the ground by embracing flexible, phased approaches rooted in mutual recognition and respect for international law. This involves:
- Instituting confidence-building measures to ease tensions and build trust between parties.
- Embedding third-party mediation from neutral actors to facilitate constructive dialogue.
- Establishing clear timelines and benchmarks to monitor progress and ensure accountability.
| Key Element | Purpose | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Inclusive Dialogue | Engage all stakeholders | Greater consensus and legitimacy |
| Confidence-Building Measures | Reduce mistrust | Improved negotiation climate |