In‚ÄĆ a meaningful geopolitical shift,‚ĀĘ the Baltic nations of Estonia, Latvia, ‚Äćand Lithuania ‚Ā£have taken decisive steps ‚Ā£to sever their longstanding ties with the Russian power ‚ĀĘgrid, signaling a robust move ‚Äčtowards energy independence and‚Ā£ enhanced integration with the European Union.This strategic decision,aimed at bolstering energy‚ĀĘ security in the face‚Ā£ of ‚Äčregional‚Ā§ tensions,reflects the Baltic states‚Äô commitment to reducing reliance on Moscow and ‚Ā§aligning their infrastructure with EU standards. As the transition unfolds, the‚ÄĆ Baltic countries are preparing to‚Äč link their electricity networks with the broader ‚ĀĘEuropean grid, a ‚Äćmaneuver that not only‚Ā£ aims to‚Äć enhance grid stability but also underscores a broader effort to‚Ā§ fortify political and economic ties within the EU amidst an increasingly uncertain geopolitical landscape.
Baltic Nations Transition from‚Äć Russian‚Äć energy Dependency
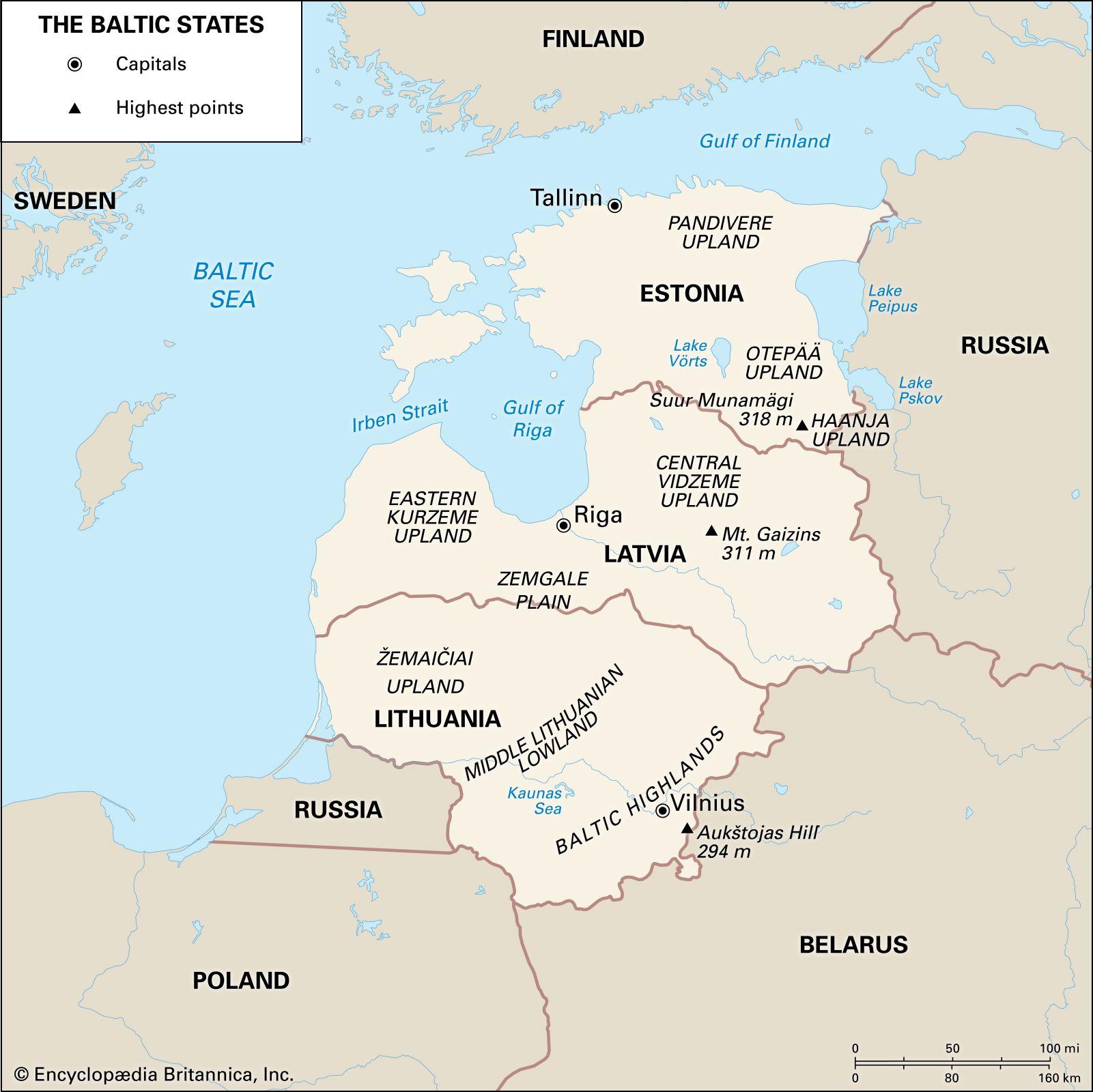
The Baltic nations ‚Ā£have made significant strides in severing their ties with‚Ā£ the Russian power grid, marking a pivotal shift‚Äč in their energy policies aimed at enhancing national security and fostering economic resilience. This move, driven by the ‚Ā§desire to mitigate geopolitical ‚Ā§risks associated with dependence ‚Ā£on Russian energy supplies, ‚ÄĆinvolves intricate planning and rapid progress of ‚Äčnew infrastructure. Key elements in this transition include:
- Establishment of Interconnections: Investments‚ÄĆ in new ‚ĀĘenergy interconnections with the European Union to ensure a robust and reliable energy supply.
- Renewable Energy Initiatives: A significant push towards renewable energy sources such as‚ĀĘ wind and solar to diversify energy‚ÄĆ portfolios.
- Infrastructure‚Äč Upgrades: Modernization of the existing ‚ĀĘenergy systems,‚Äč including grid ‚ĀĘenhancements to accommodate increased ‚Äćrenewable capacity.
As‚ĀĘ the Baltic nations focus on ‚Ā£integrating with the European electricity market, they are anticipating numerous benefits beyond energy independence. The move not ‚Äčonly aims‚Ā£ to enhance energy security but ‚ÄĆalso promises economic advantages and increased competitiveness in the EU energy landscape. The benefits expected from this ‚Äčtransition include:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Security | Reduced‚Ā£ vulnerability to external pressures from ‚Ā§unauthorized ‚ÄĆsupply disruptions. |
| Cost Efficiency | Potential long-term savings from diversified energy sources. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon ‚ÄĆemissions thru increased use of sustainable energy practices. |
Strategic Move to Strengthen Energy‚ÄĆ Security in‚Ā§ the Region

The‚Äć recent decision by the Baltic nations to ‚Ā§sever their electrical connections with the Russian power grid marks a‚ÄĆ pivotal moment in regional energy policy.By taking definitive steps toward integration with the European Union’s energy framework, these countries are‚Äć not only enhancing their energy security‚ĀĘ but also demonstrating a collective commitment to reducing reliance on ‚Äčexternal influences. Key aspects of this strategy include:
- Diversifying Energy sources: Seeking alternative ‚Äčenergy supplies to mitigate ‚ĀĘthe risks associated with dependency on a single ‚Ā§provider.
- Investing in Infrastructure: Upgrading existing power grids and‚Ā§ developing ‚ÄĆnew interconnections with‚Ā§ EU ‚Äčmember states‚Äć to facilitate smoother energy trade.
- Enhanced Resilience: ‚ĀĘImplementing measures to bolster the reliability and efficiency of energy systems amidst geopolitical tensions.
This strategic shift is not just about immediate energy needs;‚ĀĘ it reflects a broader objective‚Ā§ of aligning with‚Äč EU policies that‚Äć advocate for‚Äč sustainability and energy independence. As the Baltic states embark on this transformative journey, the ‚Äćproposed timeline for the transition reveals their commitment to timely execution. The following table summarizes the expected‚Ā§ milestones in their energy transition plan:
| Phase | Milestone | Target Date |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Completion of feasibility studies | Q1 2024 |
| Phase 2 | Infrastructure ‚Ā£upgrades initiated | Q3 2025 |
| Phase 3 | Full integration ‚Ā£with‚ĀĘ EU grid | Q2 2026 |
Implications for Regional Energy Markets and Infrastructure‚Ā£ Investment

The recent ‚Äćdecision by the Baltic nations to sever their ties with the Russian power grid marks a significant shift in the region’s energy landscape. By pivoting towards integration with the European Union‚Äôs energy framework, ‚Äćthese countries are not only enhancing their‚Ā§ energy security but also laying the groundwork‚ĀĘ for a more unified regional market. This transition is expected to ‚Ā£stimulate infrastructure investments that will ‚Äćhelp‚ĀĘ modernize‚Äč the existing ‚Ā§energy systems while promoting‚ĀĘ the adoption of renewable energy sources. Key considerations include:
- Development of cross-border interconnectors to facilitate electricity trade.
- Upgrading ‚Äćexisting facilities to accommodate fluctuating energy sources.
- Enhancing grid stability and efficiency through innovative technologies.
Furthermore,the shift‚Ā£ presents‚ÄĆ a unique possibility for attracting foreign investment and fostering partnerships that can propel innovation ‚Ā£in‚Ā§ the‚Ā£ energy sector. ‚ÄćThe anticipated demand‚ÄĆ for upgraded infrastructure ‚Äćwill likely‚ÄĆ lead to collaborations among countries‚ĀĘ within ‚Ā§the EU, as ‚Äčwell as private stakeholders focusing on sustainable energy solutions. the table below outlines potential areas for investment that‚Äč align with the strategic ‚ÄĆgoals of energy‚Ā£ independence and integration:
| Investment Area | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
| Smart Grid Technology | Enhanced efficiency and reliability |
| Renewable Energy‚Ā§ Projects | Increased renewable energy share |
| Energy Storage Solutions | Improved capacity for peak demand |
Technological Enhancements Required for EU ‚ÄćIntegration
As the ‚ĀĘBaltic ‚Ā§nations transition away from the Russian power grid, integrating with the European Union’s energy market necessitates a series of‚ĀĘ technological advancements.‚Äć Key enhancements will primarily focus on grid interoperability, which requires state-of-the-art substations and smart grid technology to ensure seamless electricity distribution across borders.To facilitate this, the ‚ÄĆfollowing technological measures are ‚Ā£essential:
- Advanced Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) ‚ÄĆsystems to‚ÄĆ monitor ‚Ā§and manage energy flows in real time.
- High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) systems to enable efficient long-distance transmission of electricity.
- Renewable Energy Integration ‚Ā§ technologies to accommodate variable energy sources, ‚Äćenhancing grid stability.
- Cybersecurity‚Ā§ Enhancements to protect‚Ā§ the grid‚Ā£ from potential cyber threats as interconnectivity increases.
Moreover, investments in energy storage technologies will be critical to buffer‚Äć against ‚Äčfluctuations ‚Ā§in supply and demand. The‚Äč following table outlines‚Ā§ potential energy storage solutions vital for the region’s ‚Äćstability:
| Storage Solution | Capacity‚Ā£ (MWh) | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Pumped Hydroelectric ‚ÄčStorage | 500+ | Long-term energy buffer |
| Lithium-ion‚Äč batteries | 20-100 | Short-term peak demand |
| Flow Batteries | 50-200 | Medium to long-term storage |
Recommendations for ‚ĀĘPolicymakers to ‚ÄćEnsure a Smooth‚Äć Transition
As the Baltic nations take significant steps‚ÄĆ to‚Ā£ sever their reliance on‚Äć the Russian power grid,a consolidated strategy is essential ‚Äćto ensure ‚Äća seamless transition into the European Union’s energy network. Policymakers must prioritize‚ÄĆ investments‚Äč in infrastructure that can support the integration‚Äć of new technologies and‚Ā£ renewable‚Ā£ energy sources.‚ĀĘ This means ‚Ā£focusing on the following key areas:
- Modernization ‚Ā£of Transmission Systems: Upgrade ‚ĀĘexisting power lines ‚Ā§and develop‚ĀĘ smart grid technologies.
- Interconnection ‚Ā§Projects: Accelerate the ‚Ā£completion of‚Äć cross-border interconnectors to facilitate energy exchange‚Ā£ within‚Ā§ the EU.
- Capacity Building: Enhance the technical skills of the workforce to adapt‚Äč to new‚ĀĘ energy technologies and practices.
In‚ÄĆ addition, collective engagement with EU energy policy frameworks will ‚Ā§be crucial. Baltic‚Äć governments ‚ĀĘshould actively participate in shaping the regional energy market, ensuring their nations‚Äô needs are ‚Äćmet while also adhering to EU standards. ‚ÄćThey ‚Ā§can focus‚Ā£ on:
- Joint Energy Initiatives: Collaborate on ‚Äćshared renewable energy projects ‚Äčthat bolster collective energy security.
- Crisis Response Mechanisms: Develop coordinated strategies to ‚Äćaddress any‚Ā£ energy supply disruptions during‚Ā§ the transition phase.
- Public ‚ÄčAwareness Campaigns: Educate citizens about ‚ÄĆthe benefits‚ĀĘ of transitioning to an EU ‚Ā§energy ‚ĀĘmodel, fostering public support for policy‚Äč measures.
future of Energy Collaboration within the European Union

The recent decision by‚Äć the Baltic nations to sever ties with the Russian power grid marks a significant‚Ā£ turning ‚Äćpoint‚Ā£ in the region’s energy strategy. This bold move ‚ĀĘreflects an overarching commitment to energy independence and security, fortifying their ‚ÄĆefforts to integrate more deeply with the European Union’s ‚Äćenergy‚ĀĘ network. By distancing themselves from‚Äć Russian influence, these countries are not just enhancing their energy stability but are‚Äć also ‚ĀĘaligning themselves with the EU’s broader objectives of promoting renewable energy sources and sustainable development.‚ĀĘ The shift includes various initiatives ‚Ā£aimed at enhancing cross-border energy‚Äć connections and creating more resilient energy infrastructure.
The collaboration between the Baltic states and ‚Äćthe EU can ‚ĀĘbe supported through a multifaceted approach that encompasses:
- Renewable Energy Projects: Joint ventures focusing on wind and solar energy will play a‚Äč crucial role in shaping a sustainable‚ÄĆ future.
- Enhanced Energy infrastructure: ‚Äč Upgrading and expanding‚ĀĘ energy transmission systems to facilitate smoother electricity flow across borders.
- Investment in Smart Technologies: Developing smart ‚Ā£grids and energy storage solutions ‚Ā£to optimize energy use and reduce‚Äć waste.
To monitor‚ÄĆ these evolving partnerships and‚Ā£ ongoing projects, the following table outlines key initiatives and expected ‚Äčoutcomes:
| Initiative | Expected‚ĀĘ Outcome |
|---|---|
| Interconnection Projects | Increased electricity trade and enhanced grid reliability |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Progress‚ÄĆ towards ‚Ā§meeting EU climate goals |
| Research and ‚ÄčDevelopment | Innovative solutions for efficiency and emission reductions |
Closing Remarks
the Baltic ‚ÄĆnations’ strategic decision to sever their connections with the Russian power grid marks a pivotal ‚ĀĘmoment in ‚Ā§their energy independence and European integration efforts.By preparing to link with the European‚Äć Union’s electrical network, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania not only reinforce their sovereignty‚Äč but also align‚Äč themselves more closely‚Äć with Western energy standards and regulations. This initiative reflects a‚Äć broader commitment‚Ā£ to energy security and‚ĀĘ a collective response to geopolitical tensions in the region. as the Baltics embark on this ‚ĀĘtransformative journey,their actions ‚ĀĘserve as a significant ‚Ā£example ‚Äčof the region’s resilience ‚Ā§and determination to forge ‚ĀĘa more secure and interconnected‚ĀĘ future. ‚ĀĘAs developments ‚Äćunfold, ‚ÄĆthe implications of this‚ĀĘ transition‚Äć for energy policy, regional stability, and EU solidarity will continue to be pivotal areas ‚ÄĆof observation in the coming months.
















