Foot-and-Mouth Disease Outbreak in Neighboring country – Hungary Today
In a concerning progress for the agricultural sector and public health, Hungary is closely monitoring an outbreak of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) that has recently emerged in a neighboring country. This highly contagious viral infection, primarily affecting cloven-hoofed animals such as cattle, sheep, and pigs, poses a important threat not only to livestock populations but also to regional economies and trade. As authorities scramble to contain the outbreak and implement preventative measures, experts are highlighting the potential repercussions for both agricultural practices and food security in Hungary. In this article, we will explore the current situation, the response from Hungarian officials, and the implications for farmers and consumers alike as the country navigates this developing crisis.
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Overview and Current Situation in Hungary’s Neighboring Country
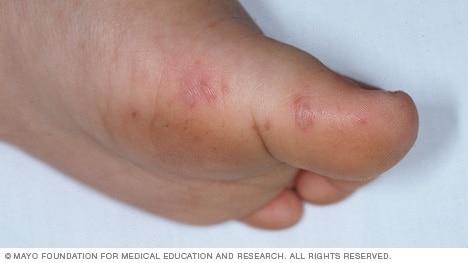
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) continues to pose a significant threat to livestock in hungary’s neighboring country. This highly contagious viral infection affects cloven-hoofed animals, leading to severe economic losses and disrupting local agricultural sectors. Over the past few months, several outbreaks have been reported, primarily affecting cattle and swine. farmers are urged to remain vigilant and implement strict biosecurity measures to mitigate the spread of the virus. Key symptoms to watch for include:
- Blisters and lesions in the mouth and on the feet
- Fever and decreased milk production
- Severe lameness in affected animals
to monitor and manage the situation effectively, local authorities have established quarantine zones where FMD has been confirmed. Surveillance efforts are ongoing, wiht vaccination campaigns being rolled out to at-risk populations. Farmers in adjacent areas are advised to adhere to stringent hygiene protocols, ensuring that the potential for cross-contamination is minimized. Below is a summary of the current situation:
| Region | Status | Number of Infected Farms |
|---|---|---|
| North Region | Outbreak Confirmed | 12 |
| Central Region | Quarantine in Effect | 5 |
| South Region | No Cases reported | 0 |
Impact of Foot-and-Mouth disease on Agriculture and Livestock in the Affected Region
The recent Foot-and-Mouth Disease outbreak in a neighboring country has raised significant concerns regarding its spillover effects on agriculture and livestock within the affected region. This highly contagious viral infection primarily impacts cloven-hoofed animals, which are essential for the agricultural economy. The immediate consequences include a sharp decline in livestock productivity due to increased morbidity rates among infected animals. As farmers grapple with the loss of productivity, they face the daunting challenge of securing their herds and safeguarding their livelihoods. The repercussions extend beyond individual farms, destabilizing local markets and leading to higher consumer prices for milk, beef, and pork.
Moreover,the need for extensive containment measures and possible culling of infected animals poses a logistical nightmare for regional authorities. The spread of the virus necessitates stringent biosecurity protocols, which include:
- Emergency vaccination programs to protect unaffected livestock.
- Movement restrictions on livestock transport to prevent further outbreaks.
- Increased surveillance in rural communities to monitor the health of animals.
The economic burden of these actions is profound, perhaps leading to long-term instability in agricultural sectors. A recent report highlighted a projected 20% decrease in livestock production in the region over the next year if the disease spreads uncontrollably. The table below summarizes the potential economic losses anticipated if containment measures are not effectively implemented:
| Sector | Projected Loss (%) |
|---|---|
| Dairy Farms | 25% |
| Beef Production | 30% |
| Pork Industry | 15% |
Response measures Implemented by Government Authorities
In response to the recent outbreak of Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) in a neighboring country, Hungarian government authorities have mobilized a series of measures aimed at preventing the spread of the virus. The Ministry of Agriculture has established an emergency task force that is coordinating efforts between local and national agencies to monitor livestock movements and enforce strict biosecurity measures across farms. Key actions include:
- Enhanced Surveillance: Increased inspections at borders and checkpoints to ensure early detection of potential outbreaks.
- Vaccination Campaigns: Implementation of a rapid vaccination program for susceptible livestock in high-risk areas.
- Public Awareness Initiatives: Launch of educational campaigns to inform farmers about FMD symptoms, prevention practices, and reporting procedures.
Furthermore,restrictions have been placed on the transport of livestock from affected regions to minimize contamination risks. Specialized veterinary teams have been deployed to affected areas for immediate response, conducting necessary tests and culling affected animals when necessary to contain the disease. A table illustrating the current status of response measures is provided below:
| Measure | Status | Implementation Date |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Task Force Established | Operational | October 15, 2023 |
| Vaccination Program Launch | In Progress | October 20, 2023 |
| Border Inspections Enhanced | Ongoing | October 16, 2023 |
Risk Assessment for Hungary: Identifying Vulnerabilities and Exposure
The recent outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) in a neighboring country has raised significant concerns regarding Hungary’s agricultural stability and public health safety. As veterinary experts assess the situation, it is indeed crucial to recognize the specific vulnerabilities within Hungary’s borders that could amplify the risks associated with this contagious disease. Key factors include:
- Proximity to Infected Regions: Hungary shares borders with countries that may not have stringent biosecurity measures in place, heightening the risk of cross-border transmission.
- Livestock Density: high concentrations of livestock in certain areas create ideal conditions for rapid spread, necessitating increased surveillance and control measures.
- Weather Conditions: Variable weather patterns can influence the movement of infected animals and vectors, complicating containment efforts.
Preparedness hinges on identifying critical areas of exposure that could exacerbate the outbreak’s impact. Hungary’s agricultural sectors must prioritize biosecurity improvements and enhance reporting systems to quickly address any suspected cases. An effective risk assessment should also consider:
| Factor | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Livestock Transport Routes | Increased chance of disease spread |
| market Access Points | High exposure to infected animals |
| Wildlife Interaction | possible transmission reservoirs |
Preventive Strategies: best Practices for Farmers and Livestock Owners
In light of the recent Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) outbreak in Hungary, it is indeed crucial for farmers and livestock owners to adopt rigorous preventive measures to safeguard their herds. Key strategies include:
- Biosecurity Protocols: Implement strict biosecurity measures by controlling farm access and maintaining clean environments.
- Vaccination: Ensure that all livestock are vaccinated according to local regulations and guidelines.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: Conduct regular health checks and keep detailed records of livestock movement and health status.
- quarantine Measures: Isolate any new animals before introducing them to established herds to prevent disease spread.
Additionally, education plays a vital role in disease prevention. farmers should train themselves and their workers on FMD symptoms and reporting protocols.Awareness campaigns can enhance understanding of the following:
| FMD Symptoms | Action to Take |
|---|---|
| Blamish on hooves | Isolate affected animal immediately |
| Excessive drooling | Seek veterinary assistance |
| Loss of appetite | Monitor closely for further signs |
The Role of Veterinary Services in Managing Outbreaks
The swift response of veterinary services is crucial during outbreaks like the recent foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) in Hungary. These agencies play an essential role in monitoring, controlling, and preventing the spread of infectious diseases among livestock. Key responsibilities include:
- surveillance and Early Detection: Constant monitoring of livestock health to quickly identify potential cases of FMD.
- Immediate Response Plans: Implementation of containment and control strategies, including quarantining affected areas.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating farmers and the general populace on symptoms, prevention, and reporting protocols.
- Collaboration with International Bodies: Coordinating with neighboring countries and organizations like the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) for unified action.
The veterinary services also ensure that vaccination programs are in place, targeting high-risk regions and populations.An effective vaccination strategy can mitigate the risk of outbreaks substantially. Here’s a brief overview of essential actions taken:
| Action | Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Vaccination Drive | Initiated in high-risk zones to protect livestock. | Ongoing |
| Surveillance Increase | Enhanced monitoring in bordering areas. | In Place |
| public Details Sessions | Conducted to inform farmers about disease signs. | Completed |
Public Health Considerations: Implications for Animal and Human health
The recent outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) in a neighboring country brings to light several public health considerations that directly impact both animal and human health. certain zoonotic diseases are known to emerge or re-emerge in regions where livestock diseases proliferate, significantly risking food safety and agriculture. Consequently, understanding the transmission pathways of FMD is crucial, as it primarily spreads among cloven-hoofed animals but can also indirectly affect human populations through disruptions in food supply chains and associated economic losses.
Considering the outbreak, several key measures should be implemented to mitigate the risks posed by FMD:
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Establishing robust monitoring systems for livestock and wildlife
- Vaccination Programs: Promoting vaccination for at-risk animal populations
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating farmers and the general public about FMD prevention
- Quarantine Protocols: Implementing strict quarantine measures to contain outbreaks
| Risk Factor | Impact on Animal Health | Impact on Human Health |
|---|---|---|
| increased Animal Movement | Higher transmission rates among livestock | potential food shortages and economic impacts |
| Biosecurity Lapses | Increased likelihood of disease spread | Compromised food safety standards |
| Climate Variability | Altered disease dynamics in animal populations | Potential emergence of new zoonotic diseases |
International Trade and Economic Implications of the Outbreak
The recent outbreak of foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) in Hungary’s neighboring country has triggered significant concerns regarding international trade.This highly contagious viral disease affects livestock, primarily cattle, sheep, and pigs, and has the potential to disrupt transboundary animal trade. With many countries imposing immediate bans on the importation of livestock and related products from affected regions, the repercussions for farmers and traders in Hungary could be severe. The situation demands a robust response not only from local authorities but also from international trade organizations to minimize economic losses and ensure swift recovery.
Considering this outbreak, the potential implications for Hungary’s economy can be substantial. Key considerations include:
- Export Restrictions: Countries may enhance border controls and restrict the movement of livestock, leading to decreased market access for Hungarian farmers.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Enhanced biosecurity measures can hinder the normal flow of goods, creating ripple effects throughout the agricultural supply chain.
- Price Volatility: Fluctuations in livestock prices can occur due to panic behavior in the market, potentially hurting both consumers and producers.
| Impact Area | Potential Consequence |
|---|---|
| Domestic Farmers | Reduced sales and income |
| Export Markets | Loss of competitive advantages |
| Consumer Prices | Increased prices for meat products |
Community Engagement and Awareness: Mobilizing Local Efforts
Considering the recent Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) outbreak in a neighboring country,ther is an urgent need for local communities to come together in awareness and proactive measures. engaging local stakeholders‚ÄĒsuch as farmers, veterinarians, and community leaders‚ÄĒis crucial. By sharing information and resources, communities can better prepare and respond to potential risks. Key strategies to consider include:
- Hosting Informational Workshops: These gatherings can provide updates and essential information on FMD signs, symptoms, and control measures.
- Creating Educational Materials: Distributing flyers and brochures that highlight prevention practices can empower community members.
- Establishing Communication Networks: Setting up local groups on social media platforms can facilitate the swift dissemination of critical updates.
Moreover, collaboration with local agricultural organizations and veterinary clinics can enhance expertise and resources available for outreach efforts.By fostering partnerships, communities can implement preventive measures effectively, minimizing the risk of FMD spreading within their borders.A community action plan could include:
| Action Item | description | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Training Sessions | Educate farmers on biosecurity practices | Ongoing |
| Monitoring Programs | Establish local surveillance for livestock health | Monthly |
| Community Meetings | Discuss updates and collective action | Quarterly |
Recommendations for Policy Enhancements and Regional Cooperation
To effectively address the challenges posed by the recent foot-and-mouth disease outbreak in the neighboring country, it is crucial to implement several key policy enhancements. Strengthening biosecurity measures is essential to prevent the spread of the disease. This includes rigorous veterinary inspections, improved surveillance methods, and the establishment of strict quarantine protocols. Additionally, public awareness campaigns should be initiated to inform farmers and the general public about best practices in disease management and prevention. These initiatives could be bolstered by partnerships with agricultural organizations to facilitate knowledge sharing and training programs for local stakeholders.
Moreover, fostering regional cooperation among affected countries is vital for a robust response. This can be achieved through the creation of a multi-national task force focused on rapid response protocols and resource sharing. Implementing a shared data management system could enhance coordination in tracking disease outbreaks and vaccination initiatives.The following table illustrates potential areas of cooperation and benefits:
| Cooperation Area | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Information Sharing | Timely updates on disease status and control measures |
| Joint Vaccination Programs | Cost-effective and comprehensive immunization efforts |
| Research Collaborations | Enhanced understanding of disease dynamics and vectors |
| Emergency Resource Allocation | Efficient distribution of resources during outbreak |
Monitoring and surveillance: Importance of Early Detection
In the face of the recent Foot-and-Mouth Disease outbreak in a neighboring country, the importance of proactive monitoring and surveillance systems cannot be overstated. By implementing state-of-the-art tracking technologies and real-time reporting mechanisms, authorities can identify potential outbreaks before they escalate. Some key strategies include:
- Regular Farm Inspections: Conducting frequent evaluations of livestock health to spot early signs of illness.
- Data Sharing Protocols: Establishing collaborations between countries for timely sharing of disease patterns and trends.
- Community involvement: Engaging farmers and local residents to report unusual animal behaviors or symptoms immediately.
Additionally, early detection not only limits the spread of the disease but also mitigates the economic impact on the agricultural sector. A swift response can reduce the need for extensive culling, as illustrated in the table below, which highlights the correlation between early intervention and containment success:
| Intervention Timing | Estimated Spread Radius (km) | Containment Cost (‚ā¨) |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate (0-24 hours) | 5 | 10,000 |
| delayed (1-3 days) | 15 | 50,000 |
| Late (3+ days) | 30 | 200,000 |
Timely responses enable effective vaccination programs and better resource allocation, ultimately safeguarding not just local livestock but also regional food security and economic stability. Ensuring rigorous monitoring practices empowers officials to act decisively, reflecting the critical nature of preparedness in agricultural health management.
Future Outlook: Navigating the Challenges ahead for Hungary and Its Neighbors
The emergence of foot-and-mouth disease in a neighboring country poses significant risks not only to its own agricultural sector but also to Hungary’s economic stability. As livestock trade and cross-border movement continue to be vital for local economies, Hungary must adopt a proactive approach to mitigate the disease’s potential spread. Key strategies may include:
- Enhanced Surveillance: Strengthening monitoring systems at border checkpoints and within agricultural areas to quickly identify and respond to any outbreaks.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating farmers and the general public about biosecurity measures to reduce the risk of transmission.
- Collaboration with Neighbors: Engaging in joint initiatives with neighboring countries to coordinate response strategies and share best practices in controlling the disease.
Moreover, as Hungary navigates this crisis, the potential impacts on trade relations and local economies cannot be underestimated. It’s essential to establish a support framework for affected farmers, allowing them to maintain viable operations in the face of adversity. This may involve:
| Support Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Financial Aid | Providing subsidies to farmers losing income due to strict livestock movement regulations. |
| Research Funding | Investing in research to develop better vaccines and treatment options for foot-and-mouth disease. |
| Emergency Protocols | Establishing rapid response teams to handle local outbreaks effectively and efficiently. |
Future Outlook
As the situation surrounding the Foot-and-Mouth Disease outbreak in our neighboring country continues to evolve,it is indeed essential for both agricultural stakeholders and the general public to remain informed and vigilant. The Hungarian authorities are actively monitoring the situation, implementing preventive measures to safeguard livestock health and prevent potential cross-border transmission. Farmers are encouraged to practice stringent biosecurity measures and report any unusual symptoms in their animals.
The implications of this outbreak extend beyond livestock health; they encompass economic stability and food security in the region. As Hungary maintains its commitment to preventing the spread of this contagious disease, collaboration between governments, veterinarians, and farmers will be crucial. Regular updates will be provided to ensure that all affected parties are aware of the latest developments.
For now, we urge everyone to stay informed and prepared as we navigate this challenging landscape together. Continued cooperation and vigilance will be key to mitigating the impact of Foot-and-Mouth Disease and securing the well-being of our agricultural sector.